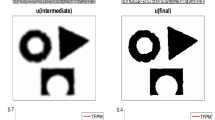
Abstract
In many problems of geophysical interest, when trying to segment images (i.e., to locate interfaces between different regions on the images), one has to deal with data that exhibit very complex structures. This occurs, for instance, when describing complex geophysical images (with layers, faults,...); in that case, segmentation is very difficult. Moreover, the segmentation process requires to take into account well data to interpolate, which implies integrating interpolation condition in the mathematical model.
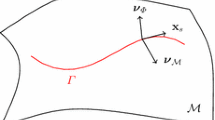
More precisely, let \(I:\Omega\rightarrow\Re\) be a given bounded image function, where Ω is an open and bounded domain that belongs to \(\Re^{n}\). Let \(S=\left\{ x_{i}\right\} _{i}\in\Omega\) be a finite set of given points (well data). The aim is to find a contour Γ⊂Ω such that Γ is an object boundary interpolating the points from S. To do that, we combine the ideas of the geodesic active contour (Caselles et al., Int. J. Comput. Vision 22-1:61-87, 1997) and of interpolation of points (Zhao et al., Comput. Vis. Image Understand. 80:295-314, 1986) in a Level Set approach developed by Osher and Sethian (J. Comput. Phys. 79:12-49, 1988). We present modelling of the proposed method. Both theoretical results (viscosity solution) and numerical results (on a velocity model for a real seismic line) are given.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adalsteinsson, D., Sethian, J.: A fast level set method for propagating interfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 118(2), 269–277 (1995)
Apprato, D., Gout, C., Sénéchal, P.: Ck reconstruction of surfaces from partial data. Math. Geol. 32(8), 969–983 (2000)
Apprato, D., Gout, C., Komatitsch, D.: A new method for Ck approximation from a set of curves: application to ship track data in the Marianas trench. Math. Geol. 34(7), 831–843 (2002)
Apprato, D., Ducassou, D., Gout, C., Laffon, E., Le Guyader, C.: Segmentation of Medical Images Sequence for Non Invasive Assessment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension, http://www.univ-pau.fr/~cgout/chubdx/index1.htm, (2004)
Alvarez, L., Lions, P.L., Morel, J.M.: Image selective smoothing and edge detection by nonlinear diffusion. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29(3), 845–866 (1992)
Barles, G.: Nonlinear Neumann boundary conditions for quasilinear degenerate elliptic equations and applications. J. Diff. Eq. 154, 191–224 (1999)
Barles, G.: Solutions de viscosité des équations de Hamilton-Jacobi. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1994)
Caselles, V., Catté, V., Coll, C., Dibos, C., Dibos, F.: A geometric model for active contours in image processing. Numer. Math. 66, 1–31 (1993)
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G.: Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vision 22-1, 61–87 (1997)
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G., Sbert, G., Sbert, C.: Minimal surfaces: a geometric three-dimensional segmentation approach. Numer. Math. 77(4), 423–451 (1997)
Chan, T., Vese, L.: An Efficient Variational Multiphase Motion for the Mumford–Shah segmentation mode. IEEE Asilomar Conf. Signals Syst. Comput. 1, 490–494 (2000)
Chan, T., Vese, L.: Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(2), 266–277 (2001)
Chen, Y., Giga, Y., Goto, S.: Uniqueness and existence of ciscosity solutions of generalized mean curvature flow equations. J. Diff. Geom. 33(3), 749–786 (1991)
Cohen, L.D.: On active contours models and balloons. Computer Vis. Graph. Image Process. Image Understand. 53(2), 211–218 (1991)
Crandall, M.G., Ishii, H., Lions, P.L.: User’s guide to viscosity solutions of second order partial differential equations. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 27(1), 1–69 (1992)
Crandall, M.G., Lions, P.L.: Viscosity solutions of Hamilton–Jacobi equations. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 277(1), 1–42 (1983)
Gout, C.: Ck surface reconstruction from surface patches. Comput. Math. Appl. 44(3–4), 389–406 (2002)
