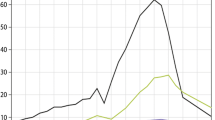
Abstract
Extreme wildfire events in recent years are shaking our established knowledge of how fire regimes respond to climate variables and how societies need to react to fire impacts. Albeit fires are stochastic and extreme in nature, the speed, intensity, and extension of new extreme fires that have occurred during the last years are unprecedented. Here, we identify common features of these emerging novel extreme wildfire events characterized by very high fire intensity and rapid rates of spread, and we review the major mechanisms behind their occurrence. We then point to the major challenges that extreme wildfire events pose to science and societies worldwide, both today and in the future. Climate change and other factors are contributing to more flammable landscapes and the promotion of unstable atmospheric conditions that ultimately promote wildfire development. Anticipating these novel conditions is a key scientific challenge with paramount implications for present and future fire management, ecosystems, and human well-being.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abatzoglou JT, Williams AP (2016) The impact of anthropogenic climate change on wildfire across western US forests. Proc Natl Acad Sci In press. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1607171113
Agne MC, Woolley T, Fitzgerald S (2016) Fire severity and cumulative disturbance effects in the post-mountain pine beetle lodgepole pine forests of the Pole Creek Fire. For Ecol Manag 366:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.02.004
Ali AA, Blarquez O, Girardin MP et al (2012) Control of the multimillennial wildfire size in boreal North America by spring climatic conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:20966–20970. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1203467109
Anderegg WRL, Trugman AT, Badgley G et al (2020) Climate-driven risks to the climate mitigation potential of forests. Science (80- ) 368. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaz7005
Archibald S (2016) Managing the human component of fire regimes: lessons from Africa. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 371:20150346. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0346
Archibald S, Roy DP, van Wilgen BW, Scholes RJ (2009) What limits fire? An examination of drivers of burnt area in Southern Africa. Glob Chang Biol 15:613–630. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01754.x
Archibald S, Lehmann CER, Gómez-dans JL, Bradstock RA (2013) Defining pyromes and global syndromes of fire regimes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:6442–6447. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1211466110/-/DCSupplemental.www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1211466110
Archibald S, Lehmann CER, Belcher C et al (2017) Biological and geophysical feedbacks with fire in the Earth System. Environ Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa9ead
Artés T, Castellnou M (2019) GWIS – Global Wildfire Information System Extreme Fire Behaviour. In: 6th International Fire behavior and fuels conference
Balch JK, Bradley BA, Abatzoglou JT et al (2017) Human-started wildfires expand the fire niche across the United States. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:2946–2951. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1617394114
Bechtold P (2019) Atmospheric moist convection. Meteorol. Train. Course Lect. Ser
Boer MM, Nolan RH, Resco de Dios V et al (2017) Changing weather extremes call for early warning of potential for catastrophic fire. Earth’s Futur 5:1196–1202. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017EF000657
Boer MM, Resco de Dios V, Bradstock RA (2020) Correspondence: unprecedented burn area of Australian mega forest fires. Nat Clim Chang:6–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-020-0716-1
Bond WJ, Stevens N, Midgley GF, Lehmann CER (2019) The trouble with trees: afforestation plans for Africa. Trends Ecol Evol 34:963–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2019.08.003
Bowman DMJS, Balch JK, Artaxo P et al (2009) Fire in the Earth system. Science 324:481–484. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1163886
Bowman DMJS, Williamson GJ, Abatzoglou JT et al (2017) Human exposure and sensitivity to globally extreme wildfire events. Nat Ecol Evol 1:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-016-0058
Bowman DMJS, Kolden CA, Abatzoglou JT et al (2020) Vegetation fires in the Anthropocene. Nat Rev Earth Environ. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-020-0085-3
Bradstock RA (2010) A biogeographic model of fire regimes in Australia: current and future implications. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 19:145–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2009.00512.x
Brooks M, D’Antonio C, Richardson DM et al (2004) Effects of invasive alien plants on fire regimes. Bioscience 54:677. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2004)054[0677:eoiapo]2.0.co;2
