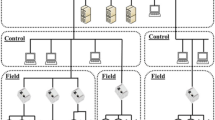
Abstract
The rapid deployment of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices have led to the development of innovative information services, unavailable a few years ago. To provide these services, IoT devices connect and communicate using networks like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet. This full-stack connection of the IoT devices has introduced a grand security challenge. This paper presents an IoT security framework to protect smart infrastructures from cyber attacks. This IoT security framework is applied to Bluetooth protocol and IoT sensors networks. For the Bluetooth protocol, the intrusion detection system (IDS) uses n-grams to extract temporal and spatial features of Bluetooth communication. The Bluetooth IDS has a precision of 99.6% and a recall of 99.6% using classification technique like Ripper algorithm and Decision Tree (C4.5). We also used AdaBoost, support vector machine (SVM), Naive Bayes, and Bagging algorithm for intrusion detection. The Sensor IDS uses discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to extract spatial and temporal features characteristics of the observed signal. Using the detailed coefficients of Biorthogonal DWT, Daubechies DWT, Coiflets DWT, Discrete Meyer DWT, Reverse Biorthogonal DWT, Symlets DWT, we present the results for detecting attacks with One-Class SVM, Local Outlier Factor, and Elliptic Envelope. The attacks used in our evaluation include Denial of Service Attacks, Impersonation Attacks, Random Signal Attacks, and Replay Attacks on temperature sensors. The One-Class SVM performed the best when compared with the results of other machine learning techniques.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
None.
References
Langner, R.: Stuxnet: dissecting a cyberwarfare weapon. IEEE Secur. Privacy 9(3), 49–51 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2011.67
Satam, P., Hariri, S.: WIDS: an anomaly based intrusion detection system for Wi-Fi (IEEE 80.211) Protocol. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manage. 18(1), 1077–1091 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSM.2020.3036138
Alipour, H., Al-Nashif, Y.B., Satam, P., Hariri, S.: Wireless anomaly detection based on IEEE 80.211 behavior analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 10(10), 2158–2170 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2015.2433898
Al-Nashif, Y., Kumar, A.A., Hariri, S., Qu, G., Luo, Y., Szidarovsky, F.: Multi-level intrusion detection system (ML-IDS). In: 5th International Conference on Autonomic Computing, ICAC 2008, pp. 131–140 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAC.2008.25
Satam, P., Alipour, H., Al-Nashif, Y., Hariri, S.: Anomaly behavior analysis of DNS protocol. J. Internet Serv. Inf. Secur. JISIS 5(4), 85–97 (2015)
Satam, P., Kelly, D., Hariri, S.: Anomaly behavior analysis of website vulnerability and security. In: Proceedings of IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, AICCSA, vol. 0 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/AICCSA.2016.7945697
Satam, P., Satam, S., Hariri, S., Alshawi, A.: Anomaly behavior analysis of IoT protocols. Model. Des. Secur. Internet Things (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119593386.ch13
Pacheco, J., Hariri, S.: IoT security framework for smart cyber infrastructures. In: Proceedings—IEEE 1st International Workshops on Foundations and Applications of Self-Systems, FAS-W 2016, pp. 242–247 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/FAS-W.2016.58
Buckman, A.H., Mayfield, M., Beck, S.B.M.: What is a smart building? Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 3(2), 92–109 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1108/SASBE-01-2014-0003
Wang, Z., Wang, L., Dounis, A.I., Yang, R.: Multi-agent control system with information fusion based comfort model for smart buildings. Appl. Energy 99, 247–254 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.05.020
Sadiku, M.N.O., Musa, S.M.: Cloud computing: opportunities and challenges. IEEE Potential 33, 34–36 (2014)
Yi, S., Li, C., Li, Q.: A survey of fog computing: Concepts, applications and issues. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing (MobiHoc) 2015 June, pp. 37–42 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2757384.2757397
Jabbar, M.A., Aluvalu, R.: Intrusion detection system for the internet of things: a review. IET Conf. Publ. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/cp.2018.1419
Berthier, R., Sanders, W.H.: Specification-based intrusion detection for advanced metering infrastructures. In: Proceedings of IEEE Pacific Rim International Symposium on Dependable Computing, PRDC, pp. 184–193 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/PRDC.2011.30
Olufowobi, H., Young, C., Zambreno, J., Bloom, G.: SAIDuCANT: specification-based automotive intrusion detection using controller area network (CAN) timing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(2), 1484–1494 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2019.2961344_rfseq1
