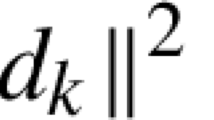Abstract
In many science and engineering applications, the discretization of linear ill-posed problems gives rise to large ill-conditioned linear systems with the right-hand side degraded by noise. The solution of such linear systems requires the solution of minimization problems with one quadratic constraint, depending on an estimate of the variance of the noise. This strategy is known as regularization. In this work, we propose a modification of the Lagrange method for the solution of the noise constrained regularization problem. We present the numerical results of test problems, image restoration and medical imaging denoising. Our results indicate that the proposed Lagrange method is effective and efficient in computing good regularized solutions of ill-conditioned linear systems and in computing the corresponding Lagrange multipliers. Moreover, our numerical experiments show that the Lagrange method is computationally convenient. Therefore, the Lagrange method is a promising approach for dealing with ill-posed problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar, R., Vogel, C.R.: Analysis of bounded variation penalty methods for ill-posed problems. Inverse Probl. 10, 1217–1229 (1994)
Avriel, M.: Nonlinear Programming: Analysis and Methods. Dover, New York (2003)
Blomgren, P., Chan, T.F.: Modular solvers for image restoration problems using the discrepancy principle. Numer. Linear Algebra Appl. 9, 347–358 (2002)
Calvetti, D., Golub, G., Reichel, L.: Estimation of the L-curve via Lanczos bidiagonalization. BIT 39, 603–619 (1999)
Calvetti, D., Reichel, L.: Tikhonov regularization of large linear problems. BIT 43, 263–283 (2003)
Chambolle, A., Lions, P.L.: Image recovery via total variation minimization and related problems. Numer. Math. 76, 167–188 (1997)
Chan, R.H., Chan, T.F., Zhou, H.M.: Continuation method for total variation denoising problems. Technical Report 95-18, University of California, Los Angeles (1995)
Chan, T.F., Golub, G.H., Mulet, P.: A nonlinear primal-dual method for total variation-based image restoration. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 20(6), 1964–1977 (1999)
Dembo, R.S., Eisenstat, S.C., Steihaug, T.: Inexact Newton methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 19, 400–408 (1982)
Dobson, D., Vogel, C.R.: Convergence of an iterative method for total variation denoising. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 34, 1779–1791 (1997)
Dobson, D.C., Santosa, F.: Recovery of blocky images from noisy and blurred data. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 56, 1181–1198 (1996)
Eisenstat, S.C., Walker, H.F.: Globally convergent inexact Newton methods. SIAM J. Optim. 4, 393–422 (1994)
Eisenstat, S.C., Walker, H.F.: Choosing the forcing term in an inexact Newton method. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 17, 16–32 (1996)
Engl, H.W.: Regularization methods for the stable solution of inverse problems. Surv. Math. Ind. 3, 71–143 (1993)
Engl, H.W., Hanke, M., Neubauer, A.: Regularization of Inverse Problems. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht (1996)
Frommer, A., Maass, P.: Fast CG-based methods for Tikhonov-Phillips problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 20, 1831–1850 (1999)
Golub, G., Heath, M., Wahba, G.: Generalized cross-validation as a method for choosing a good ridge parameter. Technometrics 21, 215–223 (1979)
Gutman, S.: Identification of discontinuous parameters in flow equations. SIAM J. Control Optim. 28, 1049–1060 (1990)
Hanke, M., Hansen, P.C.: Regularization methods for large-scale problems. Surv. Math. Ind. 3, 253–315 (1993)
Hansen, P.C.: Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve. SIAM Rev. 34(4), 561–580 (1992)
Hansen, P.C.: Regularization tools: a Matlab package for analysis and solution of discrete ill-posed problems. Numer. Alg. 6, 1–35 (1994)
Hansen, P.C.: Rank-Deficient and Discrete Ill-Posed Problems. SIAM, Philadelphia (1998)
Kelley, C.T.: Iterative Methods for Linear and Nonlinear Equations. SIAM, Philadelphia (1995)
Kilmer, M.E., O’Leary, D.P.: Choosing regularization parameters in iterative methods for ill-posed problems. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 22, 1204–1221 (2001)
Luenberger, D.G.: Linear and Nonlinear Programming, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht (2003)
Nagy, J.G., Palmer Lee, K., Perrone, L.: Iterative methods for image restoration: a Matlab object oriented approach. Numer. Alg. 36, 73–93 (2003)
Nagy, J.G., Plemmons, R.J., Torgersen, T.C.: Iterative image restoration using approximate inverse preconditioners. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 5(7), 1151–1162 (1996)
Neumaier, A.: Solving ill-conditioned and singular linear systems: a tutorial on regularization. SIAM Rev. 40, 636–666 (1998)
Nocedal, J., Wright, S.J.: Numerical Optimization. Springer, New York (1999)
Paige, C.C., Saunders, M.A.: Solution of sparse indefinite systems of linear equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 12, 617–629 (1975)
Phillips, D.L.: A technique for the numerical solution of certain integral equations of the first kind. J. Assoc. Comput. Mach. 9, 84–97 (1962)
Roggemann, M.C., Welsh, B.: Imaging Through Turbulence. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1996)
Rudin, L.I., Osher, S., Fatemi, E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D 60, 259–268 (1992)
Tikhonov, A.N., Arsenin, V.Y.: Solutions of Ill-Posed Problems. Wiley, New York (1977)
Vogel, C.R.: Nonsmooth regularization. In: Engl, H.W., Louis, A.K., Rundell, W. (eds.) Inverse Problems in Geophysical Applications, pp. 1–11. SIAM, Philadelphia (1997)
Vogel, C.R.: Computational Methods for Inverse Problems. SIAM, Philadelphia (2002)
Vogel, C.R., Oman, M.E.: Iterative methods for total variation denoising. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 17, 227–238 (1996)
Vogel, C.R., Oman, M.E.: Fast, robust total variation–based reconstruction of noisy, blurred images. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 7, 813–824 (1998)
Wahba, G.: Practical approximate solutions to linear operator equations when the data are noisy. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 14, 651–667 (1977)
Zangwill, W.I.: Nonlinear Programming: A Unified Approach. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Italian FIRB Project “Parallel algorithms and Nonlinear Numerical Optimization” RBAU01JYPN.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landi, G. The Lagrange method for the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems. Comput Optim Appl 39, 347–368 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-007-9059-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-007-9059-3