Brotons L, Duane A (2019) Correspondence: uncertainty in climate-vegetation feedbacks on fire regimes challenges reliable long-term projections of burnt area from correlative models. Fire 2:8. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire2010008
Brotons L, Aquilué N, de Cáceres M et al (2013) How fire history, fire suppression practices and climate change affect wildfire regimes in Mediterranean landscapes. PLoS One 8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0062392
Cai W, Zheng X, Weller E et al (2013) Projected response of the Indian Ocean Dipole to greenhouse warming. Nat Geosci 6:999–1007
Camp PE, Krawchuk MA (2017) Spatially varying constraints of human-caused fire occurrence in British Columbia, Canada. Int J Wildl Fire 26:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF16108
Candau JN, Fleming RA, Wang X (2018) Ecoregional patterns of spruce budworm-wildfire interactions in central Canada’s Forests. Forests 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9030137
Cardil A, de Miguel S, Silva CA et al (2020) Recent deforestation drove the spike in Amazonian fires. Environ Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/abcac7
Cardoso MF, Hurtt GC, Moore B et al (2003) Projecting future fire activity in Amazonia. Glob Chang Biol 9:656–669. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00607.x
Chen Y, Morton DC, Andela N et al (2016) How much global burned area can be forecast on seasonal time scales using sea surface temperatures? Environ Res Lett 11. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/4/045001
Collins M, Knutti R, Arblaster J et al (2013) Long-term climate change: Projections, commitments and irreversibility. In: Climate Change 2013 the Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University press, pp 1029–1136
Collins KM, Price OF, Penman TD (2015) Spatial patterns of wildfire ignitions in south-eastern Australia. Int J Wildl Fire 24:1098–1108. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF15054
CONAF (2020) Incendios Forestales en Chile. In: Visit. last time 22-04-20. https://www.conaf.cl/incendios-forestales/incendios-forestales-en-chile/
CTI Comissão Técnica Independente (2017) Análise e apuramento dos factos relativos aos incêndios que ocorreram em Pedrogão Grande, Castanheira de Pera, Ansião, Alvaiázere, Figueiró dos Vinhos, Arganil, Góis, Penela, Pampilhosa da Serra, Oleiros e Sertã, entre 17 e 24 de junho de 2017
Cunningham P, Reeder MJ (2009) Severe convective storms initiated by intense wildfires: numerical simulations of pyro-convection and pyro-tornadogenesis. Geophys Res Lett 36:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL039262
De Faria BL, Brando PM, Macedo MN, et al (2017) Current and future patterns of fire-induced forest degradation in amazonia Environ Res Lett 12:. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa69ce
de Groot WJ, Wotton M, Flannigan M (2015) Chapter 11 - Wildland fire danger rating and early warning systems. In: Wildfire hazards, risks and disasters, pp 207–228
Dentener FJ, Easterling DR, Uk RA et al (2013) IPCC Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Chapter 2: Observations: Atmosphere and Surface. Clim Chang 2013 Phys Sci Basis Work Gr I Contrib to Fifth Assess Rep Intergov Panel Clim Chang 9781107057:159–254. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.008
Di Virgilio G, Evans JP, Blake SAP et al (2019) Climate change increases the potential for extreme wildfires. Geophys Res Lett 46:8517–8526. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL083699
Dial GL, Racy JP, Thompson RL (2010) Short-term convective mode evolution along synoptic boundaries. Weather Forecast 25:1430–1446. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010WAF2222315.1
Dowdy AJ, Pepler A (2018) Pyroconvection risk in Australia: climatological changes in atmospheric stability and surface fire weather conditions. Geophys Res Lett 45:2005–2013. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL076654
Dowdy AJ, Fromm MD, McCarthy N (2017) Pyrocumulonimbus lightning and fire ignition on Black Saturday in southeast Australia. J Geophys Res 122:7342–7354. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD026577
Drobyshev I, Bergeron Y, De Vernal A et al (2016) Atlantic SSTs control regime shifts in forest fire activity of Northern Scandinavia. Sci Rep 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22532
Duane A, Brotons L (2018) Synoptic weather conditions and changing fire regimes in a Mediterranean environment. Agric For Meteorol 253–254:190–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.02.014
Duane A, Piqué M, Castellnou M, Brotons L (2015) Predictive modelling of fire occurrences from different fire spread patterns in Mediterranean landscapes. Int J Wildl Fire 24:407–418. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF14040
Duane A, Aquilué N, Canelles Q et al (2019) Adapting prescribed burns to future climate change in Mediterranean landscapes. Sci Total Environ 677:68–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.348
