Abstract
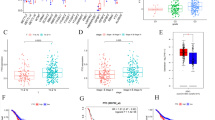
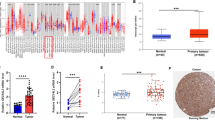
Downregulation and aberrant hypermethylation of long non-coding RNA CTC-276P9.1 have been detected in limited tumors. However, the distribution of methylated CpG sites and biological role of CTC-276P9.1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression and prognosis have not been fully clarified. The present study was to investigate the expression status and the distribution of methylated CpG sites within the three CpG islands of CTC-276P9.1, further to clarify its functional role and prognostic value in ESCC development and prognosis. Significant downregulation of CTC-276P9.1 was detected in esophageal cancer cells and ESCC tissues, and the expression of CTC-276P9.1 in ESCC tissues was associated with TNM stage, pathological differentiation, lymph node metastasis, and distant metastasis or recurrence. The expression level of CTC-276P9.1 in esophageal cancer cells was significantly reversed by treatment with 5-Aza-dC and TSA. The aberrant hypermethylation of the regions around the transcription start site was more tumor specific and associated with the expression levels of CTC-276P9.1. Moreover, histone modification may also participate in the regulation of CTC-276P9.1. Furthermore, over-expression of CTC-276P9.1 inhibited esophageal cancer cells proliferation and invasion in vitro, decreased the expression of proliferative markers and inhibited esophageal cancer cells invasion probably by regulating EMT. In addition, the dysregulation and hypermethylation of the regions around the transcription start site of CTC-276P9.1 were associated with poorer ESCC patients’ survival. These findings suggest that CTC-276P9.1 may act as a tumor suppressor and may be employed as a new prognostic factor and therapeutic target for ESCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108
Napier KJ, Scheerer M, Misra S (2014) Esophageal cancer: A review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, staging workup and treatment modalities. World J Gastrointest Oncol 6:112–120
Shahbaz Sarwar CM, Luketich JD, Landreneau RJ, Abbas G (2010) Esophageal cancer: an update. Int J Surg 8:417–422
Guohong Z, Min S, Duenmei W, Songnian H, Min L, Jinsong L, Hongbin L, Feng Z, Dongping T, Heling Y, Zhicai L, Shiyong L, Quansheng G, Xiaoyun L, Yuxia G (2010) Genetic heterogeneity of oesophageal cancer in high-incidence areas of southern and northern China. PLoS ONE 5:e9668
Messmann H (2001) Squamous cell cancer of the oesophagus. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 15:249–265
Kapranov P, Cheng J, Dike S, Nix DA, Duttagupta R, Willingham AT, Stadler PF, Hertel J, Hackermüller J, Hofacker IL, Bell I, Cheung E, Drenkow J, Dumais E, Patel S, Helt G, Ganesh M, Ghosh S, Piccolboni A, Sementchenko V, Tammana H, Gingeras TR (2007) RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 316:1484–1488
Sun M, Kraus WL (2015) From discovery to function: the expanding roles of long noncoding RNAs in physiology and disease. Endocr Rev 36:25–64
Taft RJ, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Dinger M, Mattick JS (2010) Non-coding RNAs: regulators of disease. J Pathol 220:126–139
Lipovich L, Johnson R, Lin CY (2010) MacroRNA underdogs in a microRNA world: evolutionary, regulatory, and biomedical significance of mammalian long non-protein-coding RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1799:597–615
Calore F, Lovat F, Garofalo M (2013) Non-coding RNAs and cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14:17085–17110
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, French C, Lin MF, Feldser D, Huarte M, Zuk O, Carey BW, Cassady JP, Cabili MN, Jaenisch R, Mikkelsen TS, Jacks T, Hacohen N, Bernstein BE, Kellis M, Regev A, Rinn JL, Lander ES (2009) Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 458:223–227
Beckedorff FC, Amaral MS, Deocesano-Pereira C, Verjovski-Almeida S (2013) Long non-coding RNAs and their implications in cancer epigenetics. Biosci Rep 33 pii:e00061
Dong Z, Zhang A, Liu S, Lu F, Guo Y, Zhang G, Xu F, Shi Y, Shen S, Liang J, Guo W (2017) Aberrant Methylation-mediated Silencing of lncRNA MEG3 Functions as a ceRNA in Esophageal Cancer. Mol Cancer Res 15:800–810
Vrba L, Garbe JC, Stampfer MR, Futscher BW (2015) A lincRNA connected to cell mortality and epigenetically-silenced in most common human cancers. Epigenetics 10:1074–1083