Gout, C., Le Guyader, C., Vese, L.: Image Segmentation under Interpolation conditions, Preprint, 44 pp., CAM-IPAM, Univ. of California at Los Angeles (2003)
Gout, C., Le Guyader, C., Vese, L.: Segmentation under geometrical conditions using geodesic active contours and interpolation using level set methods, Numer. Algorithms 39(1–3), 155–173 (2005)
Gout, C., Komatitsch, D.: Surface fitting of rapidly varying data using rank coding: application to geophysical surfaces. Math. Geol. 32(7), 873–888 (2000)
Le Guyader, C.: Imagerie Mathématique: Segmentation sous contraintes géométriques, Théory et Applications, Thèse de Doctorat, INSA Rouen (2004)
Le Guyader, C., Apprato, D., Gout, C.: Using a level set approach for image segmentation under interpolation conditions. Numer. Algorithms 39(1–3), 221–235 (2005)
Hvistendahl Karlsen, K., Lie, K.A., Risebro, N.H.: A fast marching method for reservoir simulation. Comput. Geosci. 4(2), 185–206 (2000)
Ishii, H., Sato, M.H.: Nonlinear oblique derivative problems for singular degenerate parabolic equations on a general domain, Preprint, Univ. Waseda, Japan, (2001)
Kichenassamy, S., Kumar, A., Olver, P. J., Tannenbaum, A., Yezzi, A.: Gradient Flows and Geometric Active Contour Models. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision ICCV, pp. 810–815 (1995)
Malladi, R., Sethian, J. A., Vemuri, B. C.: Shape modeling with front propagation: A level set approach. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Int. 17(2), 158–175 (1995)
Monsen, E., Randen, T., Sønneland, L., Odegard, J.: Geological Model Building: A Hierarchical Segmentation Approach in Mathematical Methods and Modelling in Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production, Series: Mathematics in Industry, Vol. 7 Iske, Armin; Randen, Trygve (Eds.), (2005)
Kass, M., Witkin, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: Active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vision 1(4), 133–144 (1987)
Osher, S., Fedkiw, R.: Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (2003)
Osher, S., Sethian, J.: A Fronts propagation with curvature dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79 12–49 (1988)
Randen, T., Monsen, E., Signer, C., Abrahamsen, A., Hansen, J., Sæter, J., Schlaf, J., Sønneland, L.: Three-dimensional texture attributes for seismic data analysis, in 70th Annual International Meeting, Society of Exploration Geophysics Expanded Abstracts, pp. 668–671, Calgary, Canada (2000)
Sethian, J.A.: Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods: Evolving interfaces in Computational Geometry, Fluid Mechanics, Computer Vision and Material Science. Cambridge University Press, Londres (1999)
Sethian, J.A.: Evolution, Implementation and application of level set and fast marching methods for advancing fronts. J. Comput. Phys. 169(2), 503–555 (2001)
Sethian, J.A.: A review of recent numerical algorithms for surface s moving with curvature dependent flows. J. Differential Geom. 31, 131–161 (1989)
Siddiqi, K., Lauziere, Y. B., Tannenbaum, A., Zucker, S. W.: Area and length minimizing flows for shape segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Processing 7(3), 433–443 (1998)
Symes, W.: The Rice Inversion Project, http://www.trip.caam.rice.edu/ and http://www.trip.caam.rice.edu/txt/tripinfo/other_list.html (2005)
Weickert, J., Kühne, G.: Fast methods for implicit active contours models, Preprint 61, Universität des Saarlandes, Saarbrücken (2002)
Yatziv, L., Bartesaghi, A., Sapiro, G.: A fast O(N) implementation of the fast marching algorithm. J. Comp. Phys. 212, 393–399 (2006)
Zhao, H.K., Osher, S., Merriman, B., Kang, M.: Implicit and non parametric shape reconstruction from unorganized data using a variational level set method. Comput. Vision Image Understand. 80(3), 295–314 (2000)
Zhao, H.K., Chan, T., Merriman, B., Osher, S.: A variational level set approach to multiphase motion. J. Comput. Phys. 127, 179–195 (1986)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gout, C., Guyader, C.L. Segmentation of complex geophysical structures with well data. Comput Geosci 10, 361–372 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-006-9029-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-006-9029-3