Enright NJ, Fontaine JB, Bowman DMJS et al (2015) Interval squeeze: altered fire regimes and demographic responses interact to threaten woody species persistence as climate changes. Front Ecol Environ 13:265–272. https://doi.org/10.1890/140231
European Comission (2018) FOREST FIRES - Sparking firesmart policies in the EU. Luxemburg
European Comission (2020) “EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030”
Fernandes PM, Monteiro-henriques T, Guiomar N et al (2016) Bottom-up variables govern large- fire size in Portugal. Ecosystems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-016-0010-2
Fernandes PM, Guiomar N, Rossa CG (2019) Analysing eucalypt expansion in Portugal as a fire-regime modifier. Sci Total Environ 666:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.237
Fernandez F, Guillaume B, Porterie B et al (2018) Modelling fire spread and damage in wildland-urban interfaces. In: Viegas DX (ed) Advances in Forest fire research 2018. Coimbra, Portugal, pp 1264–1274
Finney MA, Cohen JD, Forthofer JM et al (2015) Role of buoyant flame dynamics in wildfire spread. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:9833–9838. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1504498112
Flannigan M, Krawchuk M, de Groot WJ et al (2009) Implications of changing climate for global wildland fire. Int J Wildl Fire 18:483–507. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF08187
Fromm M, Tupper A, Rosenfeld D et al (2006) Violent pyro-convective storm devastates Australia’s capital and pollutes the stratosphere. Geophys Res Lett 33:L05815. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL025161
Fry DL, Stephens SL, Collins BM et al (2014) Contrasting spatial patterns in active-fire and fire-suppressed mediterranean climate old-growth mixed conifer forests. PLoS One:9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088985
Ganteaume A (2018) Role of the ornamental vegetation in the propagation of the Rognac fire (SE France, 2016). In: Fire continuum conference: preparing for the future of wildland fire. Missoula, USA, p 35
Gauthier S, Bernier P, Kuuluvainen T et al (2015) Boreal forest health and global change. Science (80- ) 349:819–822
Gollner MJ, Hakes R, Caton S, Kohler K (2015) Pathways for building fire spread at the wildland urban interface
Gómez-González S, Ochoa-Hueso R, Pausas JG (2020) Afforestation falls short as a biodiversity strategy. Science (80- ) 368:1439
Grams CM, Beerli R, Pfenninger S et al (2017) Balancing Europe’s wind-power output through spatial deployment informed by weather regimes. Nat Clim Chang. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3338
Haines DA (1988) A lower atmosphere severity index for wildland fire. Natl Weather Dig 13:23–27
Harvey JE, Axelson JN, Smith DJ (2018) Disturbance-climate relationships between wildfire and western spruce budworm in interior British Columbia. Ecosphere 9:e02126. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.2126
International Union for Conservation of Nature (2020) The Bonn Challenge
James PMA, Robert LE, Wotton BM et al (2017) Lagged cumulative spruce budworm defoliation affects the risk of fire ignition in Ontario. Canada: Ecol Appl 27:532–544. https://doi.org/10.1002/eap.1463
Jobbágy E, Baldi G, Nosetto M (2012) Tree plantation in South America and the water cycle: impacts and emergent oportunities. In: Schlichter T, Montes L (eds) Forests in development: a vital balance. Springer, pp 1–83
Jolly WM, Cochrane MA, Freeborn PH et al (2015) Climate-induced variations in global wildfire danger from 1979 to 2013. Nat Commun:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8537
Kelly LT, Brotons L (2017) Using fire to promote biodiversity. Science (80- ) 355:1264–1265. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam7672
Kelly LT, Giljohann KM, Duane A et al (2020) Fire and biodiversity in the Anthropocene. Science 370. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb0355
Kitzberger T, Brown PM, Heyerdahl EK et al (2007) Contingent Pacific-Atlantic Ocean influence on multicentury wildfire synchrony over western North America. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:543–548. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606078104
Konings AG, Williams AP, Gentine P (2017) Sensitivity of grassland productivity to aridity controlled by stomatal and xylem regulation. Nat Geosci 10:284–288
Kovacs K, Ranson KJ, Sun G, Kharuk VI (2004) The relationship of the Terra MODIS fire product and anthropogenic features in the central Siberian landscape. Earth Interact 8:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1175/1087-3562(2004)8<1:trottm>2.0.co;2
Krawchuk M, Moritz M (2011) Constraints on global fire activity vary across a resource gradient. Ecology 92:121–132
Krawchuk MA, Moritz M, Parisien M-A et al (2009) Global pyrogeography: the current and future distribution of wildfire. PLoS One 4:e5102. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005102
