Abstract
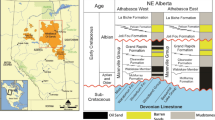
Artificial neural network-trained models were used to predict gas hydrate saturation distributions in permafrost-associated deposits in the Eileen Gas Hydrate Trend on the Alaska North Slope (ANS), USA and at the Mallik research site in the Beaufort-Mackenzie Basin, Northwest Territories, Canada. The database of Logging-While-Drilling (LWD) and wireline logs collected at five wells (Mount Elbert, Iġnik Sikumi, and Kuparuk 7–11–12 wells at ANS, plus 2L-38 and 5L-38 wells at the Mallik research site) includes more than 10,000 depth points, which were used for training, validation, and testing the machine learning (ML) models. Data used in training the ML models include the well logs of density, porosity, electrical resistivity, gamma radiation, and acoustic wave velocity measurements. Combinations of two or three out of these five well logs were found to reliably predict the gas hydrate saturation with accuracy varying between 80 and 90% when compared to the gas hydrate saturations derived from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)-based technique. The ML models trained on data from three ANS wells achieved high fidelity predictions of gas hydrate saturation at the Mallik site. The results obtained in this study indicate that ML models trained on data from one geological basin can successfully predict key reservoir parameters for permafrost-associated gas hydrate accumulations within another basin. A generalized approach for selecting a well log combination that can improve model accuracy is discussed. Overall, the study outcome supports earlier work demonstrating that ML models trained on non-NMR well logs are a viable alternative to physics-driven methods for predicting gas hydrate saturations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karpatne, A., Ebert-Uphoff, I., Ravela, S., Babaie, H.A., Kumar, V.: Machine learning for the geosciences: challenges and opportunities. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 31, 1544–1554 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2018.2861006
Lary, D.J., Alavi, A.H., Gandomi, A.H., Walker, A.L.: Machine learning in geosciences and remote sensing. Geosci. Front. 7, 3–10 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2015.07.003
Caté, A., Perozzi, L., Gloaguen, E., Blouin, M.: Machine learning as a tool for geologists. Lead. Edge. 36, 215–219 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1190/tle36030215.1
Karpatne, A., Watkins, W., Read, J., Kumar, V.: Physics-Guided Neural Networks (PGNN): an Application in Lake Temperature Modeling. (2017)
Racah, E., Beckham, C., Maharaj, T., Kahou, S.E., Prabhat, Pal C : ExtremeWeather: A large-scale climate dataset for semi-supervised detection, localization, and understanding of extreme weather events. (2016)
Raschka, S., Mirjalili, V.: Python machine learning: machine learning and deep learning with Python, scikit-learn, and TensorFlow 2, 3rd edn. Packt Publishing (2019)
Collett, T., Johnson, A., Knapp, C., Boswell, R.: Natural gas hydrates—energy resource potential and associated geologic hazards. American Association of Petroleum Geologists (2009)
Uchida, S., Soga, K., Klar, A., Yamamoto, K.: Geomechanical study of the Mallik gas hydrate production field trials. Bull. Geol. Surv. Canada. 601, 191–204 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4095/291751
Anderson, B.J., Kurihara, M., White, M.D., Moridis, G.J., Wilson, S.J., Pooladi-Darvish, M., Gaddipati, M., Masuda, Y., Collett, T.S., Hunter, R.B., Narita, H., Rose, K., Boswell, R.: Regional long-term production modeling from a single well test, mount Elbert gas hydrate stratigraphic test well. Alaska North Slope. Mar. Pet. Geol. 28, 493–501 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.01.015
Boswell, R., Schoderbek, D., Collett, T.S., Ohtsuki, S., White, M., Anderson, B.J.: The Iġnik Sikumi field experiment, Alaska north slope: design, operations, and implications for CO 2 –CH 4 exchange in gas hydrate reservoirs. Energy Fuel. 31, 140–153 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b01909
Collett, T.S., Zyrianova, M. V, Okinaka, N., Wakatsuki, M., Boswell, R., Marsteller, S., Minge, D., Crumley, S., Itter, D., Hunter, R.D.: Design and operations of the Hydrate 01 Stratigraphic test well, Alaska North Slope, http://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/70213245, (2020)
Yamamoto, K., Terao, Y., Fujii, T., Ikawa, T., Seki, M., Matsuzawa, M., Kanno, T.: Operational overview of the first offshore production test of methane hydrates in the Eastern Nankai Trough. In: Day 3 Wed, May 07, 2014. OTC (2014)
