Abstract
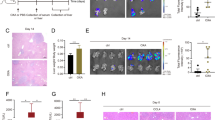
In this study, we investigated the therapeutic efficacy of EGFR2R-lytic hybrid peptide for the treatment of liver metastasis from colon carcinoma. The cytotoxic activity of the hybrid peptide against luciferase-expressing human colon cancer (HCT-116-luc) cells was determined by the WST-8 assay. The experimental mouse model of liver metastases was generated by splenic injection of HCT-116-luc cells. The hybrid peptide was intravenously injected into mice the day after cell implantation at a dose of 5 mg/kg and this was repeated on alternate days for a total of 7 doses. Saline-treated mice were used as controls. Tumor growth and therapeutic responses were monitored by an IVIS imaging system. It was shown that the hybrid peptide exhibited potent cytotoxic activity against HCT-116-luc cells and the liver metastases were significantly reduced after intravenous injections of hybrid peptide compared with controls. Furthermore, Kaplan–Meier analysis showed that hybrid peptide-treated mice had significantly longer survival than controls. In addition, bright-field and ex vivo imaging of liver tissue revealed that mice treated with the hybrid peptide had significantly fewer tumors compared with controls. These results demonstrated that the EGFR2R-lytic hybrid peptide is a potential treatment option for patients with colorectal cancer metastases in the liver.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- Luc:
-
Luciferase
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- AST:
-
Aspartate transaminase
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase
References
Hawk ET, Linburg PJ, Viner JL (2002) Epidemiology and prevention of colorectal cancer. Surg Clin N Am 82(5):905–941
Patanaphan V, Salazar OM (1993) Colorectal cancer: metastatic patterns and prognosis. South Med J 86(1):38–41
Scheele J, Stangl R, Altendorf-Hofmann A (1990) Hepatic metastases from colorectal carcinoma: impact of surgical resection on the natural history. Br J Surg 77(11):1241–1246
Clark ME, Smith RR (2014) Liver-directed therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol 5(5):374–387
Tol J, Punt CJ (2010) Monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a review. Clin Ther 32(3):437–453
Reubi JC, Maecke HR (2008) Peptide-based probes for cancer imaging. J Nucl Med 49(11):1735–1738
Thundimadathil J (2012) Cancer treatment using peptides: current therapies and future prospects. J. Amino Acids 2012:967347
Kohno M, Horibe T, Haramoto M, Yano Y, Ohara K, Nakajima O, Matsuzaki K, Kawakami K (2011) A novel hybrid peptide targeting EGFR-expressing cancers. Eur J Cancer 47(5):773–783
Tada N, Horibe T, Haramoto M, Ohara K, Kohno M, Kawakami K (2011) A single replacement of histidine to arginine in EGFR-lytic hybrid peptide demonstrates the improved anticancer activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 407(2):383–388
Kawamoto M, Horibe T, Kohno M, Kawakami K (2011) A novel transferrin receptor-targeted hybrid peptide disintegrates cancer cell membrane to induce rapid killing of cancer cells. BMC Cancer 11:359–372
Yang L, Horibe T, Kohno M, Haramoto M, Ohara K, Puri RK, Kawakami K (2012) Targeting interleukin-4 receptor α with hybrid peptide for effective cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 11(1):235–243
Horibe T, Kawamoto M, Kohno M, Kawakami K (2012) Cytotoxic activity to acute myeloid leukemia cells by Antp-TPR hybrid peptide targeting Hsp90. J Biosci Bioeng 114(1):96–103
Gaowa A, Horibe T, Kohno M, Sato K, Harada H, Hiraoka M, Tabata Y, Kawakami K (2014) Combination of hybrid peptide with biodegradable gelatin hydrogel for controlled release and enhancement of anti-tumor activity in vivo. J Control Release 176:1–7
Amador ML, Hidalgo M (2004) Epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 4(1):51–62
Otten MA, van der Bij GJ, Verbeek SJ, Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV, Beelen RH, van de Winkel JG, van Egmond M (2008) Experimental antibody therapy of liver metastases reveals functional redundancy between Fc gammaRI and Fc gammaRIV. J Immunol 181(10):6829–6836
Kohno M, Horibe T, Ohara K, Ito S, Kawakami K (2014) The membrane-lytic peptides K8L9 and melittin enter cancer cells via receptor endocytosis following subcytotoxic exposure. Chem Biol 21(11):1522–1532
Haramoto M, Kohno M, Nakajima O, Horibe T, Kiyohara M, Fukazawa H, Togawa T, Kawakami K (2010) Pancreatic cancer therapy with a novel pump for controlled drug release. Oncol Rep 23(2):365–370
Xu H, Yu Y, Marciniak D, Rishi AK, Sarkar FH, Kucuk O, Majumdar AP (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-related protein inhibits multiple members of the EGFR family in colon and breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 4(3):435–442