Kroger M (2012) Global tree plantation expansion: a review. ICAS Rev Pap Ser:1–25
Kukavskaya EA, Buryak LV, Shvetsov EG et al (2016) The impact of increasing fire frequency on forest transformations in southern Siberia. For Ecol Manag 382:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.10.015
Lareau NP, Clements CB (2016) Environmental controls on pyrocumulus and pyrocumulonimbus initiation and development. Atmos Chem Phys 16:4005–4022. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-4005-2016
Le Fer D, Parker VT (2005) The effect of seasonality of burn on seed germination in chaparral: the role of soil moisture. Madroño 52:166–174. https://doi.org/10.3120/0024-9637(2005)52[166:teosob]2.0.co;2
Li S, Li X (2017) Global understanding of farmland abandonment: a review and prospects. J Geogr Sci 27:1123–1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-017-1426-0
Lionello P, Scarascia L (2018) The relation between climate change in the Mediterranean region and global warming. Reg Environ Chang 18:1481–1493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-018-1290-1
Matt Jolly W, Parsons R, Morgan Varner J et al (2012) Do mountain pine beetle outbreaks change the probability of active crown fire in lodgepole pine forests? Comment. Ecology 93:941–946
McLauchlan KK, Higuera PE, Miesel J et al (2020) Fire as a fundamental ecological process: research advances and frontiers. J Ecol 108:2047–2069. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.13403
McRae R, Sharples JJ, Fromm M (2015) Linking local wildfire dynamics to pyroCb development. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 15:417–428. https://doi.org/10.5194/NHESS-15-417-2015
McWethy DB, A P, Garcia R, Holz A, Gonza’lez ME, Veblen TT et al (2018) Landscape drivers of recent fire activity (2001- 2017). PLoS One:1–24
Meigs GW, Zald HSJ, Campbell JL et al (2016) Do insect outbreaks reduce the severity of subsequent forest fires? Environ Res Lett 11. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/4/045008
Mermoz M, Kitzberger T, Veblen TT (2005) Landscape influences on occurrence and spread of wildfires in patagonian forests and shrublands. Ecology 86:2705–2715. https://doi.org/10.1890/04-1850
Metlen KL, Skinner CN, Olson DR et al (2018) Regional and local controls on historical fire regimes of dry forests and woodlands in the Rogue River Basin, Oregon, USA. For Ecol Manag 430:43–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2018.07.010
Miles L, Grainger A, Phillips O (2004) The impact of global climate change on tropical forest biodiversity in Amazonia the impact of global climate change on tropical forest biodiversity. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 13:553–565. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-822X.2004.00105.x
Millar CI, Stephenson NL (2015) Temperate forest health in an era of emerging megadisturbance. Science (80- ) 349:823–826. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa9933
Miller CH, Tang W, Sluder E et al (2018) Boundary layer instabilities in mixed convection and diffusion flames with an unheated starting length. Int J Heat Mass Transf 118:1243–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.11.040
Mills GA, McCaw L (2010) Atmospheric Stability Environments and Fire Weather in Australia - extending the Haines Index
Moreira F, Ascoli D, Safford H et al (2020) Wildfire management in Mediterranean-type regions: paradigm change needed. Environ Res Lett 15. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab541e
Moritz MA, Batllori E, Bradstock RA et al (2014) Learning to coexist with wildfire. Nature 515:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13946
Ndalila MN, Williamson GJ, Bowman DMJS (2018) Geographic patterns of fire severity following an extreme Eucalyptus forest fire in southern Australia: 2013 Forcett-Dunalley Fire. Fire 1:40. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire1030040
Nolan RH, Boer MM, Collins L et al (2020) Causes and consequences of eastern Australia’s 2019–20 season of mega-fires. Glob Chang Biol 26:1039–1041. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14987
Olson DM, Dinerstein E, Wikramanayake ED et al (2001) Terrestrial ecoregions of the world: a new map of life on earth. Bioscience 51:933. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0933:TEOTWA]2.0.CO;2
Parisien M-A, Moritz M (2009) Environmental controls on the distribution of wildfire at multiple spatial scales. Ecol Monogr 79:127–154. https://doi.org/10.1890/07-1289.1
Pausas JG, Fernández-Muñoz S (2011) Fire regime changes in the Western Mediterranean Basin: from fuel-limited to drought-driven fire regime. Clim Chang 110:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0060-6
Pausas JG, Paula S (2012) Fuel shapes the fire-climate relationship: evidence from Mediterranean ecosystems. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 21:1074–1082. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2012.00769.x
