Abstract
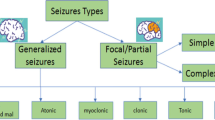
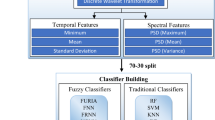
Electroencephalogram (EEG) is the most important monitoring methodology for the detection of epileptic seizure diseases. In this paper, EEG based epileptic seizure detection is assessed by employing Bern-Barcelona EEG and Bonn University EEG database. The proposed technique contains three major steps: decomposition, feature extraction and classification. Initially, decomposition using variational mode decomposition delivers an effective frequency localization. After decomposition, semantic feature extraction is carried-out by employing differential entropy and peak-magnitude of root mean square ratio for achieving optimal feature subsets and also for the rejection of irrelevant and redundant features. After finding the feature information, a superior classifier named as random forest is employed for classifying the normality and abnormality of seizure. The experimental result shows that the proposed approach distinguishes the normality and abnormality of seizure EEG signals in terms of sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predictive value with a superior recognition accuracy.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arunkumar, N., Ramkumar, K., Venkatraman, V., Abdulhay, E., Fernandes, S.L., Kadry, S., Segal, S.: Classification of focal and non-focal EEG using entropies. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 94, 112–117 (2017)
Biju, K.S., Hakkim, H.A., Jibukumar, M.G.: Ictal EEG classification based on amplitude and frequency contours of IMFs. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 37(1), 172–183 (2017)
Sharma, R., Pachori, R.B.: Classification of epileptic seizures in EEG signals based on phase space representation of intrinsic mode functions. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(3), 1106–1117 (2015)
Temko, A., Nadeu, C., Marnane, W., Boylan, G., Lightbody, G.: EEG signal description with spectral-envelope-based speech recognition features for detection of neonatal seizures. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 15(6), 839–847 (2011)
Li, S., Zhou, W., Yuan, Q., Liu, Y.: Seizure prediction using spike rate of intracranial EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 21(6), 880–886 (2013)
Tzallas, A.T., Tsipouras, M.G., Fotiadis, D.I.: Epileptic seizure detection in EEGs using time–frequency analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 13(5), 703–710 (2009)
Wang, N., Lyu, M.R.: Extracting and selecting distinctive EEG features for efficient epileptic seizure prediction. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 19(5), 1648–1659 (2015)
Parvez, M.Z., Paul, M.: Epileptic seizure prediction by exploiting spatiotemporal relationship of EEG signals using phase correlation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 24(1), 158–168 (2016)
Wang, Y., Markert, R.: Filter bank property of variational mode decomposition and its applications. Signal Process. 120, 509–521 (2016)
Guo, L., Rivero, D., Dorado, J., Munteanu, C.R., Pazos, A.: Automatic feature extraction using genetic programming: an application to epileptic EEG classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(8), 10425–10436 (2011)
Sharif, B., Jafari, A.H.: Prediction of epileptic seizures from EEG using analysis of ictal rules on Poincaré plane. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 145, 11–22 (2017)
Chu, H., Chung, C.K., Jeong, W., Cho, K.H.: Predicting epileptic seizures from scalp EEG based on attractor state analysis. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 143, 75–87 (2017)
Hassan, A.R., Subasi, A.: Automatic identification of epileptic seizures from EEG signals using linear programming boosting. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 136, 65–77 (2016)
Tawfik, N.S., Youssef, S.M., Kholief, M.: A hybrid automated detection of epileptic seizures in EEG records. Comput. Electr. Eng. 53, 177–190 (2016)
Dhiman, R., Saini, J.S.: Biogeography based hybrid scheme for automatic detection of epileptic seizures from EEG signatures. Appl. Soft Comput. 51, 116–129 (2017)
Ahammad, N., Fathima, T., Joseph, P.: Detection of epileptic seizure event and onset using EEG. Biomed. Res. Int. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/450573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravi Kumar, M., Srinivasa Rao, Y. Epileptic seizures classification in EEG signal based on semantic features and variational mode decomposition. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 6), 13521–13531 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-1995-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-1995-4