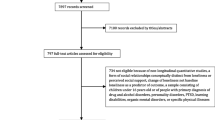
Abstract
It is estimated that nearly 20 million adults in the United States have a substance use disorder (SUD), and 8.4 million of those adults have a comorbid mental disorder. Roughly half of those adults with a SUD and a psychiatric comorbidity fail to receive adequate treatment for either the SUD or the mental disorder (combined or separately). However, this sub-population has shown positive treatment outcomes (e.g., improved quality of life and increased length of stay in a recovery home) when allotted the proper resources to treat the overlapping symptomologies associated with their multiple diagnoses. Many individuals with SUD and psychiatric comorbidity receive community-based support from recovery residences, a ubiquitous form of aftercare treatment in the United States. The aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship between psychiatric severity index scores (a proxy for psychiatric comorbidity that measures social functioning, impairment, symptoms, and behavior), length of stay in Oxford Houses (OHs), and quality of life. The present study found a significant negative relationship between length of stay and psychiatric severity scores, and between psychiatric severity scores and quality of life scores. Psychiatric severity was observed to predict decreased quality of life, while length of stay predicted decreased psychiatric severity. Psychiatric severity mediated the relationship between length of stay and quality of life based on house composition.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aase, D. M., Jason, L. A., Ferrari, J. R., Li, Y., & Scott, G. (2015). Comorbid mental health and substance abuse issues among individuals in recovery homes: Prospective environmental mediators. Mental Health and Substance Use: Dual Diagnosis, 7(2), 170–183
Bishop, P. D., Jason, L. A., & Ferrari, J. R. (1998). A survival analysis of communal-living, self-help, addiction recovery participants. American Journal of Community Psychology, 26(6), 803–821
Bovasso, G. B., Alterman, A. I., Cacciola, J. S., & Cook, T. G. (2001). Predictive validity of the Addiction Severity Index’s composite scores in the assessment of 2-year outcomes in a methadone maintenance population. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 15(3), 171–176. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-164X.15.3.171
Brown, M. (2012). Effectiveness of Housing First for non-chronically homeless individuals who are high utilizers of inpatient psychiatric treatment. College of Science and Health Theses and Dissertations. https://via.library.depaul.edu/csh_etd/29.
Chancellor, J., Layous, K., Margolis, S., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2017). Clustering by well-being in workplace social networks: Homophily and social contagion. Emotion, 17(8), 1166–1180. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000311
Daigre, C., Grau-López, L., Rodríguez-Cintas, L., Ros-Cucurull, E., Sorribes-Puertas, M., Esculies, O., Bones-Rocha, K., & Roncero, C. (2017). The role of dual diagnosis in health-related quality of life among treatment-seeking patients in Spain. Quality of Life Research: An International Journal of Quality of Life Aspects of Treatment, Care & Rehabilitation, 26(12), 3201–3209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-017-1668-4
Davis, M. I., & Jason, L. A. (2005). Sex differences in social support and self-efficacy within a recovery community. American Journal of Community Psychology, 36, 259–274
Dixon, L., Myers, P., Johnson, J., & Corty, E. (1996). Screening for mental illness with the Addiction Severity Index. American Journal on Addictions, 5, 301–307.
Doogan, N. J., Light, J. M., Stevens, E. B., & Jason, L. A. (2019). Quality of life as a predictor of social relationships in Oxford House. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 101, 79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2019.03.006
Drake, R. E., Brunette, M. F., & Mueser, K. T. (1998). Substance use disorders and social functioning in schizophrenia. In K. T. Mueser & N. Tarrier (Eds.), Handbook of social functioning. (pp. 280–289). Allyn & Bacon.
Ellis, B., Bernichon, T., Yu, P., Robertsand James, T., & Herrell, M. (2004). Effect of social support on substance abuse relapse in a residential treatment setting for women. Evaluation and Program Planning, 27(2), 213–221.