Kumar, P., Collett, T.S., Shukla, K.M., Yadav, U.S., Lall, M.V., Vishwanath, K.: India National gas Hydrate Program Expedition-02: operational and technical summary. Mar. Pet. Geol. 108, 3–38 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.021
Boswell, R., Myshakin, E., Moridis, G., Konno, Y., Collett, T.S., Reagan, M., Ajayi, T., Seol, Y.: India National gas Hydrate Program Expedition 02 summary of scientific results: numerical simulation of reservoir response to depressurization. Mar. Pet. Geol. 108, 154–166 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.09.026
Yang, S., Liang, J., Lei, Y., Gong, Y., Xu, H., Wang, H., Lu, J., Holland, M., Schultheiss, P., Wei, J., others: GMGS4 gas hydrate drilling expedition in the South China Sea. Fire ice. 17, 7–11 (2017)
Flemings, P., Boswell, R., Collett, T., Cook, A., Divins, D., Frye, M., Guerine, G., Goldberg, D., Malinverno, A., Meazell, K., Morrison, J., Pettigrew, T., Phillips, S., Santra, M., Sawyer, D., Shedd, W., Thomas, C., You, K.: GOM2: Prospecting, Drilling and Sampling Coarse-Grained Hydrate Reservoirs in the Deepwater Gulf of Mexico. (2017)
Archie, G.E.: The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. Trans. AIME. 146, 54–62 (1942). https://doi.org/10.2118/942054-G
Lu, S., McMechan, G.A.: Estimation of gas hydrate and free gas saturation, concentration, and distribution from seismic data. GEOPHYSICS. 67, 582–593 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1468619
Singh, H., Seol, Y., Myshakin, E.M.: Prediction of gas hydrate saturation using machine learning and optimal set of well-logs. Comput. Geosci. 25, 267–283 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-020-10004-3
Lee, M.W., Hutchinson, D.R., Collett, T.S., Dillon, W.P.: Seismic velocities for hydrate-bearing sediments using weighted equation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth. 101, 20347–20358 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1029/96JB01886
Helgerud, M.B., Dvorkin, J., Nur, A., Sakai, A., Collett, T.: Elastic-wave velocity in marine sediments with gas hydrates: effective medium modeling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 2021–2024 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1029/1999GL900421
Kumar, D., Dash, R., Dewangan, P.: Methods of gas hydrate concentration estimation with field examples. Goehorizons. 76–86 (2009)
Collett, T.S., Lee, M.W.: Well log characterization of natural gas-hydrates. Petrophysics - SPWLA J. Form. Eval. Reserv. Descr. 53, 348–367 (2012)
Jain, V., Saumya, S., Vij, J., Singh, J., Singh, B., Pattnaik, S., Oli, A., Kumar, P., Collett, T.S.: New technique for accurate porosity estimation from logging-while-drilling nuclear magnetic resonance data, NGHP-02 expedition, offshore. India. Mar. Pet. Geol. 108, 570–580 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.001
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J.: The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction. Springer New York (2013)
Breiman, L., Friedman, J.H., Olshen, R.A., Stone, C.J.: Classification And Regression Trees. Routledge (2017)
Dudani, S.A.: The distance-weighted k-nearest-neighbor rule. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. SMC-6, 325–327 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1976.5408784
Pal, S.K., Mitra, S.: Multilayer perceptron, fuzzy sets, and classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 3, 683–697 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1109/72.159058
Friedman, J.H.: Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann. Stat. 19, (1991). https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176347963
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: Generalized additive models. Stat. Sci. 1, (1986). https://doi.org/10.1214/ss/1177013604
Robbins, H., Monro, S.: A stochastic approximation method. Ann. Math. Stat. 22, 400–407 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177729586
Singh, H., Seol, Y., Myshakin, E.M.: Automated well-log processing and lithology classification by identifying optimal features through unsupervised and supervised machine-learning algorithms. SPE J. 25, 2778–2800 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2118/202477-PA
Dallimore, S.R., Yamamoto, K., Wright, J.F., Bellefleur, G.: Scientific results from the JOGMEC/NRCan/Aurora Mallik 2007-2008 gas hydrate production research well program, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories. Canada. Geol. Surv. Canada. 601, (2012). https://doi.org/10.4095/291751
