Abstract
We have designed, implemented and assessed an EBMT system that can be dubbed the “purest ever built”: it strictly does not make any use of variables, templates or patterns, does not have any explicit transfer component, and does not require any preprocessing or training of the aligned examples. It uses only a specific operation, proportional analogy, that implicitly neutralizes divergences between languages and captures lexical and syntactic variations along the paradigmatic and syntagmatic axes without explicitly decomposing sentences into fragments. Exactly the same genuine implementation of such a core engine was evaluated on different tasks and language pairs. To begin with, we compared our system on two tasks of a previous MT evaluation campaign to rank it among other current state-of-the-art systems. Then, we illustrated the “universality” of our system by participating in a recent MT evaluation campaign, with exactly the same core engine, for a wide variety of language pairs. Finally, we studied the influence of extra data like dictionaries and paraphrases on the system performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aha DW (1997) Editorial. Artif Intell Rev 11:7–10
Aha DW (1998) Feature weighting for lazy learning algorithms. In: Liu H, Motoda H (eds) Feature extraction, construction and selection: A data mining perspective. Kluwer Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 13–32
Akiba Y, Federico M, Kando N, Nakaiwa H, Paul M, Tsujii J (2004) Overview of the IWSLT04 evaluation campaign. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp 1–12
Allison L, Dix TI (1986) A bit string longest common subsequence algorithm. Inform Proc Lett 23:305–310
Amores JG, Mora JP (1998) Machine translation of motion verbs from English to Spanish. In: Martín-Vide C (ed) pp 191–206
Aramaki E, Kurohashi S (2004) Example-based machine translation using structual translation examples. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp 91–94
Bender O, Zens R, Matusov E, Ney H (2004) Alignment templates: the RWTH SMT system. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp. 79–84
Bertoldi N, Cattoni R, Cettolo M, Federico M (2004) The ITC-irst statistical machine translation system for IWSLT-2004. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, 51–58
Blanchon H, Boitet C, Brunet-Manquat F, Tomokiyo M, Hamon A, Hung VT, Bey Y (2004) Towards fairer evaluations of commercial MT systems on basic travel expressions corpora. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, 21–26
Bloomfield L (1933) Language. Holt. New York, NY
Brown PE, Della Pietra VJ, Della Pietra SA, Mercer RL (1993) The mathematics of statistical machine translation: Parameter estimation. Comput Ling 19:263–311
Carl M (1998) A constructivist approach to machine translation. In: Proceedings of the joint conference on new methods in language processing and computational natural language learning, NeMLaP3/CoNLL98. Macquarie University, [Sydney, Australia], pp 247–256
Carl M (2006) A system-theoretic view of EBMT. Mach Translat 19:147–167
Carl M, Way A (eds) (2003) Recent advances in example-based machine translation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Claveau V, L’Homme M-C (2005) Apprentissage par analogie pour la structuration de terminologie—Utilisation comparée de ressources endogènes et exogènes [Analogical learning of terminological structure—Comparison of the use of endogenous and exogenous resources]. In: TIA 2005: 6èmes rencontres terminologie et intelligence artificielle. Rouen, France, p 10
Damper RI, Eastman JEG (1996) Pronouncing text by analogy. In: COLING-96: The 16th international conference on computational linguistics. Copenhagen, Denmark, pp 268–269
Delhay A, Miclet L (2004) Analogical equations in sequences: Definition and resolution. In: Paliouras G, Sakakibara Y (eds) Grammatical inference: Algorithms and applications, 7th international colloquium, ICGI 2004. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 127–138
Doddington G (2002) Automatic evaluation of machine translation quality using n-gram co-occurrence statistics. In: ARPA workshop on human language technology notebook proceedings. San Diego, CA, pp 139–145
Dorr BJ (1994) Machine translation divergences. Comput Ling 20:597–633
