Abstract
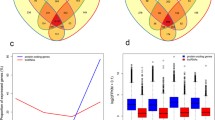
PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) are the largest class of small noncoding RNAs in animal cells; they cooperate with PIWI proteins to safeguard the genome. Although several studies have established that piRNAs can be biomarkers of cancer, it is still difficult to elucidate the exact function of piRNAs. In addition, researchers need to further investigate the interplay between piRNAs and piRNA groups in tumorigenesis. To identify cancer-associated piRNA-modules, we performed a weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA) on piRNA expression data from 11 types of cancer. Thereafter, genes associated with hub piRNAs in modules were predicted, and functional analysis of these genes was used to interpret the relation between piRNA and cancer. The results indicated that these piRNA modules have significant associations with cancer. A module with a high correlation coefficient (cor: −0.83, p value: 1.86E−128) was found; it was especially relevant to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Moreover, we found that hub piRNAs in modules may contribute to metastasis. This finding advances the understanding of piRNA function and its association with human cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, V.N.: Small RNAs just got bigger: Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) in mammalian testes. Genes Dev. 20(15), 1993–1997 (2006)
O’Donnell, K.A., Boeke, J.D.: Mighty Piwis defend the germline against genome intruders. Cell 129(1), 37–44 (2007)
Hale, B.J., Yang, C.X., Ross, J.W.: Small RNA regulation of reproductive function. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 81(2), 148–159 (2014)
Doms, A., Schroeder, M.: GoPubMed: exploring PubMed with the gene ontology. Nucleic Acids Res. 33(Web Server issue), 783–786 (2005)
Zhang, B., Horvath, S.: A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 4 (2005). Article 17
Cheng, J., Guo, J.M., Xiao, B.X., Miao, Y., Jiang, Z., Zhou, H., Li, Q.N.: piRNA, the new non-coding RNA, is aberrantly expressed in human cancer cells. Clin. Chim. Acta 412(17–18), 1621–1625 (2011)
Vinolas, N., Aya, F., Navarro, A., Marrades, R.M., Cordeiro, A., Fernandez, A., Chic, N., Gimferrer, J.M., Ramirez, J., Molins, L et al.: piRNA-651 as a prognostic marker in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 33(15), 11043 (2015)
Li, D., Luo, Y., Gao, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Tan, S., Zhang, Y., Duan, J., Yang, Y.: piR-651 promotes tumor formation in non-small cell lung carcinoma through the upregulation of cyclin D1 and CDK4. Int. J. Mol. Med. 38(3), 927–936 (2016)
Cheng, J., Deng, H.X., Xiao, B.X., Zhou, H., Zhou, F., Shen, Z.S., Guo, J.M.: piR-823, a novel non-coding small RNA, demonstrates in vitro and in vivo tumor suppressive activity in human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 315(1), 12–17 (2012)
Yan, H., Wu, Q.L., Sun, C.Y., Ai, L.S., Deng, J., Zhang, L., Chen, L., Chu, Z.B., Tang, B., Wang, K., et al.: piRNA-823 contributes to tumorigenesis by regulating de novo DNA methylation and angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 29(1), 196–206 (2015)
Li, Y., Wu, X., Gao, H., Jin, J., Li, A., Kim, Y., Wang, F., Wang, J., Nelson, R., Mu, B., et al.: piR-32052, PiR-39894 and PiR-43607, three novel dicer-independent Piwi-interacting RNAs derived from the same PiRNA cluster, are up-regulated in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Modern Pathol. 27, 244a–244a (2014)
Busch, J., Ralla, B., Jung, M., Wotschofsky, Z., Trujillo-Arribas, E., Schwabe, P., Kilic, E., Fendler, A., Jung, K.: Piwi-interacting RNAs as novel prognostic markers in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 34(1), 61 (2015)
Martinez, V.D., Enfield, K.S.S., Rowbotham, D.A., Lam, W.L.: An atlas of gastric PIWI-interacting RNA transcriptomes and their utility for identifying signatures of gastric cancer recurrence. Gastric Cancer 19(2), 660–665 (2016)