Enez-Darcin A., Nurmedov, S., Noyan, C. O., Yilmaz, O., & Dilbaz, N. (2015). Psychiatric comorbidity among inpatients in an addiction clinic and its association with the process of addiction. Düşünen Adam: Journal of Psychiatry and Neurological Sciences, 28(3), 196–203.
Flatt, J. D., Agimi, Y., & Albert, S. M. (2012). Homophily and health behavior in social networks of older adults. Family & Community Health: The Journal of Health Promotion & Maintenance, 35(4), 312–321. https://doi.org/10.1097/FCH.0b013e3182666650
Franken, H. A. I., & Hendriks, V. M. (2001). Screening and diagnosis of anxiety and mood disorders in substance abuse patients. American Journal on Addictions, 10(1), 30–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/105504901750160448
Granovetter, M. (1985). Economic action and social structure: The problem of embeddedness. American Journal of Sociology, 91, 481–510
Groh, D. R., Jason, L. A., Ferrari, J. R., & Davis, M. I. (2009). Oxford house and alcoholics anonymous: The impact of two mutual-help models on abstinence. In L.A. Jason, & J.R. Ferrari (Eds.). Recovery from addiction in communal living settings: The Oxford House model [Special Issue]. Journal of Groups in Addiction & Recovery, 4, 23–31.
Hawkins, R. L., & Abrams, C. (2007). Disappearing acts: The social networks of formerly homeless individuals with co-occurring disorders. Social Science & Medicine, 65, 2031–2042
Hayes, A. F. (2009). Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Communication Monographs, 76, 408–420. https://doi.org/10.1080/03637750903310360
Huston, T. L., & Levinger, G. (1978). Interpersonal attraction and relationships. Annual Review of Psychology, 29, 115–156. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ps.29.020178.000555
Iskandar, S., van Crevel, R., Hidayat, T., Siregar, I. M. P., Achmad, T. H., van der Ven, A. J., & De Jong, C. A. (2013). Severity of psychiatric and physical problems is associated with lower quality of life in methadone patients in Indonesia. The American Journal on Addictions, 22, 425–431. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1521-0391.2012.00334.x
Jason, L. A., Davis, M. I., Ferrari, J. R., & Anderson, E. (2007). Longitudinal analysis of Oxford House. Addictive Behaviors, 32(4), 803–818
Jason, L. A., & Ferrari, J. (2010). Oxford House recovery homes: Characteristics and effectiveness. Psychological Services, 7, 92–102. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017932
Jason, L. A., Ferrari, J. R., Dvorchak, P. A., Groessl, E. J., & Molloy, J. P. (1999). The characteristics of alcoholics in self-help residential treatment settings: A multi-site study of Oxford House. Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly, 15, 53–63. https://doi.org/10.1300/J020v15n01_05.
Jason, L. A., Light, J. M., Stevens, E. B., & Beers, K. (2014). Dynamic social networks in recovery homes. American Journal of Community Psychology, 53, 324–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10464-013-9610-6.
