Abstract
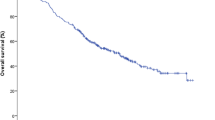
Lymph nodes are common sites of oligometastases for several primaries. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) represents an effective treatment but no consensus exists regarding dose and fractionation. Aim of this trial was to evaluate safety and efficacy of high-dose SBRT. We included patients with 1 to 3 lymph node metastases. Primary end-point was safety, while secondary end-points were in-field local control (LC), out-field lymph nodal progression free survival (LPFS), distant metastasis free survival (DMFS), progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). 64 lesions in 52 patients were treated from 2015 to 2019. Most common primary tumor was genitourinary cancer (75%), in particular prostate cancer (65.4%). With a median follow-up of 24.4 months (range 3–49), treatment was very well tolerated, with only 4 (7.7%) patients reporting acute side effects, all classified as grade 1, in the form of pain, fatigue, nocturia and dysuria. No toxicity ≥ grade 2 were reported. Rates of LC at 1, 2 and 3 years were 97.9%, 82.1% and 82.1%. Male sex (HR 0.12, p value 0.014) was associated with improved LC. LPFS at 1, 2 and 3 years were 69.6%, 49.6% and 46.1%, respectively, and DMFS was 81.74%, 67.5% and 58.5%, respectively. Presence of lesions in other organs was correlated with inferior DMFS (HR 3.82, p = 0.042). PFS at 1, 2 and 3 years were 67.4%, 42.4% and 31.86%, respectively. OS at 1, 2 and 3 years were 97.3%, 94.2%, 84%, respectively and significantly correlated with in-field recurrence (HR 8.72, p = 0.000). Our prospective trial confirms safety and efficacy of SBRT in the management of lymph node metastases. Registered Clinical trial NCT02570399.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR (1995) Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol 13:8–10
Niibe Y, Hayakawa K (2010) Oligometastases and oligo-recurrence: the new era of cancer therapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol 40(2):107–111. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyp167
Ruiterkamp J, Ernst MF (2011) The role of surgery in metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-8049(11)70142-3
Rai R, Rai S (2004) Preoperative probability model for predicting overall survival after resection of pulmonary metastases from colorectal cancer. Br J Surg. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.4653
Pawlik TM, Scoggins CR, Zorzi D et al (2005) Effect of surgical margin status on survival and site of recurrence after hepatic resection for colorectal metastases. Ann Surg 241(5):715–724. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000160703.75808.7d
Sardenberg RAS, de Figueiredo LP, Haddad FJ, Gross JL, Younes RN (2010) Pulmonary metastasectomy from soft tissue sarcomas. Clinics 65(9):871–876. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1807-59322010000900010
Corbin KS, Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR (2013) Extracranial oligometastases: a subset of metastases curable with stereotactic radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 31(11):1384–1390. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.45.9651
Kang JK, Kim MS, Kim JH et al (2010) Oligometastases confined one organ from colorectal cancer treated by SBRT. Clin Exp Metastasis 27(4):273–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-010-9325-0
Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R et al (2016) ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 27(8):1386–1422. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw235
Alongi F, Arcangeli S, Filippi AR, Ricardi U, Scorsetti M (2012) Review and uses of stereotactic body radiation therapy for oligometastases. Oncologist 17(8):1100–1107. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0092
De Bari B, Alongi F, Buglione M et al (2014) Salvage therapy of small volume prostate cancer nodal failures: a review of the literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 90(1):24–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.11.003
Franceschini D, De Rose F, Franzese C et al (2019) Predictive Factors for Response and survival in a cohort of oligometastatic patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol 104(1):111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.12.049
Bonomo P, Cipressi S, Saieva C et al (2013) Clinical outcome of stereotactic body radiotherapy for abdominal lymph node metastases. Tumori 99(5):611–616. https://doi.org/10.1700/1377.15311
Alongi F, Fogliata A, Clerici E et al (2012) Volumetric modulated arc therapy with flattening filter free beams for isolated abdominal/pelvic lymph nodes: Report of dosimetric and early clinical results in oligometastatic patients. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-7-204
Corv R, Lamanna G, Vagge S et al (2013) Once-weekly stereotactic radiotherapy for patients with oligometastases: compliance and preliminary efficacy. Tumori 99(2):159–163. https://doi.org/10.1700/1283.14186
Jereczek-Fossa BA, Piperno G, Ronchi S et al (2014) Linac-based stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastatic patients with single abdominal lymph node recurrent cancer. Am J Clin Oncol Cancer Clin Trials 37(3):227–233. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e3182610878