Balin-Gauthier D, Delord JP, Rochaix P, Mallard V, Thomas F, Hennebelle I, Bugat R, Canal P, Allal C (2006) In vivo and in vitro antitumor activity of oxaliplatin in combination with cetuximab in human colorectal tumor cell lines expressing different level of EGFR. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 57(6):709–718
Wu XZ, Ma F, Wang XL (2010) Serological diagnostic factors for liver metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 16(32):4084–4088
Rajput A, Dominguez San Martin I, Rose R, Beko A, Levea C, Sharratt E, Mazurchuk R, Hoffman RM, Brattain MG, Wang J (2008) Characterization of HCT116 human colon cancer cells in an orthotopic model. J Surg Res 147(2):276–281
Ishizu K, Sunose N, Yamazaki K, Tsuruo T, Sadahiro S, Makuuchi H, Yamori T (2007) Development and characterization of a model of liver metastasis using human colon cancer HCT-116 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 30(9):1779–1783
Kyriazis AP, DiPersio L, Michael GJ, Pesce AJ, Stinnett JD (1978) Growth patterns and metastatic behavior of human tumors growing in athymic mice. Cancer Res 38(10):3186–3190
Kozlowski JM, Fidler IJ, Campbell D, Xu ZL, Kaighn ME, Hart IR (1984) Metastatic behavior of human tumor cell lines grown in the nude mouse. Cancer Res 44(8):3522–3529
Giavazzi R, Jessup JM, Campbell DE, Walker SM, Fidler IJ (1986) Experimental nude mouse model of human colorectal cancer liver metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 77(6):1303–1308
Suemizu H, Monnai M, Ohnishi Y, Ito M, Tamaoki N, Nakamura M (2007) Identification of a key molecular regulator of liver metastasis in human pancreatic carcinoma using a novel quantitative model of metastasis in NOD/SCID/gammacnull (NOG) mice. Int J Oncol 31(4):741–751
Fidler IJ (1990) Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: twenty-eighth G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res 50(19):6130–6138
Bouvet M, Tsuji K, Yang M, Jiang P, Moossa AR, Hoffman RM (2006) In vivo color-coded imaging of the interaction of colon cancer cells and splenocytes in the formation of liver metastases. Cancer Res 66(23):11293–11297
Fu XY, Besterman JM, Monosov A, Hoffman RM (1991) Models of human metastatic colon cancer in nude mice orthotopically constructed by using histologically intact patient specimens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(20):9345–9349
Wang X, Fu X, Hoffman RM (1992) A new patient-like metastatic model of human lung cancer constructed orthotopically with intact tissue via thoracotomy in immunodeficient mice. Int J Cancer 51(6):992–995
An Z, Jiang P, Wang X, Moossa AR, Hoffman RM (1999) Development of a high metastatic orthotopic model of human renal cell carcinoma in nude mice: benefits of fragment implantation compared to cell-suspension injection. Clin Exp Metastasis 17(3):265–270
Humphries MJ, Olden K, Yamada KM (1986) A synthetic peptide from fibronectin inhibits experimental metastasis of murine melanoma cells. Science 233(4762):467–470
Komazawa H, Saiki I, Igarashi Y, Azuma I (1993) Inhibition of tumor metastasis by a synthetic polymer containing a cell-adhesive RGDS peptide. J Bioact Compat Polym 8:258–274
Schimanski CC, Linnemann U, Berger MR (1999) Sensitive detection of K-ras mutations augments diagnosis of colorectal cancer metastases in the liver. Cancer Res 59(20):5169–5175
Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ, O’Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Tebbutt NC, Simes RJ, Chalchal H, Shapiro JD, Robitaille S, Price TJ, Shepherd L, Au HJ, Langer C, Moore MJ, Zalcberg JR (2008) K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 359(17):1757–1765
Acknowledgments
We thank Mitsuko Tachi, Yoshie Masuda and Nanako Okushima (Department of Pharmacoepidemiology, Kyoto University) for their technical assistance in cell culture and animal studies. This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientist (A) (Grant No. 23680089) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. This study was also supported in part by a collaboration research fund from Olympus Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Koji Kawakami serves as a scientific advisor to Olympus Corporation. None of the other authors have any potential competing interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaowa, A., Horibe, T., Kohno, M. et al. Potent anti-tumor effects of EGFR-targeted hybrid peptide on mice bearing liver metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 33, 87–95 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9760-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9760-z