Hajisalem, V., Babaie, S.: A hybrid intrusion detection system based on ABC-AFS algorithm for misuse and anomaly detection. Comput. Netw. 136, 37–50 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2018.02.028
Satam, P., Satam, S., Hariri, S.: Bluetooth Intrusion Detection System (BIDS). Proceedings of IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, AICCSA , 2018 November (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/AICCSA.2018.8612809
Jin, J., Gubbi, J., Marusic, S., Palaniswami, M.: An information framework for creating a smart city through internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 1(2), 112–121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2013.2296516
Ferreira, H.G.C., Dias Canedo, E., De Sousa, R.T.: IoT architecture to enable intercommunication through REST API and UPnP using IP, ZigBee and arduino. In: International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications, pp. 53–60 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/WiMOB.2013.6673340
Karagiannis, V., Chatzimisios, P., Vazquez-Gallego, F., Alonso-Zarate, J.: A survey on application layer protocols for the Internet of Things. Trans. IoT Cloud Comput. 3(1), 11–17 (2015)
Manadhata, P.K., Wing, J.M.: An attack surface metric. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 37(3), 371–386 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSE.2010.60
Soliman, M., Abiodun, T., Hamouda, T., Zhou, J., Lung, C.H.: Smart home: integrating internet of things with web services and cloud computing. Proc. Int. Conf. Cloud Comput. Technol. Sci. CloudCom 2, 317–320 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/CloudCom.2013.155
Sweldens, W.: The lifting scheme: a custom-design construction of biorthogonal wavelets. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 3(2), 186–200 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1006/acha.1996.0015
Wahid, K.A., Dimitrov, V.S., Jullien, G.A., Badawy, W.: An analysis of Daubechies discrete wavelet transform based on algebraic integer encoding scheme. In: Proceedings—3rd International Workshop on Digital and Computational Video, DCV 2002, pp. 27–34 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/DCV.2002.1218740
Graps, A.: An introduction to wavelets. IEEE Comput. Sci. Eng. 2(2), 50–61 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1109/99.388960
Xu, L., Zhang, D., Wang, K.: Wavelet-based cascaded adaptive filter for removing baseline drift in pulse waveforms. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 52(11), 1973–1975 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2005.856296
Szewczyk, R., Grabowski, K., Napieralska, M., Sankowski, W., Zubert, M., Napieralski, A.: A reliable iris recognition algorithm based on reverse biorthogonal wavelet transform. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 33(8), 1019–1026 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2011.08.018
Phinyomark, A., Limsakul, C., Phukpattaranont, P.: An optimal wavelet function based on wavelet denoising for multifunction myoelectric control, pp. 1098–1101 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/ecticon.2009.5137236
Davis, J., Goadrich, M.: The relationship between precision-recall and roc curves. In: ICML ’06: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine Learning, pp. 233–240 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1145/1143844.1143874
Satam, S., Satam, P., Hariri, S.: Multi-level Bluetooth Intrusion Detection System. In: Proceedings of IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, AICCSA 1–8 November 2020 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/AICCSA50499.2020.9316514
Brown, P., Cocke, J., Pietra, S.D., Pietra, V.D., Jelinek, F., Mercer, R., Roossin, P.: A statistical approach to French/English translation. Biol. Artif. Intell. Syst. 16(2), 547–561 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-3117-6_27
Satam, S.: Bluetooth anomaly based intrusion detection system by Shalaka Satam A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree of Master of Science In the Graduate C (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work is partly supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) Dynamic Data-Driven Application Systems (DDDAS) award number FA9550-18-1- 0427, National Science Foundation (NSF) research projects NSF-1624668 and NSF-1849113, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 70NANB18H263 and Department of Energy/National Nuclear Security Administration under Award Number(s) DE-NA0003946.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
None.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
None.
Informed consent
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satam, S., Satam, P., Pacheco, J. et al. Security framework for smart cyber infrastructure. Cluster Comput 25, 2767–2778 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03482-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03482-2