Bignardi M, Navarria P, Mancosu P et al (2011) Clinical outcome of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for abdominal lymph node metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(3):831–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.05.032
Franzese C, Lopci E, Di Brina L et al (2017) 11C-Choline-pet guided stereotactic body radiation therapy for lymph node metastases in oligometastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Invest. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357907.2017.1375116
Franzese C, Fogliata A, Comito T et al (2017) Stereotactic/hypofractionated body radiation therapy as an effective treatment for lymph node metastases from colorectal cancer: an institutional retrospective analysis. Br J Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20170422
Kim JH, Kim MS, Yoo SY, Lim SM, Lee GH, Yi KH (2010) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for refractory cervical lymph node recurrence of nonanaplastic thyroid cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 142(3):338–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2009.12.034
Choi CW, Cho CK, Yoo SY et al (2009) Image-guided stereotactic body radiation therapy in patients with isolated para-aortic lymph node metastases from uterine cervical and corpus cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(1):147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.07.020
Kim MS, Cho CK, Yang KM, Lee DH, Moon SM, Shin YJ (2009) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for isolated paraaortic lymph node recurrence from colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 15(48):6091–6095. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.6091
Nicosia L, Franzese C, Mazzola R et al (2020) Recurrence pattern of stereotactic body radiotherapy in oligometastatic prostate cancer: a multi-institutional analysis. Strahlentherapie und Onkol 196(3):213–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-019-01523-9
Triggiani L, Alongi F, Buglione M et al (2017) Efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy in oligorecurrent and in oligoprogressive prostate cancer: New evidence from a multicentric study. Br J Cancer 116(12):1520–1525. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.103
Macchia G, Lazzari R, Colombo N et al (2020) A Large, Multicenter, retrospective study on efficacy and safety of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in oligometastatic ovarian cancer (MITO RT1 study): A Collaboration of MITO, AIRO GYN, and MaNGO Groups. Oncologist. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0309
Nicosia L, Franzese C, Mazzola R et al (2019) Recurrence pattern of stereotactic body radiotherapy in oligometastatic prostate cancer: a multi-institutional analysisRezidivmuster nach stereotaktischer Radiotherapie beim oligometastasierten Prostatakarzinom: eine multiinstitutionelle Analyse. Strahlentherapie Onkol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-019-01523-9
Yeung R, Hamm J, Liu M, Schellenberg D (2017) Institutional analysis of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for oligometastatic lymph node metastases. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-017-0820-1
Franzese C, Cozzi L, Franceschini D et al (2016) Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy with volumetric-modulated arcs and high-intensity photon beams for the treatment of abdomino-pelvic lymph-node metastases. Cancer Invest. https://doi.org/10.1080/07357907.2016.1197235
Franzese C, Comito T, Toska E et al (2018) Predictive factors for survival of oligometastatic colorectal cancer treated with Stereotactic body radiation therapy. Radiother Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2018.10.024
Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S et al (2019) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard of care palliative treatment in patients with oligometastatic cancers (SABR-COMET): a randomised, phase 2, open-label trial. Lancet 393(10185):2051–2058. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32487-5
Mazzola R, Figlia V, Rigo M et al (May 2020) Feasibility and safety of 1.5 T MR-guided and daily adapted abdominal-pelvic SBRT for elderly cancer patients: geriatric assessment tools and preliminary patient-reported outcomes. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03230-w
Bell LJ, Eade T, Kneebone A et al (2017) Initial experience with intra-fraction motion monitoring using Calypso guided volumetric modulated arc therapy for definitive prostate cancer treatment. J Med Radiat Sci 64(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmrs.224
Funding
No funding were used for the present work.\
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franzese, C., Comito, T., Tripoli, A. et al. Phase II trial of high dose stereotactic body radiation therapy for lymph node oligometastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 37, 565–573 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-020-10047-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-020-10047-x