Abstract
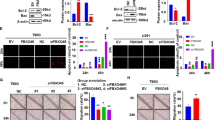
An unfortunate consequence of improvements in the treatments of advanced primary cancers is the concurrent increase of metastatic brain tumors. Despite of unfavorable clinical prognosis, radiation therapy is still the only viable treatment option for brain metastases. Expression of c-Met induces cell migration and invasion in many cancers, which are indispensable steps for metastasis. Accordingly, we examined the effects of gene silencing of c-Met on brain metastasis to evaluate the possibility of c-Met as a potential target. MDA-MB-435 cells were transfected with c-Met targeting short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs). Effects of c-Met shRNAs on the expression of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) related proteins, in vitro migration, and in vivo brain metastasis were examined. Expression of mesenchymal markers and in vitro migration of MDA-MB-435 cells were significantly inhibited by introduction of c-Met shRNAs. When c-Met-silenced MDA-MB-435 cells were stereotactically implanted into the brains of immune-compromised mice or injected into the right internal carotid arteries, c-Met-silenced MDA-MB-435 cells produced significantly smaller tumor masses or survival time was significantly prolonged, respectively, compared with MDA-MB-435 cells transfected with control shRNA. The data reveal the novel function of c-Met in the process of brain metastasis and its potential as a preventive and/or therapeutic target in this disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MBT:
-
Metastatic brain tumor
- RTK:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- SF:
-
Scatter factor
- ICA:
-
Internal carotid artery
- BLBC:
-
Basal-like breast cancer
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
References
Patchell RA (2003) The management of brain metastases. Cancer Treat Rev 29:533–540
Bladt F, Riethmacher D, Isenmann S et al (1995) Essential role for the c-met receptor in the migration of myogenic precursor cells into the limb bud. Nature 376:768–771
Schmidt C, Bladt F, Goedecke S et al (1995) Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor is essential for liver development. Nature 373:699–702
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E, Vande Woude GF (2003) Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:915–925
Garcia S, Dales JP, Charafe-Jauffret E et al (2007) Overexpression of c-Met and of the transducers PI3K, FAK and JAK in breast carcinomas correlates with shorter survival and neoangiogenesis. Int J Oncol 31:49–58
Christensen JG, Schreck R, Burrows J et al (2003) A selective small molecule inhibitor of c-Met kinase inhibits c-Met-dependent phenotypes in vitro and exhibits cytoreductive antitumor activity in vivo. Cancer Res 63:7345–7355
Hochgrafe F, Zhang L, O’Toole SA et al (2010) Tyrosine phosphorylation profiling reveals the signaling network characteristics of Basal breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 70:9391–9401
Previdi S, Maroni P, Matteucci E et al (2010) Interaction between human-breast cancer metastasis and bone microenvironment through activated hepatocyte growth factor/Met and beta-catenin/Wnt pathways. Eur J Cancer 46:1679–1691
Ponzo MG, Lesurf R, Petkiewicz S et al (2009) Met induces mammary tumors with diverse histologies and is associated with poor outcome and human basal breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:12903–12908
Nieman MT, Prudoff RS, Johnson KR, Wheelock MJ (1999) N-Cadherin promotes motility in human breast cancer cells regardless of their e-cadherin expression. J Cell Biol 147:631–643
Hazan RB, Phillips GR, Qiao RF et al (2000) Exogenous expression of n-cadherin in breast cancer cells induces cell migration, invasion, and meta. J Cell Biol 148:779–790
Shattuck DL, Miller JK, Carraway KL, Sweeney C (2008) Met receptor contributes to trastuzumab resistance of Her2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 68:1471–1477
Benedettini E, Sholl LM, Peyton M et al (2010) Met activation in non-small cell lung cancer is associated with de novo resistance to EGFR inhibitors and the development of brain metastasis. Am J Pathol 177:415–423
Kong DS, Song SY, Kim DH et al (2009) Prognostic significance of c-Met expression in glioblastomas. Cancer 115:140–148
Eder JP, Vande Woude GF, Boerner SA, LoRusso PM (2009) Novel therapeutic inhibitors of the c-Met signaling pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15:2207–2214
Rakha EA, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO (2008) Basal-like breast cancer: a critical review. J Clin Oncol 26:2568–2581
Yehiely F, Moyano JV, Evans JR et al (2006) Deconstructing the molecular portrait of basal-like breast cancer. Trends Mol Med 12:537–544
Goncalves A, Charafe-Jauffret E, Bertucci F et al (2008) Protein profiling of human breast tumor cells identifies novel biomarkers associated with molecular subtypes. Mol Cell Proteomics 7:1420–1433
Garcia S, Dales JP, Charafe-Jauffret E et al (2007) Poor prognosis in breast carcinomas correlates with increased expression of targetable CD146 and c-Met and with proteomic basal-like phenotype. Hum Pathol 38:830–841
Ponzo MG, Park M (2010) The met receptor tyrosine kinase and basal breast cancer. Cell Cycle 9:1043–1050
Turner N, Lambros MB, Horlings HM et al (2010) Integrative molecular profiling of triple negative breast cancers identifies amplicon drivers and potential therapeutic targets. Oncogene 29:2013–2023
Schneider BP, Winer EP, Foulkes WD et al (2008) Triple-negative breast cancer: risk factors to potential targets. Clin Cancer Res 14:8010–8018
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R et al (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC et al (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Acknowledgments
We thank Chang In Kim, Hea Mi Kim, and Hye Rin Lee for their technical support. This work was supported by the Korea Healthcare technology R&D project, Ministry for Health & Welfare Affairs, Republic of Korea (A092255), the Samsung Medical Center grant, #GFO1130011, and the Samsung Biomedical Research Institute grant, no. SBRI C-B0-218-3 (D.H. Nam) and SBRI GL1B33011 (K.M. Joo).
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Se Jeong Lee and Ho Jun Seol: contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.J., Seol, H.J., Lee, H.W. et al. Gene silencing of c-Met leads to brain metastasis inhibitory effects. Clin Exp Metastasis 30, 845–854 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-013-9584-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-013-9584-7