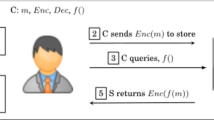
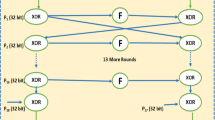
Abstract
The risks of misusing new and developing technology are increasing on a daily basis. In these technologies, electronic communication (e-communication) anonymously delivers sensitive information. It is a challenging task in e-communication to conceal the identity of the original users and preserve misuse risk protection (i.e., security and privacy) with low computations. On the other hand, anonymous communication may be detrimental. For security and privacy maintenance, we use the concept of Misuse Risk Protection (MRP) for low computations and High-Performance Computing (HPC). To overcome these challenges, the researchers use the concept of blind signature, blind singcryption and ID-based signcryption for e-communication environments. We analyzed blind and ID-based signcryption schemes and their security hardness, which is based on different Discrete Logarithm Problems (DLP) such as Elliptic Curve DLP (ECDLP), Hyperelliptic Curve DLP (HECDLP), and bilinear pairing etc. In this paper, we also investigated that the proposed schemes attain the desired MRP features, HPC (e.g., low computation and communication overheads) than the existing schemes, which makes the newly proposed scheme more suitable for low-power environments. Finally, all schemes with small key sizes provide low computation and communication overhead. Due to low computation and communication overheads, it is considered efficient.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ullah, S., Din, N.: Blind signcryption scheme based on hyper elliptic curves cryptosystem. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 14(2), 917–932 (2021)
Shamsherullah, N., Arif, U., I., Noor-Ul-Amin, R., U., Insaf, U.: Blind signcryption scheme based on hyper elliptic curve for untraceable payment system. In: Proc. 13th International Conference on Statistical Sciences 28, 337–344 (2015)
Yu, H.F., Zhao, H.X., Wang, Z.C., Yi, W.: Self-certified blind signcryption scheme based on ECC. Comput. Eng. 11, 1–8 (2010)
Song, M.M., Zhang, Z., Xie, W.J.: Certificateless blind signcryption scheme without pairing. J. Guangxi Univ. Nationalities (Natural Science Edition) 1 (2011)
Chaum, D.L.: Blind signatures for untraceable payments. pp. 199–203 (1983)
Tsai, C.H., Su, P.C.: An ECC-based blind signcryption scheme for multiple digital documents. Secur. Commun. Netw. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8981606
Xiao-lin, L.Z., Zhou, W., Jin, Y.: A proxy signature scheme based on hyperelliptic curve. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 30, 8 (2009)
Yang, C.: Digital signature scheme based on secret sharing. J. Chongqing Univ. Posts Telecommun. (Natural Science Edition) 27(3), 418–421 (2015)
Wei, L.F.: Design of hyperelliptic curve system digital signature in identity authentication. 8878, 88,780X (2013)
Nelasa, A., Fedoronchak, T.: Usage of hyperelliptic curves in the digital signature protocol. pp. 51–53 (2006)
Singh, S., Iqbal, M.S., Jaiswal, A.: Survey on techniques developed using digital signature: public key cryptography. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 117, 16 (2015)
Obiri, I.A., Xia, Q., Xia, H., Affum, E., Abla, S., Gao, J.: Personal health records sharing scheme based on attribute based signcryption with data integrity verifiable. J. Comput. Secur. 30, 1–34 (2022)
Zhou, Y., Guo, J., Li, F.: Certificateless public key encryption with cryptographic reverse firewalls. J. Syst. Architect. 109, 101754 (2020)
Adams, C., Lloyd, S.: Understanding Public-Key Infrastructure: Concepts, Standards, and Deployment Considerations. Sams Publishing, Carmel (1999)