Dorr BJ, Pearl L, Hwa R, Habash N (2002) DUSTer: A method for unraveling cross-language divergences for statistical word-level alignment. In: Richardson S (ed) Machine translation: From research to real users (Fifth conference of the Association for Machine Translation in the Americas AMTA-2002. Tiburon, CA, USA, ...), Springer, Berlin, pp 31–43
Gentner D (1983) Structure mapping: a theoretical model for analogy. Cognitive Sci 7:155–170
Habash N (2002) Generation-heavy hybrid machine translation. In: Proceedings of the international natural language generation conference (INLG’02). New York, NY, pp 185–191
Harris ZS (1954) Distributional structure. Word 10:146–162
Harris Z (1982) A grammar of English on mathematical principles. J Wiley, New York, NY
Hathout N (2001) Analogies morpho-synonymiques: Une méthode d’acquisition automatique de liens morphologiques à partir d’un dictionnaire de synonymes [Morpho-synonymic analogies: A method of automatically acquiring morphological links starting from a synonym dictionary]. In: TALN-Récital 2001: 8ème conférence sur le traitement automatique des langues naturelles et 5ème rencontre des étudiants chercheurs en informatique pour le traitement des langues. Tours, France, pp 223–232
Hofstadter D, Fluid Analogies Research Group (1994) Fluid concepts and creative analogies. Basic Books, New York, NY
Hou H, Deng D, Zou G, Yu H, Liu Y, Xiong D, Liu Q (2004) An EBMT system based on word alignment. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp 47–49
Hutchins J (2006) Example-based machine translation: a review and commentary. Mach Translat 19:116–130
Ilie L (1998) On ambiguity in internal contextual languages. In: Martín-Vide C (ed) pp 29–46
Itkonen E (1999) Grammaticalization: Abduction, analogy, and rational explanation. In: Shapiro M, Haley M (eds) The Peirce seminar papers: Essays in semiotic analysis vol IV. Berghahn Books. Oxford, England, pp 159–175
Joshi A, Vijay-Shanker K, Weir D (1991) The convergence of mildly context-sensitive grammar formalisms. In: Sells P, Shieber SM, Wasow T (eds) Foundational issues in natural language processing. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 31–81
Lee Y-S, Roukos S (2004) IBM spoken language translation system evaluation. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp 39–46
Lepage Y (1998) Solving analogies on words: An algorithm. In: COLING-ACL ’98: 36th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and 17th international conference on computational linguistics. Montreal, Quebec, Canada, pp 728–735
Lepage Y (2001) Analogy and formal languages. In: Proceedings of the joint meeting of the sixth conference on formal grammar and the seventh conference on the mathematics of language (FG/MOL 2001). Helsinki, Finland, pp 1–12
Lepage Y (2003) De l’analogie rendant compte de la commutation en linguistique [On analogy considering commutation in linguistics]. Mémoire d’habilitation à diriger les recherches. Université de Grenoble, Grenoble, France
Lepage Y (2004) Lower and higher estimates of the number of “true analogies” between sentences contained in a large multilingual corpus. In: Coling: 20th international conference on computational linguistics. Geneva, Switzerland, pp 736–742
Lepage Y, Peralta G (2004) Using paradigm tables to generate new utterances similar to those existing in linguistic resources. In: Proceedings of the fourth international conference on language resources and evaluation (LREC-2004). Lisbon, Portugal, pp 243–246
Levenshtein VI Levenshte
 n, VI] (1965) [Dvoichnye kody s ispravleniem vypadeni
n, VI] (1965) [Dvoichnye kody s ispravleniem vypadeni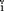 , vstavok i zameshcheni
, vstavok i zameshcheni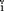 simbolov. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR] 163:845–848; appeared (1966) as Binary codes capable of correcting deletions, insertions and reversals, Sov Phys Dokl 10:707–710
simbolov. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR] 163:845–848; appeared (1966) as Binary codes capable of correcting deletions, insertions and reversals, Sov Phys Dokl 10:707–710Martín-Vide C (ed) (1998) Mathematical and computational analysis of natural language. John Benjamins, Amsterdam, The Netherlands/Philadelphia, PA
Papineni K, Roukos S, Ward T, Zhu W-J (2002) bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: 40th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, pp 311–318
