Abstract
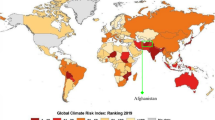
Through an examination of global climate change models combined with hydrological data on deteriorating water quality in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), we elucidate the ways in which the MENA countries are vulnerable to climate-induced impacts on water resources. Adaptive governance strategies, however, remain a low priority for political leaderships in the MENA region. To date, most MENA governments have concentrated the bulk of their resources on large-scale supply side projects such as desalination, dam construction, inter-basin water transfers, tapping fossil groundwater aquifers, and importing virtual water. Because managing water demand, improving the efficiency of water use, and promoting conservation will be key ingredients in responding to climate-induced impacts on the water sector, we analyze the political, economic, and institutional drivers that have shaped governance responses. While the scholarly literature emphasizes the importance of social capital to adaptive governance, we find that many political leaders and water experts in the MENA rarely engage societal actors in considering water risks. We conclude that the key capacities for adaptive governance to water scarcity in MENA are underdeveloped.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abderrahman WA (2001) Water demand management in Saudi Arabia. In: Faruqui NI, Biswas AK, Bino MJ (eds) Water management in Islam. IDRC, Ottawa and UNU Press, Tokyo
Achthoven TV, Merabet Z, Shalaby K, Van Steenbergen F (2004) Balancing productivity and environmental pressure in Egypt. Agriculture and Rural Development Working Paper No 13, World Bank
Adger WN (2003) Social capital, collective action, and adaptation to climate change. Econ Geogr 79(4):387–404
Adger WN, Huq S, Brown K, Conway D, Hulme M (2003) Adaptation to climate change in the developing world. Prog Dev Stud 3(3):179–195
Akkad D (2009) Severe drought affects 1.3 million in Syria. Christ Sci Monit, 18 September, p 6
Al-Kharabsheh A (2000) Ground-water modelling and long-term management of the Azraq basin as an example of arid area conditions (Jordan). J Arid Environ 44(2):143–153
Allan JA (1997) Virtual water: a long term solution for water short Middle Eastern economies? Occasional Paper 3, School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS), University of London
Allan JA (2001) The Middle East water question: hydropolitics and the global economy. I.B. Tauris, London
Alpert P, Krichak SO, Shafir H, Haim D, Osetinsky I (2008) Climatic trends to extremes employing regional modeling and statistical interpretation over the Eastern Mediterranean. Glob Planet Change 63:163–170
Arnell NW (1999) Climate change and global water resources. Glob Environ Change 9:S31–S49
Assaf H (2008) Climate change in the Levant and North Africa region: an assessment of implications for water resources, regional state of awareness and preparedness, and the road ahead. Presented at the climate change, water and, the policy-making process in the Levant and North Africa, Issam Fares Institute, American University of Beirut, 4 August 2009
Auty RM (2001) The political state and the management of mineral rents in capital surplus economies: Botswana and Saudi Arabia. Resour Policy 27:77–86
Ayeb H (2002) Hydraulic politics: the Nile and Egypt’s water use: a crisis for the twenty first century? In: Bush R (ed) Counter-revolution in Egypt’s countryside. Zed Books, London
Bajjali W, Al-Hadidi K (2005) Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater in Azraq Basin, Jordan using environmental isotopes and GIS techniques. In: 25th annual ESRI international user conference, San Diego, California, 25–29 July 2005. http://events.esri.com/uc/2005/papers/index.cfm
Bazza M, Najib R (2003) Towards improved water demand management in agriculture in the Syrian Arab Republic. FAO: first national symposium on management and rationalization of water resources use in agriculture organized by the University of Damascus, 28–29 April
Bouchaou L, Michelot JL, Vengosh A, Hsissou Y, Qurtobi M, Gaye CB, Bullen TD, Zuppi GM (2008) Application of multiple isotopic and geochemical tracers for investigation of recharge, salinization, and residence time of water in the Souss-Massa aquifer, Southwest of Morocco. J Hydrol 352:267–287
Bou-Zeid E, El Fadel M (2002) Climate change and water resources in Lebanon and the Middle East. J Water Resour Plan Manage 128:343–355
Brown O, Crawford A (2009) Rising temperatures, rising tensions climate change and the risk of violent conflict in the Middle East. International Institute for Sustainable Development
Center for Environment and Development in the Arab World (CEDARE) (2005) Status of integrated water resources management in the Arab Region. UNDP and the Arab Water Council, Cairo
Cline R (2007) Global warming and agriculture: impact estimates by country. Peterson Institute for International Economics, Washington DC
