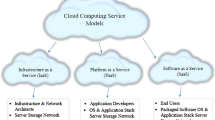
Abstract
Cloud computing is a promising next-generation computing paradigm that offers significant economic benefits to both commercial and public entities. Furthermore, cloud computing provides accessibility, simplicity, and portability for its customers. Due to the unique combination of characteristics that cloud computing introduces (including on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service), digital investigations face various technical, legal, and organizational challenges to keep up with current developments in the field of cloud computing. There are a wide variety of issues that need to be resolved in order to perform a proper digital investigation in the cloud environment. This paper examines the challenges in cloud forensics that are identified in the current research literature, alongside exploring the existing proposals and technical solutions addressed in the respective research. The open problems that need further effort are highlighted. As a result of the analysis of literature, it is found that it would be difficult, if not impossible, to perform an investigation and discovery in the cloud environment without relying on cloud service providers (CSPs). Therefore, dependence on the CSPs is ranked as the greatest challenge when investigators need to acquire evidence in a timely yet forensically sound manner from cloud systems. Thus, a fully independent model requires no intervention or cooperation from the cloud provider is proposed. This model provides a different approach to a forensic acquisition and analysis system (FAAS) in an Infrastructure as a Service model. FAAS seeks to provide a richer and more complete set of admissible evidences than what current CSPs provide, with no requirement for CSP involvement or modification to the CSP’s underlying architecture.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zargari, S., Benford, D.: Cloud forensics: concepts, issues, and challenges. In: 2012 Third International Conference on Emerging Intelligent Data and Web Technologies, pp. 236–243. IEEE, Bucharest (2012)
Higgings, K.: Dropbox, Word Press Used as Cloud Cover in New APT Attacks. http://www.darkreading.com/attacks-breaches/dropbox-wordpress-used-as-cloud-cover-in-new-apt-attacks/d/d-id/1140098?
Dzombeta, S., Stantchev, V., Colomo-palacios, R., Brandis, K., Haufe, K.: Governance of Cloud Computing Services for the Life Sciences. IEEE Computer Society (2014)
Hooper, C., Martini, B., Choo, K.-K.R.: Cloud computing and its implications for cybercrime investigations in Australia. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 29, 152–163 (2013)
Stantchev, V., Colomo-Palacios, R., Niedermayer, M.: Cloud computing based systems for healthcare. Sci. World J. 2014, 1–74 (2014)
Ruan, K., Carthy, J.: Cloud forensic maturity model. In: Digital Forensics and Cyber Crime, pp. 22–41. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg (2012)
Dykstra, J., Sherman, A.T.: Design and implementation of FROST: digital forensic tools for the openstack cloud computing platform. Digit. Investig. 10, S87–S95 (2013)
Murphy, B.: e-Discovery in the Cloud Not as Simple as You Think. http://www.forbes.com/sites/jasonvelasco/2011/11/29/e-discovery-in-the-cloud-not-as-simple-as-you-think/
Ruan, K.: Designing a forensic-enabling cloud ecosystem. In: Cybercrime and cloud forensics, pp. 331–344. IGI Global, USA (2013)
Mell, P., Grance, T.: The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing. Recommendations of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (2011)
Poisel, R., Malzer, E., Tjoa, S.: Evidence and cloud computing?: the virtual machine introspection approac. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. Ubiquitous Comput. Dependable Appl. 4, 135–152 (2012)
Martini, B., Choo, K.-K.R.: An integrated conceptual digital forensic framework for cloud computing. Digit. Investig. 9, 71–80 (2012)
Zawoad, S., Hasan, R.: Digital Forensics in the Cloud (2013)
Sang, T.: A log based approach to make digital forensics easier on cloud computing. In: 2013 Third International Conference on Intelligent System Design and Engineering Applications, pp. 91–94. IEEE (2013)
Patrascu, A., Patriciu, V.: Beyond digital forensics. A cloud computing perspective over incident response and reporting. In: Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics (SACI), pp. 455–460. Timisoara (2013)
Ruan, K., Carthy, J.: Cloud computing reference architecture and its forensic implications: a preliminary analysis. Digit. Forensics Cyber Crime. 1–21 (2013)
Birk, D.: Technical challenges of forensic investigations in cloud computing environments. In: Workshop on Cryptography and Security in Clouds, pp. 1–6. Zurich, Switzerland (2011)
Dykstra, J., Sherman, A.T.A.: Understanding issues in cloud forensics?: two hypothetical case studies. In: Proceedings of the 2011 ADFSL Conference on Digital Forensics Security and Law, pp. 1–10 (2011)
Shah, J.J., Malik, L.G.: Cloud forensics: issues and challenges. In: 2013 6th International Conference on Emerging Trends Engineering Technology 138–139 (2013)
Reilly, D., Wren, C., Berry, T.: Cloud computing?: pros and cons for computer forensic investigations. Int. J. Multimed. Image Process. 1, 26–34 (2011)
Birk, D., Wegener, C.: Technical issues of forensic investigations in cloud computing environments. In: 2011 Sixth IEEE International Workshop on Systematic Approaches to Digital Forensic Engineering, pp. 1–10. IEEE, Okland (2011)