Dallimore, S.R., Collett, T.S., Taylor, A.E., Uchida, T., Weber, M., Chandra, A., Mroz, T.H., Caddel, E.M., Inoue, T.: Scientific results from the Mallik 2002 gas hydrate production research well program, Mackenzie Delta, northwest territories. Canada: Preface. Bull. Geol. Surv. Canada. 585, (2005)
Rose, K., Boswell, R., Collett, T.: Mount Elbert gas hydrate stratigraphic test well, Alaska north slope: coring operations, core sedimentology, and lithostratigraphy. Mar. Pet. Geol. 28, 311–331 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.02.001
Yoneda, J., Jin, Y., Muraoka, M., Oshima, M., Suzuki, K., Walker, M., Otsuki, S., Kumagai, K., Collett, T.S., Boswell, R., Okinaka, N.: Multiple physical properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments recovered from Alaska North Slope 2018 Hydrate-01 stratigraphic test well. Mar. Pet. Geol. 123, 104748 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104748
Géron, A.: Hands-on machine learning with Scikit-learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: concepts, tools, and techniques to build intelligent systems. O’Reilly Media. (2019)
Collett Denver, CO (United States)], T.S. [United S.G.S., Lewis Oklahoma City, OK (United States)], R.E. [Schlumberger W.L.S., Dallimore Pacific Geoscience Centre, Sidney, BC (Canada)], S.R. [Geological S. of C.: JAPEX/JNOC/GSC et al. Mallik 5L-38 gas hydrate production research well downhole well-log and core montages. Natural Resources Canada, Geological Survey of Canada, Vancouver, BC (Canada), Canada (2005)
Yang, X.W., Murray, D.R., Noguchi, S., Fujii, T., Fujii, K., Yamamoto, K., Dallimore, S., R: geophysical well-log montage for the Aurora/JOGMEC/NRCan Mallik 2L-38 Gas Hydrate Production Research Well. (2012)
Collett, T.S., Lewis, R.E., Winters, W.J., Lee, M.W., Rose, K.K., Boswell, R.M.: Downhole well log and core montages from the mount Elbert gas hydrate stratigraphic test well. Alaska North Slope. Mar. Pet. Geol. 28, 561–577 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.03.016
Schoderbek, D., Farrell, H., Howard, J., Raterman, K., Silpngarmlert, S., Martin, K., Smith, B., Klein, P.: ConocoPhillips gas hydrate production test. , Pittsburgh, PA, and Morgantown, WV (United States) (2013)
Boswell, R., Collett, T.S., Suzuki, K., Yoneda, J., Haines, S.S., Okinaka, N., Tamaki, M., Crumley, S., Itter, D., Hunter, R.: Alaska north slope 2018 Hydrate-01 stratigraphic test well: technical results. Presented at the. (2020)
2011 2012 IGNIK SIKUMI DATASETS, https://netl.doe.gov/oil-gas/methane-hydrates/2011-2012-IGNIK-SIKUMI-DATASETS
WELL LOG DATA FROM THE 2007 MT ELBERT TEST, https://netl.doe.gov/node/6865
van Stein, B., van Leeuwen, M., Back, T.: Local subspace-based outlier detection using global neighbourhoods. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data). pp. 1136–1142. IEEE (2016)
Ugborugbo, O., Rao, T.: Impact of Borehole Washout on Acoustic Logs and Well-to-Seismic Ties. In, Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers (2009)
Bikmukhametov, T., Jäschke, J.: Combining machine learning and process engineering physics towards enhanced accuracy and explainability of data-driven models. Comput. Chem. Eng. 138, 106834 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2020.106834
Singh, S., Kanli, A.I., Sevgen, S.: A general approach for porosity estimation using artificial neural network method: a case study from Kansas gas field. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 60, 130–140 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11200-015-0820-2
Kleinberg, R.L., Flaum, C., Collett, T.S.: Magnetic resonance log of JAPEX/JNOC/GSC et al. Mallik 5L-38 gas hydrate production research well: gas hydrate saturation, growth habit, and relative permeability. Bull. Surv. Canada. 585, 114 (2005)
Haines, S.S., Collett, T., Boswell, R., Lim, T., Okinaka, N., Suzuki, K., Fujimoto, A.: Gas hydrate saturation estimation from acoustic log data in the 2018 Alaska north slope Hydrate-01 stratigraphic test well. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH10). US Department of Energy – NETL program. Singapore. (2020)
Song, S., Hou, J., Dou, L., Song, Z., Sun, S.: Geologist-level wireline log shape identification with recurrent neural networks. Comput. Geosci. 134, 104313 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2019.104313
Pontes, F.J., Amorim, G.F., Balestrassi, P.P., Paiva, A.P., Ferreira, J.R.: Design of experiments and focused grid search for neural network parameter optimization. Neurocomputing. 186, 22–34 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.12.061