Shamir, A.: Identity-based cryptosystems and signature schemes. pp. 47–53 (1984)
Al-Riyami, S.S., Paterson, K.G.: Certificateless public key cryptography. pp. 452–473 (2003)
Balasubramanian, T.: Indian J. Res. Commun. Eng. (IJRCE) 3(1), 17–27 (2015)
Chaudhari, S., Pahade, M., Bhat, S., Sawant, T., Jadhav, C.: A survey on methods of cryptography and data encryption. Methods Cryptogr. Data Encrypt. 3, 440–43 (2017)
Ullah, S., Jiangbin, Z., Hussain, M.T., Din, N., Ullah, F., Farooq, M.U.: A perspective trend of hyperelliptic curve cryptosystem for lighted weighted environments. J. Inf. Security Appl. 70, 103346 (2022)
Zheng, Y.: Digital signcryption or how to achieve cost(signature & encryption) \(<<\) cost(signature) + cost(encryption) pp 165–179 (1997)
Zhang, P., Li, Y., Chi, H.: An elliptic curve signcryption scheme and its application. Wirel. Commun. Mobile Comput. 2022 (2022)
Zia, M., Ali, R.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of blind signcryption scheme based on elliptic curve. Electron. Lett. 55(8), 457–459 (2019)
Yu, X., He, D.: A new efficient blind signcryption. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 13(6), 662–664 (2008)
Awasthi, A.K., Lal, S.: An efficient scheme for sensitive message transmission using blind signcryption. arXiv:cs/0504095 (2005)
Ullah, R., Umar, A.I., ul Amin, I., et al.: Blind signcryption scheme based on elliptic curves pp. 51–54 (2014)
Nasar, S.A.W., Javaid, Q., et al.: Efficient signcryption schemes based on hyperelliptic curve cryptosystem. pp. 84–87 (2011)
Ch, S.A., Uddin, N., Sher, M., Ghani, A., Naqvi, H., Irshad, A.: An efficient signcryption scheme with forward secrecy and public verifiability based on hyper elliptic curve cryptography. Multimedia Tools Appl. 74(5), 1711–1723 (2015)
Nizamuddin, S.A.Ch., Sher, M.: Public verifiable signcryption schemes with forward secrecy based on hyperelliptic curve cryptosystem. pp. 135–142 (2012)
Zheng, Y.: Signcryption and its applications in efficient public key solutions. pp. 291–312 (1997)
Ma, C., Chen, K.: Publicly verifiable authenticated encryption. Electron. Lett. 39(3), 281–282 (2003)
Shin, J.B., Lee, K., Shim, K.: New dsa-verifiable signcryption schemes. pp. 35–47 (2002)
Stallings, W.: Cryptography and network security principles and practices. 4th edition (2006)
Nyberg, K., Rueppel, R.A.: Message recovery for signature schemes based on the discrete logarithm problem. pp. 182–193 (1994)
Zhou, X.W.: Improved signcryption schemes based on hyper-elliptic curves cryptosystem. Appl. Mech. Mater. 20, 546–552 (2010)
Shuaib, M., Hassan, N.H., Usman, S., Alam, S., Bhatia, S., Mashat, A., Kumar, A., Kumar, M.: Self-sovereign identity solution for blockchain-based land registry system: a comparison. Mobile Inf. Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8930472
Ullah, S., Li, X.Y., Lan, Z.: A novel trusted third party based signcryption scheme. Multimedia Tools Appl. 79(31), 22749–22769 (2020)
Malone-Lee, J.: Identity-based signcryption, cryptology eprint archive. Report 98 (2002)
Boneh, D., Franklin, M.: Identity-based encryption from the weil pairing. pp. 213–229 (2001)
Yu, Y., Yang, B., Sun, Y., Zhu, S.I.: Identity based signcryption scheme without random oracles. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 31(1), 56–62 (2009)
Jin, Z., Wen, Q., Du, H.: An improved semantically-secure identity-based signcryption scheme in the standard model. Comput. Electr. Eng. 36(3), 545–552 (2010)
Li, F., Liao, Y., Qin, Z.: Analysis of an identity-based signcryption scheme in the standard model. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 94(1), 268–269 (2011)