Zaferullah, Z., Anwar, F., Anwar, Z.: Digital forensics for eucalyptus. In: 2011 Frontiers of Information Technology, pp. 110–116. IEEE, Islamabad (2011)
Wolski, R.: https://www.usenix.org/conference/lisa-09/eucalyptus-open-source-infrastructure-cloud-computing
Damshenas, M., Dehghantanha, A., Mahmoud, R., Shamsuddin, S.: Forensics investigation challenges in cloud computing environments. cyber security. In: 2012 International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Digital Forensic (CyberSec), pp. 190–194. IEEE, Kuala Lumpur (2012)
Marty, R.: Cloud application logging for forensics. In: Proceedings of the 2011 ACM Symposium on Applied Computing—SAC ’11, p. 178 (2011)
Almulla, S., Iraqi, Y., Jones, A.: A state-of-the-art review of cloud. In: 2014 ADFSL 9, pp. 7–28 (2014)
Zawoad, S., Hasan, R.: Cloud Forensics: A Meta-Study of Challenges, Approaches, and Open Problems, pp. 1–15 (2013). arXiv:1302.6312
Guo, H., Jin, B., Shang, T.: Forensic investigations in cloud environments. In: 2012 International Conference on Computer Science and Information Processing (CSIP), pp. 248–251. IEEE, Xi’an, Shaanxi (2012)
Zawoad, S., Hasan, R.: I Have the Proof?: Providing Proofs of Past Data Possession in Cloud Forensics (2012)
Ruan, K., Carthy, J., Kechadi, T., Crosbie, M.: Cloud forensics?: an overview. Adv. Digit. Forensics VII 15–26 (2011)
Sibiya, G., Venter, H.S., Fogwill, T.: Digital forensic framework for a cloud environment. In: IST\(\_\)Africa 2012 Conference Proceedings, pp. 1–8 (2012)
Taylor, M., Haggerty, J., Gresty, D., Lamb, D.: Forensic investigation of cloud computing systems. Netw. Secur. 2011, 4–10 (2011)
Crosbie, M.: Hack the cloud: ethical hacking and cloud forensics. In: Cybercrime and Cloud Forensics, p. 17. IGI Global, USA (2013)
Ruan, K., Carthy, J., Kechadi, T., Baggili, I.: Cloud forensics definitions and critical criteria for cloud forensic capability: an overview of survey results. Digit. Investig. 10, 34–43 (2013)
Ko, R.K.L., Jagadpramana, P., Mowbray, M., Pearson, S., Kirchberg, M., Liang, Q., Lee, B.S.: TrustCloud: a framework for accountability and trust in cloud computing. In: 2011 IEEE World Congress on Services, pp. 584–588. IEEE, Washington, DC (2011)
Dykstra, J., Sherman, A.T.: Acquiring forensic evidence from infrastructure-as-a-service cloud computing: exploring and evaluating tools, trust, and techniques. Digit. Investig. 9, S90–S98 (2012)
Amazon Web Services: AWS CloudTrail?: User Guide (2014)
Pichan, A., Lazarescu, M., Soh, S.T.: Cloud forensics: technical challenges, solutions and comparative analysis. Digit. Investig. 13, 38–57 (2015)
Delport, W., Olivier, M.S., Kohn, M.: Isolating a cloud instance for a digital forensic. In: ISSA (2011)
Li, J., Chen, X., Huang, Q., Wong, D.S.: Digital provenance: enabling secure data forensics in cloud computing. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. (2013)
Yan, C.: Cybercrime forensic system in cloud computing. In: Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Image Analysis and Signal Processing, IASP 2011, pp. 612–613 (2011)
Catryna, B.: Review of the Cybercrime Legislation Amendment Bill (2011)
Marangos, N., Rizomiliotis, P., Mitrou, L.: Time synchronization?: pivotal element in cloud forensics. Secur. Commun. Netw. (2014)
Chen, G., Du, Y., Qin, P., Du, J.: Suggestions to digital forensics in Cloud computing ERA. In: 2012 3rd IEEE International Conference on Network Infrastructure and Digital Content, pp. 540–544. IEEE, Beijing (2012)
Grispos, G.: Calm before the storm?: the challenges of cloud computing in digital forensics 4, 28–48 (2012)
Al Fahdi, M., Clarke, N.L., Furnell, S.M.: Challenges to digital forensics: a survey of researchers & practitioners attitudes and opinions. In: 2013 Information Security for South Africa—Proceedings of the ISSA 2013 Conference, pp. 1–8 (2013)
Taylor, M., Haggerty, J., Gresty, D., Hegarty, R.: Digital evidence in cloud computing systems. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 26, 304–308 (2010)
Kumar, M.: Computer Investigations. http://thehackernews.com/2011/09/offline-windows-analysis-and-data.html
Geethakumari, G., Belorkar, A.: Regenerating cloud attack scenarios using LVM2 based system snapshots for forensic analysis. Int. J. Cloud Comput. Serv. Sci. 1, 134–141 (2012)
Raghavan, S.: Digital forensic research: current state of the art. CSI Trans. ICT. 1, 91–114 (2012)
Sleuthkit: Open Source Digital Forensics. http://www.sleuthkit.org/index.php
X-Ways: X-Ways technology. http://www.x-ways.net/
Trenwith, P.M., Venter, H.: Digital forensic readiness in the cloud. Inf. Secur. S. Afr. 2013, 1–5 (2013)
NIST: NIST Cloud Computing Forensic Science Challenges NIST Cloud Computing. USA (2014)
Dykstra, J.: Cybercrime and cloud forensics. In: Ruan, K. (ed.) Cybercrime and Cloud Forensics, pp. 156–185. IGI Global, USA (2013)
Thethi, N., Keane, A.: Digital Forensics Investigations in the Cloud. In: 2014 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference, pp. 1475–1480 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alqahtany, S., Clarke, N., Furnell, S. et al. A forensic acquisition and analysis system for IaaS. Cluster Comput 19, 439–453 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-015-0509-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-015-0509-x