Liao M, Li B, Zhang S, Liu Q, Liao W, Xie W, Zhang Y (2017) Relationship between LINC00341 expression and cancer prognosis. Oncotarget 8:15283–15293
Zhu YP, Bian XJ, Ye DW, Yao XD, Zhang SL, Dai B, Zhang HL, Shen YJ (2014) Long noncoding RNA expression signatures of bladder cancer revealed by microarray. Oncol Lett 7:1197–1202
Yu G, Li C, Xie W, Wang Z, Gao H, Cao L, Hao L, Zhang Y (2017) Long non-coding RNA C5orf66-AS1 is downregulated in pituitary null cell adenomas and is associated with their invasiveness. Oncol Rep 38:1140–1148
Feng L, Houck JR, Lohavanichbutr P, Chen C (2017) Transcriptome analysis reveals differentially expressed lncRNAs between oral squamous cell carcinoma and healthy oral mucosa. Oncotarget 8:31521–31531
Zhi H, Ning S, Li X, Li Y, Wu W, Li X (2014) A novel reannotation strategy for dissecting DNA methylation patterns of human long intergenic non-coding RNAs in cancers. Nucleic Acids Res 42:8258–8270
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Sasaki M, Anast J, Bassett W, Kawakami T, Sakuragi N, Dahiya R (2003) Bisulfite conversion-specific and methylation-specific PCR: a sensitive technique for accurate evaluation of CpG methylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 309:305–309
Yu L, Liu C, Vandeusen J, Becknell B, Dai Z, Wu YZ, Raval A, Liu TH, Ding W, Mao C, Liu S, Smith LT, Lee S, Rassenti L, Marcucci G, Byrd J, Caligiuri MA, Plass C (2005) Global assessment of promoter methylation in a mouse model of cancer identifies ID4 as a putative tumor-suppressor gene in human leukemia. Nat Genet 37:265–274
Wei G, Luo H, Sun Y, Li J, Tian L, Liu W, Liu L, Luo J, He J, Chen R (2015) Transcriptome profiling of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma reveals a long noncoding RNA acting as a tumor suppressor. Oncotarget 6:17065–17080
Heilmann K, Toth R, Bossmann C, Klimo K, Plass C, Gerhauser C (2017) Genome-wide screen for differentially methylated long noncoding RNAs identifies Esrp2 andlncRNA Esrp2-as regulated by enhancer DNA methylation with prognostic relevance for humanbreast cancer. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.246 [Epub ahead of print]
Ma X, Yu L, Wang P, Yang X (2017) Discovering DNA methylation patterns for long non-coding RNAs associated with cancer subtypes. Comput Biol Chem 69:164–170
Endoh M, Tamura G, Honda T, Homma N, Terashima M, Nishizuka S, Motoyama T (2005) RASSF2, a potential tumour suppressor, is silenced by CpG island hypermethylation in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 93:1395–1399
Homma N, Tamura G, Honda T, Matsumoto Y, Nishizuka S, Kawata S, Motoyama T (2006) Spreading of methylation within RUNX3 CpG island in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci 97:51–56
Jenuwein T, Allis CD (2001) Translating the histone code. Science 293:1074–1080
Wang Y, Chen T, Huang H, Jiang Y, Yang L, Lin Z, He H, Liu T, Wu B, Chen J, Kamp DW, Liu G (2017) miR-363-3p inhibits tumor growth by targeting PCNA in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 8:20133–20144
Karimian H, Arya A, Fadaeinasab M, Razavi M, Hajrezaei M, Karim Khan A, Mohd Ali H, Abdulla MA, Noordin MI (2017) Kelussia odoratissima Mozaff. activates intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in breast cancer cells associated with S phase cell cycle arrest via involvement of p21/p27 in vitro and in vivo. Drug Des Dev Ther 11:337–350
Wang SC (2014) PCNA: a silent housekeeper or a potential therapeutic target? Trends Pharmacol Sci 35:178–186
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139:871–890
Zeisberg M, Neilson EG (2009) Biomarkers for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Investig 119:1429–1437
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA (2009) The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Investig 119:1420–1428
Acknowledgements
We thank the cases for taking part in this study. This study was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81472335 and 81572441), Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Nos. H2015206196 and H2015206420).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wei Guo, Shengnan Liu, and Zhiming Dong have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Liu, S., Dong, Z. et al. Aberrant methylation-mediated silencing of lncRNA CTC-276P9.1 is associated with malignant progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 35, 53–68 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-018-9881-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-018-9881-2