Selvi, S.S.D., Vivek, S.S., Vinayagamurthy, D., Rangan, C.P.: Id based signcryption scheme in standard model pp. 35–52 (2012)
Ji-kai, T.: An efficient id-based signcryption scheme. Microelectr. Comput. (2010)
Shamir, A.: Identity-based cryptosystems and signature schemes. pp. 47–53 (1984)
Barreto, P.S., Libert, B., McCullagh, N., Quisquater, J.J.: Efficient and provably-secure identity-based signatures and signcryption from bilinear maps. pp. 515–532 (2005)
Boyen, X.: Multipurpose identity-based signcryption: a swiss army knife for identity-based cryptography. Cryptology 2003, 383–399 (2003)
Chen, L., Malone-Lee, J.: Improved identity-based signcryption. pp. 362–379 (2005)
Chow, S.S., Yiu, S.M., Hui, L.C., Chow, K.: Efficient forward and provably secure id-based signcryption scheme with public verifiability and public ciphertext authenticity. pp. 352–369 (2003)
Libert, B., Quisquater, J.J.: New identity based signcryption schemes from pairings. IACR Cryptol. 2003, 23 (2003)
Li, F.G., Hu, Y.P., Li, G.: An efficient identity-based signcryption scheme. Chin. J. Comput. 29(9), 1641 (2006)
Nayak, B.: A secure id-based signcryption scheme based on elliptic curve cryptography. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Stud. 6, 150–156 (2017)
Libert, B., Quisquater, J.: A new identity based signcryption scheme from pairings. pp. 155–158 (2003)
Pandey, S.K., Barua, R.: Construction of identity-based signcryption schemes. pp. 1–14 (2010)
Nalla, D., Reddy, K.C.: Signcryption scheme for identity-based cryptosystems. IACR Cryptol. 2003, 66 (2003)
Lal, S., Kushwah, P.: Id based generalized signcryption. IACR Cryptol. 2008, 84 (2008)
Lai, X., Huang, X., He, D.: An ID-based efficient signcryption key encapsulation scheme. pp. 1–6 (2008)
Ch, S.A., Amin, N., et al.: Signcryption schemes with forward secrecy based on hyperelliptic curve cryptosystem. pp. 244–247 (2011)
Ch, S.A., Sher, M., et al.: Public verifiable signcryption schemes with forward secrecy based on hyperelliptic curve cryptosystem. pp. 135–142 (2012)
Ch, S.A., Sher, M., Ghani, A., Naqvi, H., Irshad, A., et al.: An efficient signcryption scheme with forward secrecy and public verifiability based on hyper elliptic curve cryptography. Multimedia Tools Appl. 74(5), 1711–1723 (2015)
Premalatha, J., Sathya, K., Rajasekar, V.: Secure signcryption on hyperelliptic curve with sensor based random number
Kumar, P., Singh, A., Tyagi, A.D.: Implementation of hyperelliptic curve based signcryption approach. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 4(7), 1–15 (2013)
Ganesan, R., Gobi, M., Vivekanandan, K.: A novel digital envelope approach for a secure e-commerce channel. Int. J. Netw. Secur. 11(3), 121–127 (2010)
Barreto, P., Lynn, B., Scott, M.: Efficient implementation of pairing-based cryptosystems. J. Cryptol. 17, 321–334 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00145-004-0311-z
Dey, K., Debnath, S.K., Stănică, P., Srivastava, V.: A post-quantum signcryption scheme using isogeny based cryptography. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 69, 103280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jisa.2022.103280
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first and last authors are corresponding authors and remaining co-authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ullah, S., Jiangbin, Z., Hussain, M.T. et al. An investigating study of blind and ID-based signcryption schemes for misuse risk protection and high performance computing. Cluster Comput 27, 721–735 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-023-03969-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-023-03969-0