Abstract
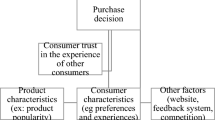
In this paper, we conduct a two-stage study to examine whether and how consumer reviews influence other consumers. In the first stage, we utilize a difference-in-difference specification to identify the causal effect of online reviews on sales and apply the proposed model to electronic appliances on a large Chinese retail website. In the second stage, we design a computational model with agents guided by case-based decision theory and we calibrate the simulated market to the real data. The literature identifies two channels for the effect of reviews on sales: the awareness effect and the persuasive effect. We find evidence for both effects, but we find the persuasive effect is slightly larger than the awareness effect. This suggests that consumers who have had a bad experience should not hesitate to leave bad reviews. We also find evidence that consumers are concerned whether reviews are genuine, but that the method used by this website of tying a “user grade” to volume of previous purchases may be an effective way of communicating whether a reviewer is a genuine customer. We use the computational model to predict unobserved consumer behavior: consumers’ loyalty. We find the loyalty of artificial consumers is relatively high but falls. We also believe the case-based decision theory simulation approach may help estimate other unobserved consumer behaviors.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
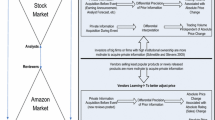
Technically, the consumer numbers on Tmall also include a secondary site called Taobao, which we consider as a combined market since both Tmall and Taobao are operated under Alibaba Group and the targeting consumers are the same.
References
Berger, J., Sorensen, A. T., & Rasmussen, S. J. (2010). Positive effects of negative publicity: When negative reviews increase sales. Marketing Science, 29(5), 815–827.
Bhui, R. (2018). Case-based decision neuroscience: Economic judgment by similarity. In R.W. Morris, A.M. Bornstein, & A. Shenhav (Eds.), Goal-Directed Decision Making (pp. 67–103). London: Academic Press.
Camera, G., & Casari, M. (2009). Cooperation among strangers under the shadow of the future. American Economic Review, 99(3), 979–1005.
Chen, I. J., & Popovich, K. (2003). Understanding customer relationship management (CRM): People, process and technology. Business Process Management Journal, 9(5), 672–688.
Chen, Y., & Xie, J. (2008). Online consumer review: Word-of-mouth as a new element of marketing communication mix. Management Science, 54(3), 477–491.
Chen, P. Y., Wu, S. Y., & Yoon, J. (2004). The impact of online recommendations and consumer feedback on sales. ICIS 2004Proceedings, 58, 711–724.
Cheung, C. M., & Thadani, D. R. (2012). The impact of electronic word-of-mouth communication: A literature analysis and integrative model. Decision Support Systems, 54(1), 461–470.
Chevalier, J. A., & Mayzlin, D. (2006). The effect of word of mouth on sales: Online book reviews. Journal of Marketing Research, 43(3), 345–354.
Clemons, E. K., Gao, G. G., & Hitt, L. M. (2006). When online reviews meet hyperdifferentiation: A study of the craft beer industry. Journal of Management Information Systems, 23(2), 149–171.
Coleman, J. S., Katz, E., & Menzel, H. (1966). Medical innovation: A diffusion study. New York, NY: Bobbs-Merrill Co..
Dellarocas, C., Zhang, X. M., & Awad, N. F. (2007). Exploring the value of online product reviews in forecasting sales: The case of motion pictures. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 21(4), 23–45.
Dhar, V., & Chang, E. A. (2009). Does chatter matter? The impact of user-generated content on music sales. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 23(4), 300–307.
Dobbs, R., Chen, Y., Orr, G., Manyika, J., & Chang, E. (2013). China's E-tail revolution: Online shopping as a catalyst for growth. McKinsey Global Institute. Retrieved from: https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey/Featured%20Insights/Asia%20Pacific/China%20e%20tailing/MGI_China_e%20tailing_Full_report_March_2013.pdf. Accessed 5 Jul 2020.
Duan, W., Gu, B., & Whinston, A. B. (2008a). Do online reviews matter?—An empirical investigation of panel data. Decision Support Systems, 45(4), 1007–1016.
Duan, W., Gu, B., & Whinston, A. B. (2008b). The dynamics of online word-of-mouth and product sales—An empirical investigation of the movie industry. Journal of Retailing, 84(2), 233–242.
Elberse, A., & Eliashberg, J. (2003). Demand and supply dynamics for sequentially released products in international markets: The case of motion pictures. Marketing Science, 22(3), 329–354.