Liashchynskyi, P., Liashchynskyi, P.: Grid Search. Random Search, Genetic Algorithm, A Big Comparison for NAS (2019)
Scalero, R.S., Tepedelenlioglu, N.: A fast new algorithm for training feedforward neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 40, 202–210 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1109/78.157194
Kanfar, R., Shaikh, O., Yousefzadeh, M., Mukerji, T.: Real-time well log prediction from drilling data using deep learning. Int. Pet. Technol. Conf. 2020, IPTC 2020. (2020). https://doi.org/10.2523/iptc-19693-ms
Baldi, P., Sadowski, P.: The dropout learning algorithm. Artif. Intell. 210, 78–122 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2014.02.004
Glorot, X., Statistics, Y.B.B.T.-P. of the T.I.C. on A.I. and: Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks, http://proceedings.mlr.press/v9/glorot10a/glorot10a.pdf
Saputro, O.D., Maulana, Z.L., Latief, F.D.E.: Porosity Log Prediction Using Artificial Neural Network. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 739, 012092 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/739/1/012092
Elsayed, M., Glatz, G., El-Husseiny, A., Alqubalee, A., Adebayo, A., Al-Garadi, K., Mahmoud, M.: The effect of clay content on the spin–spin NMR relaxation time measured in porous media. ACS Omega. 5, 6545–6555 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04228
Arief, H.A., Wiktorski, T., Thomas, P.J.: A survey on distributed fibre optic sensor data modelling techniques and machine learning algorithms for multiphase fluid flow estimation. Sensors. 21, 2801 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082801
Truc, G., Rahmanian, N., Pishnamazi, M.: Assessment of cubic equations of state: machine learning for rich carbon-dioxide systems. Sustainability. 13, 2527 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052527
Collett, T.S., Lee, M.W., Agena, W.F., Miller, J.J., Lewis, K.A., Zyrianova, M.V., Boswell, R., Inks, T.L.: Permafrost-associated natural gas hydrate occurrences on the Alaska north slope. Mar. Pet. Geol. 28, 279–294 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.12.001
Boswell, R., Collett, T.S., Myshakin, E., Ajayi, T., Seol, Y.: The increasingly complex challenge of gas hydrate reservoir simulation. In: proceedings of the 9th international conference on gas hydrates (ICGH9). Denver. (2017)
Medioli, B.E., Wilson, N., Dallimore, S.R., Paré, D., Brennan-Alpert, P., Oda, H.: Sedimentology of the cored interval, JAPEX/JNOC/GSC et al. Mallik 5L-38 gas hydrate production well, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories. (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was performed in support of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fossil Energy Crosscutting Technology Research Program. The research was executed through the NETL Research and Innovation Center’s Hydrate Research Field Work Proposal. This research was supported in part by an appointment to the National Energy Technology Laboratory Research Participation Program, sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy. The authors would like to express their sincere appreciation to the U.S. DOE-NETL, and the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry for providing the permission to disclose this research. Any use of trade, product, or firm names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. or Japanese Government.
Disclaimer
This project was funded by the United States Department of Energy, National Energy Technology Laboratory, in part, through a site support contract. Neither the United States Government nor any agency thereof, nor any of their employees, nor the support contractor, nor any of their employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, apparatus, product, or process disclosed, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference herein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the United States Government or any agency thereof. The views and opinions of authors expressed herein do not necessarily state or reflect those of the United States Government or any agency thereof.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2445 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chong, L., Singh, H., Creason, C.G. et al. Application of machine learning to characterize gas hydrate reservoirs in Mackenzie Delta (Canada) and on the Alaska north slope (USA). Comput Geosci 26, 1151–1165 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-022-10151-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-022-10151-9