Jason, L. A., Olson, B. D., Ferrari, J. R., & Lo Sasso, A. T. (2006). Communal housing settings enhance substance abuse recovery. American Journal of Public Health, 91, 1727–1729
Jason, L. A., Stevens, E. B., Light, J. M., & Doogan, N. J. (2020). An empirically based theory of the relationships among social embeddedness, economic viability, learned recovery skills and perceived quality of life in recovery homes. Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly, 38, 126–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/07347324.2019.1633977
Kassanits, J., Bobak, T. J., Stevens, E., Guerrero, M., Light, J., & Jason, L. A. (2020). The relationship of Oxford Houses across heterogeneous house and setting characteristics. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1037/ort0000437
Laudet, A. B., Magura, S., Vogel, H. S., & Knight, E. (2000). Recovery challenges among dually diagnosed individuals. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 18(4), 321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0740-5472(99)00077-X
Majer, J. M., Chapman, H. M., & Jason, L. A. (2016). Comparative analysis of treatment conditions upon psychiatric severity levels at two years among justice involved persons. Advances in Dual Diagnosis, 9(1), 38–47. https://doi.org/10.1108/ADD-07-2015-0015
Majer, J. M., Jason, L. A., Ferrari, J. R., & North, C. S. (2002a). Comorbidity among Oxford House residents: A preliminary outcome study. Addictive Behaviors, 27(5), 837–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4603(01)00214-3
Majer, J. M., Jason, L. A., Ferrari, J. R., Venable, L. B., & Olson, B. D. (2002b). Social support and self-efficacy for abstinence: Is peer identification an issue? Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 23, 209–215
Majer, J. M., Jason, L. A., North, C. S., Ferrari, J. R., Porter, N. S., Olson, B. D., & Molloy, J. P. (2008). A longitudinal analysis of psychiatric severity upon outcomes among substance abusers residing in self-help settings. American Journal of Community Psychology, 42, 145–153
McLellan, T., Kushner, H., Metzger, D., Peters, R., Smith, I., Grissom, G., Pettinati, H., & Argeriou, M. (1992). The Fifth Edition of the Addiction Severity Index. Journal of Substance Treatment, 9, 199–213
McPherson, M., Smith-Lovin, L., & Cook, J. M. (2001). Birds of a feather: Homophily in social networks. Annual Review of Sociology, 27, 415–444
Meyers, R. J., & Miller, W. R. (Eds.). (2001). A community reinforcement approach to addiction treatment. Cambridge University Press.
Morisano, D., Babor, T. F., & Robaina, K. A. (2014). Co-occurrence of substance use disorders with other psychiatric disorders: Implications for treatment services. Nordic Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 31(1), 5–25
Noordsy, D. L., Schwab, B., Fox, L., & Drake, R. E. (1996). The role of self-help programs in the rehabilitation of persons with severe mental illness and substance use disorders. Community Mental Health Journal, 32(1), 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02249369
Ouimette, P. C., Finney, J. W., & Moos, R. H. (1999). Two-year posttreatment functioning and coping of substance abuse patients with posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 13(2), 105–114
Polanyi, K. (1944). The great transformation. NY: Rinehart.
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2004). SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, and Computers, 36, 717–731
Ritsher, J. B., McKellar, J. D., Finney, J. W., Otilingam, P. G., & Moos, R. H. (2002). Psychiatric comorbidity, continuing care and mutual help as predictors of five-year remission from substance use disorders. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 63, 709–715
SAMHSA. (2016). SAMHSA announces a working definition of “recovery” from mental disorders and substance use disorders. https://www.samhsa.gov/newsroom/press-announcements/201112220800S.
Schaefer, J. A., Cronkite, R. C., & Hu, K. U. (2011). Differential relationships between continuity of care practices, engagement in continuing care, and abstinence among subgroups of patients with substance use and psychiatric disorders. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 72, 611–621
Shand, F., Gates, J., Fawcett, J., & Mattick, R. P. (2003). Guidelines for the treatment of alcohol problems. Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing.
Tracy, E. M., & Johnson, P. J. (2007). Personal social networks of women with co-occurring substance use and mental disorders. Journal of Social Work Practice in the Addictions, 7(1–2), 69–90. https://doi.org/10.1300/J160v07n01_05
Trumbetta, S. L., Mueser, K. T., Quimby, E., Bebout, R., & Teague, G. B. (1999). Social networks and clinical outcomes of dually diagnosed homeless persons. Behavior Therapy, 30(3), 407–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/S00057894(99)80018-5
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the financial support from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (Grant Number AA022763).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bobak, T.J., Majer, J.M. & Jason, L.A. An Examination of Psychiatric Severity and Social Cohesion Outcomes within Oxford Houses. Community Ment Health J 58, 328–333 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-021-00825-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-021-00825-6