Krishnan, P., Ghosh, S., Graham, K., Mackey, J.R., Kovalchuk, O., Damaraju, S.: Piwi-interacting RNAs and PIWI genes as novel prognostic markers for breast cancer. Oncotarget 7(25), 37944–37956 (2016)
Firmino, N., Martinez, V.D., Rowbotham, D.A., Enfield, K.S.S., Bennewith, K.L., Lam, W.L.: HPV status is associated with altered PIWI-interacting RNA expression pattern in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 55, 43–48 (2016)
Rizzo, F., Rinaldi, A., Marchese, G., Coviello, E., Sellitto, A., Cordella, A., Giurato, G., Nassa, G., Ravo, M., Tarallo, R., et al.: Specific patterns of PIWI-interacting small noncoding RNA expression in dysplastic liver nodules and hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 7(34), 54650–54661 (2016)
Chu, H.Y., Hui, G.Y., Yuan, L., Shi, D., Wang, Y.B., Du, M.L., Zhong, D.Y., Ma, L., Tong, N., Qin, C., et al.: Identification of novel piRNAs in bladder cancer. Cancer Lett. 356(2), 561–567 (2015)
Martinez, V.D., Vucic, E.A., Thu, K.L., Hubaux, R., Enfield, K.S., Pikor, L.A., Becker-Santos, D.D., Brown, C.J., Lam, S., Lam, W.L.: Unique somatic and malignant expression patterns implicate PIWI-interacting RNAs in cancer-type specific biology. Sci. Rep. 5, 10423 (2015)
Pretty, R.: WGCNA-package WGCNA weighted gene co-expression network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 9(1), 559 (2011)
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N.S., Wang, J.T., Ramage, D., Amin, N., Schwikowski, B., Ideker, T.: Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13(11), 2498–2504 (2003)
Zhang, H., Ren, Y., Xu, H.M., Pang, D.Y., Duan, C., Liu, C.G.: The expression of stem cell protein Piwil2 and piR-932 in breast cancer. Surg. Oncol. 22(4), 217–223 (2013)
Peng, L.P., Song, L., Liu, C.Y., Lv, X.H., Li, X.P., Jie, J., Zhao, D., Li, D.: piR-55490 inhibits the growth of lung carcinoma by suppressing mTOR signaling. Tumor Biol. 37(2), 2749–2756 (2016)
Zhang, B., Kirov, S., Snoddy, J.: WebGestalt: an integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological contexts. Nucleic Acids Res 33(Web Server issue), W741–W748 (2005)
Wang, J., Duncan, D., Shi, Z., Zhang, B.: WEB-based GEne SeT analysis toolkit (WebGestalt): update 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Web Server issue), W77–W83 (2013)
Byers, T., Wender, R.C., Jemal, A., Baskies, A.M., Ward, E.E., Brawley, O.W.: The American Cancer Society challenge goal to reduce US cancer mortality by 50% between 1990 and 2015: results and reflections. CA 66(5), 359 (2016)
Chen, W., Zheng, R., Baade, P.D., Zhang, S., Zeng, H., Bray, F., Jemal, A., Yu, X.Q., He, J.: Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA 66(2), 115 (2016)
Yan, H., Wu, Q.L., Sun, C.Y., Ai, L.S., Deng, J., Zhang, L., Chen, L., Chu, Z.B., Tang, B., Wang, K.: piRNA-823 contributes to tumorigenesis by regulating de novo DNA methylation and angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 29(1), 196 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61571341, 61201312 and 91530113, Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 2013 0203110017), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Nos BDY171416, JBZ170301, JB140306 and 20101164977), the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province in China (2015JM6275, 2017JM6024).
Author contributions Yajun Liu and Junying Zhang participated in the design of the study and drafted the manuscript. Yajun Liu conducted the data analysis. Aimin Li, Yuanyuan Zhang, and Yaoyao Li proposed numerous constructive ideas and revised the manuscript in detail. In addition, Xiguo Yuan, Zhongzhen He, Zhaowen Liu, and Shouheng Tuo contributed some insights into this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with respect to the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Li, A. et al. Identification of PIWI-interacting RNA modules by weighted correlation network analysis. Cluster Comput 22 (Suppl 1), 707–717 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1194-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-1194-8