Abstract
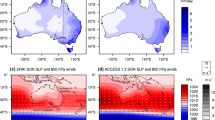
The natural evaporation in the Dead-Sea is a very important meteorological parameter to the local industries at Sdom. It was found that the pan evaporation in Sdom has recently increased by 20–25%. In this paper we explore the reasons for this increase. It is found that both large-scale and local climatic changes have contributed to the evaporation increase in the Dead Sea Valley. The large-scale (global) change potentially associated with the global warming, resulted in changes of the frequencies of some synoptic systems in the region. The local change is a result of the recent Dead-Sea drying, which reduced the local Dead-Sea breeze while intensifying the Mediterranean-Sea breeze penetrating the Dead Sea Valley. It is suggested that while the local effect was the dominant climatic change factor in the Dead-Sea Valley in the 1970–1990, the global effect becomes the dominant one in the more recent evaporation increase in the Dead-Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert P, Eppel A (1985) A proposed index for mesoscale activity. J Clim Appl Meteorol 24:472–480
Alpert P, Cohen A, Neumann J, Doron E (1982) A model simulation of the summer circulation from the Eastern Mediterranean past Lake Kinneret in the Jordan Valley. Mon Weather Rev 100:994–1006
Alpert P, Shafir H, Issahary D (1997) Recent changes in the climate of the Dead Sea Valley. Clim Change 7:1–25
Alpert P, Osetinsky I, Ziv B, Shafir H (2004) Semi-objective classification for daily synoptic systems: application to the Eastern Mediterranean climate change. Int J Climatol 24:1001–1011
Alpert P, Price C, Krichak S, Ziv B, Saaroni H, Osetinsky I (2006a) Mediterranean climate and some tropical teleconnections. Nuovo Cimento Soc Ital Fis C Geophys Space Phys 29(1):89–97
Alpert P, Krichak S, Shafir H, Jin F, Kalmikov A, Sharon A, Dayan M, Cohen M, Lati Y (2006b) The impact of the sea canal on the Dead-Sea evaporation. A First Year Report to the Dead-Sea Works. Tel-Aviv University, 25p (in Hebrew)
Alpert P, Krichak S, Shafir H, Jin F, Potchter O, Yaakov Y, Cohen M, Lati Y, Aharoni M, Cohen O (2008) The impact of the sea canal on the Dead-Sea evaporation. A Third Year Report to the Dead-Sea Works. Tel-Aviv University, 26p (in Hebrew)
Anati DA, Shasha S (1989) Dead Sea surface level changes. Isr J Earth Sci 38:29–32
Ashbel D (1939) The influence of the Dead Sea on the climate of its neighborhood. Q J R Meteorol Soc 115:185–194
Ashbel D (1975) Forty five years of observations in the climate and hydrology of the Dead Sea. The Hebrew Univ. of Jerusalem, p 183 (in Hebrew)
Bitan A (1974) The wind regime in the north-west section of the Dead Sea. Arch Meteorol Geophys Bioklimatol 22(Ser. B):313–335
Bitan A (1977) The influence of the special shape of the Dead Sea and its environment on the local wind system. Arch Meteorol Geophys Bioklimatol 24(Ser. B):283–301
Cohen S, Stanhill G (1996) Contemporary climate change in the Jordan Valley. J Appl Meteorol 35:1051–1058
Klein C (1982) Morphological evidence of lake level changes, Western Shore of the Dead Sea. Isr J Earth Sci 31:67–94
Osetinsky I (2006) Climate changes over the E. Mediterranean—a synoptic systems classification approach. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Tel-Aviv, pp 138
Saaroni H, Ziv B, Edelson J, Alpert P (2003) Long-term variations in summer temperatures over the Eastern Mediterranean. Geophys Res Lett 30(18):1946. doi:10.1029/2003GL017742. 8 pp
Stanhill G (1994) Changes in the rate of evaporation from the Dead Sea. Int J Climatol 14:465–471
Steinhorn I (1981) A hydro-graphical and physical study of the Dead Sea during the destruction of its long-term meromictic stratification. Ph.D. Thesis, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, pp 323
Ziv B, Saaroni H, Baharad A, Yekutieli D, Alpert P (2005) Indications for aggravation in summer heat conditions over the Mediterranean basin. Geophys Res Lett 32:L12706. doi:10.1029/2005GL022796
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafir, H., Alpert, P. Regional and local climatic effects on the Dead-Sea evaporation. Climatic Change 105, 455–468 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9892-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9892-8