Payn T, Carnus JM, Freer-Smith P et al (2015) Changes in planted forests and future global implications. For Ecol Manag 352:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2015.06.021
Peterson DA, Hyer EJ, Campbell JR et al (2016) A conceptual model for development of intense pyrocumulonimbus in Western North America. Mon Weather Rev 145:2235–2255. https://doi.org/10.1175/mwr-d-16-0232.1
Pickrell J, Pennisi E (2020) Record U.S. and Australian fires raise fears for many species. Science (80- ) 370:18–19. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.370.6512.18
Pitman AJ, Narisma GT, McAneney J (2007) The impact of climate change on the risk of forest and grassland fires in Australia. Clim Chang 84:383–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-007-9243-6
Potter BE, Anaya MA (2015) A wildfire-relevant climatology of the convective environment of the United States. Int J Wildl Fire
Povak NA, Hessburg PF, Salter RB (2018) Evidence for scale-dependent topographic controls on wildfire spread. Ecosphere 9. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.2443
Price OF, Bradstock RA (2010) The effect of fuel age on the spread of fire in sclerophyll forest in the Sydney region of Australia. Int J Wildl Fire 19:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1071/WF08167
Radeloff VC, Helmers DP, Anu Kramer H et al (2018) Rapid growth of the US wildland-urban interface raises wildfire risk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:3314–3319. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1718850115
Raible CC, Ziv B, Saaroni H, Wild M (2010) Winter synoptic-scale variability over the Mediterranean Basin under future climate conditions as simulated by the ECHAM5. Clim Dyn 35:473–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-009-0678-5
Resco de Dios V (2020) Plant-fire interactions. Managing F, Springer Nature Switzerland
Rhein M, Rintoul SR (2013) Observations: ocean - AR5 IPCC
Rodrigues A, Ribeiro C, Raposo J et al (2019) Effect of canyons on a fire propagating laterally over slopes. Front Mech Eng 5:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmech.2019.00041
Rogers BM, Balch JK, Goetz S et al (2020) Focus on changing fire regimes: interactions with climate, ecosystems, and society. Environ Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab6d3a
Roos CI, Rittenour TM, Swetnam TW et al (2020) Fire suppression impacts on fuels and fire intensity in the Western U.S.: insights from archaeological luminescence dating in northern New Mexico. Fire 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire3030032
Rothermel RC (1991) Predicting behavior and size of crown fires in the northern Rocky Mountains. USDA Forest Service, Intermountain Research Station, Research Paper INT-438, Odgen, UT
Ruffault J, Curt T, Martin-StPaul NK et al (2018) Extreme wildfire events are linked to global-change-type droughts in the northern Mediterranean. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 18:847–856. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-847-2018
Sánchez-Benítez A, García-Herrera R, Barriopedro D et al (2018) June 2017: the earliest European summer mega-heatwave of reanalysis period. Geophys Res Lett 45:1955–1962. https://doi.org/10.1002/2018GL077253
Sanginés de Cárcer P, Vitasse Y, Peñuelas J et al (2017) Vapor–pressure deficit and extreme climatic variables limit tree growth. Glob Chang Biol 24:1108–1122. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13973
San-Miguel-Ayanz J, Schulte E, Schmuck G et al (2012) Comprehensive monitoring of wildfires in Europe: the European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS). In: InTech (ed) Approaches to managing disaster—assessing hazards, emergencies and disaster impacts
Schoennagel T, Balch JK, Brenkert-Smith H et al (2017) Adapt to more wildfire in western North American forests as climate changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:4582–4590. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1617464114
Sharples JJ, Hilton JE (2020) Modeling vorticity-driven wildfire behavior using near-field techniques. Front Mech Eng 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmech.2019.00069
Sharples JJ, Cary GJ, Fox-Hughes P et al (2016) Natural hazards in Australia: extreme bushfire. Clim Chang 139:85–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-016-1811-1
Sommerfeld A, Senf C, Buma B et al (2018) Patterns and drivers of recent disturbances across the temperate forest biome. Nat Commun 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06788-9
Stehfest E, van Zeist WJ, Valin H et al (2019) Key determinants of global land-use projections. Nat Commun 10:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09945-w
Stephens SL, Skinner CN, Gill SJ (2003) Dendrochronology-based fire history of Jeffrey pine - mixed conifer forests in the Sierra San Pedro Martir, Mexico. Can J For Res 33:1090–1101. https://doi.org/10.1139/x03-031