Engel, J. F., Kegerreis, R. J., & Blackwell, R. D. (1969). Word-of-mouth communication by the innovator. Journal of Marketing, 33(3), 15–19.
Feldman, S., & Spencer, M. (1965). The effect of personal influence in the selection of consumer services. In P. D. Bennett (Ed.), Marketing and economic development (pp. 440–452). Chicago, IL: American Marketing Association.
Fonseca, M. A., & Peters, K. (2018). Will any gossip do? Gossip does not need to be perfectly accurate to promote trust. Games and Economic Behavior, 107, 253–281.
Foster, A. D., & Rosenzweig, M. R. (1995). Learning by doing and learning from others: Human capital and technical change in agriculture. Journal of Political Economy, 103(6), 1176–1209.
Gayer, G., Gilboa, I., & Lieberman, O. (2007). Rule-based and case-based reasoning in housing prices. The BE Journal of Theoretical Economics, 7(1), 1–35.
Gilboa, I., & Schmeidler, D. (1995). Case-based decision theory. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 110(3), 605–639.
Godes, D., & Mayzlin, D. (2004). Using online conversations to study word-of-mouth communication. Marketing Science, 23(4), 545–560.
Grosskopf, B., Sarin, R., & Watson, E. (2015). An experiment on case-based decision making. Theory and Decision, 79(4), 639–666.
Gu, B., Park, J., & Konana, P. (2012). Research note—The impact of external word-of-mouth sources on retailer sales of high-involvement products. Information Systems Research, 23(1), 182–196.
Guilfoos, T., & Pape, A. D. (2016). Predicting human cooperation in the Prisoner’s dilemma using case-based decision theory. Theory and Decision, 80(1), 1–32.
Har Lee, C., Cyril Eze, U., & Oly Ndubisi, N. (2011). Analyzing key determinants of online repurchase intentions. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 23(2), 200–221.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Gwinner, K. P., Walsh, G., & Gremler, D. D. (2004). Electronic word-of-mouth via consumer-opinion platforms: What motivates consumers to articulate themselves on the internet? Journal of Interactive Marketing, 18(1), 38–52.
Hu, N., Liu, L., & Zhang, J. J. (2008). Do online reviews affect product sales? The role of reviewer characteristics and temporal effects. Information Technology and Management, 9(3), 201–214.
Johnson, J. R., & Payne, G. F. (1968). Sagebrush reinvasion as affected by some environmental influences. Rangeland Ecology & Management/Journal of Range Management Archives, 21(4), 209–213.
Kinjo, K., & Sugawara, S. (2016). Predicting empirical patterns in viewing Japanese Tv dramas using case-based decision theory. The BE Journal of Theoretical Economics, 16(2), 679–709.
Kirman, A. P., & Vriend, N. J. (2000). Learning to be loyal, A study of the Marseille fish market. In A. P. Kirman, & N. J. Vriend (Eds.), Interaction and market structure (pp. 33–56). Berlin: Springer.
Lee, M. K., Shi, N., Cheung, C. M., Lim, K. H., & Sia, C. L. (2011). Consumer's decision to shop online: The moderating role of positive informational social influence. Information & Management, 48(6), 185–191.
Pape, A. D., & Kurtz, K. J. (2013). Evaluating case-based decision theory: Predicting empirical patterns of human classification learning. Games and Economic Behavior, 82, 52–65.
Park, D. H., & Kim, S. (2008). The effects of consumer knowledge on message processing of electronic word-of-mouth via online consumer reviews. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 7(4), 399–410.
Stigler, G. J. (1961). Economic problems in measuring changes in productivity. In: Output, input, and productivity measurement (pp. 47-78). National Bureau of Economic Research. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Thamizhvanan, A., & Xavier, M. J. (2013). Determinants of customers' online purchase intention: An empirical study in India. Journal of Indian Business Research, 5(1), 17–32.
Van den Bulte, C., & Lilien, G. L. (2001). Medical innovation revisited: Social contagion versus marketing effort. American Journal of Sociology, 106(5), 1409–1435.
Yang, F. X. (2017). Effects of restaurant satisfaction and knowledge sharing motivation on eWOM intentions: The moderating role of technology acceptance factors. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research, 41(1), 93–127.
Zhu, F., & Zhang, X. (2010). Impact of online consumer reviews on sales: The moderating role of product and consumer characteristics. Journal of Marketing, 74(2), 133–148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, M., Pape, A.D. The Impact of Online Consumer Reviews on Online Sales: The Case-Based Decision Theory Approach. J Consum Policy 43, 463–490 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10603-020-09464-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10603-020-09464-y