Paul H (1920) Prinzipien der Sprachgeschichte [Principles of the history of language]. Niemayer, Tübingen, Germany
Polański K (1984) Słownik syntaktyczno-generatywny czasowników polskich [Syntactic-generative dictionary of Polish verbs]. Wydawnictwo im. Ossolińskich, Warszawa
Reichert J, Waibel A (2004) The ISL EDTRL system. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, 61–64
Sager N (1981) Natural language information processing: A computer grammar of English and its applications. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Salkoff M (1973) Une grammaire en chaîne du français [A string grammar of French]. Dunod, Paris, France
Sasayama M, Ren F, Kuroiwa S (2003) Super-function based Japanese-English machine translation system. In: NLPK-KE 2003: International conference on natural language processing and knowledge engineering. Beijing, China, pp 555–560
Sato S (1991) Example-based machine translation. PhD thesis, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
de Saussure F (1955) Cours de linguistique générale [A course in general linguistics]. Payot, Lausanne, Switzerland
Shieber SM (1985) Evidence against the context-freeness of natural language. Ling Philos 8:333–343
Skousen R (1989) Analogical modeling of language. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Stephen GA (1994) String searching algorithms. World Scientific, Singapore
Stroppa N, Yvon F (2005) An analogical learner for morphological analysis. In: CoNLL-2005: Ninth conference on computational natural language learning. Ann Arbor, MI, pp 120–127
Sumita E (2003) EBMT using DP-matching between word sequences. In: Carl M, Way A, (eds) Recent advances in example-based machine translation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 189–209
Sumita E, Akiba Y, Doi T, Finch A, Imamura K, Okuma H, Paul M, Shimohata M, Watanabe T (2004) EBMT, SMT, hybrid and more: ATR spoken language translation system. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp 13–20
Sumita E, Iida H (1991) Experiments and prospects of example-based machine translation. In: 29th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Berkeley, CA, pp 185–192
Takezawa T, Sumita E, Sugaya F, Yamamoto H, Yamamoto S (2002) Toward a broad-coverage bilingual corpus for speech translation of travel conversations in the real world. In: LREC 2002: Third international conference on language resources and evaluation. Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, pp 147–152
Thayer I, Ettelaie E, Knight K, Marcu D, Munteanu DS, Och FJ, Tipu Q (2004) The ISI/USC system. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp 59–60
Turian JP, Shen L, Melamed ID (2003) Evaluation of machine translation and its evaluation. In: MT Summit IX: Proceedings of the ninth machine translation summit New Orleans, USA, pp 386–393
Ukkonen E (1985) Algorithms for approximate string matching. Inform Control 64: 100–118
Vogel S, Hewavitharna S, Kolss M, Waibel A (2004) The ISL statistical translation system for spoken language translation. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp 65–72
Wagner RA, Fischer MJ (1974) The string-to-string correction problem. J Assoc Comput Mach 21:168–173
Wu D (1997) Stochastic inversion transduction grammars and bilingual parsing of parallel corpora. Comput Ling 23:377–403
Yamamoto K (2004) Interaction between paraphraser and transfer for spoken language translation.
 J Nat Lang Proc 11.5:63–86
J Nat Lang Proc 11.5:63–86Yang M, Zhao T, Liu H, SHi X, Jiang H (2004) Auto word alignment based Chinese-English EBMT. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp 27–29
Zuo Y, Zhou Y, Zong C (2004) Multi-engine based Chinese-to-English translation system. In: Proceedings of the international workshop on spoken language translation. Kyoto, Japan, pp 73–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lepage, Y., Denoual, E. Purest ever example-based machine translation: Detailed presentation and assessment. Machine Translation 19, 251–282 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10590-006-9010-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10590-006-9010-x





 n, VI] (1965) [Dvoichnye kody s ispravleniem vypadeni
n, VI] (1965) [Dvoichnye kody s ispravleniem vypadeni J Nat Lang Proc 11.5:63–86
J Nat Lang Proc 11.5:63–86