Stewart SR (2018) Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Ophelia
Syphard AD, Keeley JE, Pfaff AH, Ferschweiler K (2017) Human presence diminishes the importance of climate in driving fire activity across the United States. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:13750–13755. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1713885114
Tang Y, Zhong S, Luo L et al (2015) The potential impact of regional climate change on fire weather in the United States. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 105:1–21
Taszarek M, Allen J, Púčik T et al (2019) A climatology of thunderstorms across Europe from a synthesis of multiple data sources. J Clim 32:1813–1837. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-18-0372.1
Tatli H, Türkeş M (2013) Climatological evaluation of Haines forest fire weather index over the Mediterranean Basin. Meteorol Appl n/a-n/a. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1367
te Beest M, Cromsigt JPGM, Ngobese J, Olff H (2012) Managing invasions at the cost of native habitat? An experimental test of the impact of fire on the invasion of Chromolaena odorata in a South African savanna. Biol Invasions 14:607–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-011-0102-z
Tedim F, Leone V, Amraoui M et al (2018) Defining extreme wildfire events: difficulties, challenges, and impacts. Fire 1:9. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire1010009
Terres JM, Scacchiafichi LN, Wania A et al (2015) Farmland abandonment in Europe: identification of drivers and indicators, and development of a composite indicator of risk. Land Use Policy 49:20–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2015.06.009
Trigo RM, Osborn TJ, Corte-Real JM (2002) The North Atlantic oscillation influence on Europe: climate impacts and associated physical mechanisms. Clim Res 20:9–17. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr020009
Ursino N, Romano N (2014) Wild forest fire regime following land abandonment in the Mediterranean region. Geophys Res Lett:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GL061560.Received
Valor T, González-Olabarria JR, Piqué M, Casals P (2017) The effects of burning season and severity on the mortality over time of Pinus nigra spp. salzmannii (Dunal) Franco and P. sylvestris L. For Ecol Manag 406:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2017.08.027
Van Wilgen BW (2009) The evolution of fire and invasive alien plant management practices in fynbos. S Afr J Sci 105:335–342. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajs.v105i9/10.106
Verkerk PJ, Martinez de Arano I, Palahí M (2018) The bio-economy as an opportunity to tackle wildfires in Mediterranean forest ecosystems. For Policy Econ 86:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forpol.2017.10.016
Victoria State Government (2020) Victoria’s bushfire emergency: biodiversity response and recovery
Wang M, Ullrich P, Millstein D (2020) Future projections of wind patterns in California with the variable-resolution CESM: a clustering analysis approach. Clim Dyn 54:2511–2531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05125-5
Werth PA, Potter BE, Clements CB, et al (2011) Synthesis of knowledge of extreme fire behavior : volume I for fire managers. USDA. I
Williams AP, Allen CD, Macalady AK et al (2013) Temperature as a potent driver of regional forest drought stress and tree mortality. Nat Clim Chang 3:292–297
Williams AP, Abatzoglou JT, Gershunov A et al (2019) Observed impacts of anthropogenic climate change on wildfire in California. Earth’s Futur 7:892–910. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019EF001210
Wintle BA, Legge S, Woinarski JCZ (2020) Trends in Ecology & Evolution Science and Society After the Mega fi res : What Next for Australian Wildlife ? Trends in Ecology & Evolution. Trends Ecol Evol xx:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2020.06.009
Yuan W, Zheng Y, Piao S et al (2019) Increased atmospheric vapor pressure deficit reduces global vegetation growth. Sci Adv:1–14
Acknowledgements
We thank José Luís Ordoñez for his advice in composing the figures here included.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was funded by the Spanish Government through the INMODES (CGL2014-59742-C2-2-R) project. This research has also received funding from the Generalitat de Catalunya’s CERCA Programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.D. and L.B. conceived the study. A.D. reviewed all the wildfires and articles cited, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper. M.C. and L.B. contributed to the knowledge generation and integration and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(PDF 110 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duane, A., Castellnou, M. & Brotons, L. Towards a comprehensive look at global drivers of novel extreme wildfire events. Climatic Change 165, 43 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-021-03066-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-021-03066-4