Conway D (2005) From headwater tributaries to international river: observing and adapting to climate variability and change in the Nile Basin. Glob Environ Change 15(2):99–114
Conway D, Hulme M (1996) The impacts of climate variability and climate change in the Nile Basin on future water resources in Egypt. Water Resour Dev 12(3):277–296
Cullen H, Haggard S, Magaloni B (2009) Grievance and opportunity: food prices, political regime, and protest. Paper presented at the international studies association’s annual meeting, New York, NY, 15 February
Das Gupta S, LaPlante B, Meisner C, Yan J (2007) Impact of sea level rise on developing countries: a comparative study. Policy Res Work Pap 4136. World Bank, Washington, DC
De Rosa DA (1997) Agricultural trade and rural development in the Middle East and North Africa: recent developments and North Africa. Policy Res Work Pap 1732. World Bank, Washington, DC
De-Shalit A (1995) From the political to the objective: the dialectics of zionism and the environment. Environ Pol 4(1):70–87
Dietz T, Ostrom E, Stern PC (2003) The struggle to govern the commons. Science 302:1907–1912
Economist (2008) Buying the farm: Saudi Arabia. Econ 388(8594):39
Economist (2009a) Green shoots. Econ 390(8623):67–68
Economist (2009b) Petrodollars v smallholders. Econ 391(8628):48
Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia (2008) Climate change in ESCWA region: reasons for concern, Arab league meeting, Damascus, Syria, 13–15 April 2008
Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency (1999) Initial national communication on climate change for the United Nations framework convention on climate change. Cairo
Eid H, El-Marsafawy SM, Ouda SA (2007) Assessing the economic impacts of climate change on agriculture in Egypt. Pol Res Work Pap. The World Bank, Washington, DC
Elarabawy M, Tosswell P (1998) An appraisal of the Southern Valley Development Project in Egypt. J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 47(4):167–185
Elarabawy M, Attia B et al (2000) Integrated water resources management for Egypt. J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 49(3):111–125
Elhadj E (2008) Saudi Arabia’s agricultural project: from dust to dust. Middle East Rev Int Aff 12(2):29–37
Elmusa S, Sowers J (2009) Damietta mobilizes for its environment. Middle East Report Online. http://www.merip.org/mero/mero102109.html. Accessed 21 October 2009
El Raey M (2008) Impact of climate change on the Nile Delta region. Paper presented at climate change in Egypt conference, Cairo, 11 November
Evans P (1996) State–society synergy. University of California Press, Berkeley
Evans G (2008a) Conflict potential in a world of climate change. Address to Bucerius Summer School on Global Governance Berlin, 29 August
Evans JP (2008b) 21st century climate change in the Middle East. Clim Change 92:417–432
Evans JP (2009) Global warming impact on the dominant precipitation processes in the Middle East. Theor Appl Climatol, Published online 19 May
Fahmy N (2002) Politics of Egypt: state–society relationship. Routledge, New York
Falkenmark M (1986) Fresh water—time for a modified approach. Ambio 15(4):192–200
Farber E, Vengosh A, Gavrieli I, Marie A, Bullen TD, Mayer B, Holtzman R, Segal M, Shavit U (2004) The origin and mechanisms of salinization of the Lower Jordan River. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:1989–2006
Fayyad M (2009) Current status of climate change research and policy in the Levant. Presented at “Climate change, water and the policy-making process in the Levant and North Africa,” American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon, 4 August 2009
Fischhendler I (2008) Institutional conditions for IWRM: the Israeli case. Ground Water 46(1):91–102
Food and Agriculture Organization (2005) Fertilizer use in Egypt. http://www.fao.org/docrep/008/y5863e/y5863e00.HTM
Ford N (2003) Tapping into Libyan resources. Middle East 332:50
Gao X, Giorgi F (2008) Increased aridity in the Mediterranean region under greenhouse gas forcing estimated from high resolution simulations with a regional climate model. Glob Planet Change 62:195–209
GLOWA (2009) GLOWA Jordan River, phase II final report: an integrated approach to sustainable management of water resources under global change. http://download.glowa-jordan-river.com/GLOWAJR_report_phaseII.pdf
Gorenflo A, Brusilovsky M, Faigon M, Liberman B (2007) High pH operation in seawater reverse osmosis permeate: first results from the world’s largest SWRO plant in Ashkelon. Desalination 203:82–90
Gvirtzman H, Garven G, Gvirtzman G (1997) Hydrogeological modeling of the saline hot springs at the Sea of Galilee, Israel. Water Res Res 33(5):913–926
Hopkins N, Mehanna S, el Haggar S (2001) People and pollution: cultural constructions and social action in Egypt. American University in Cairo Press, Cairo, Egypt
Inbar Y (2007) New standards for treated wastewater reuse in Israel. Wastewater reuse—risk assessment, decision-making and environmental security. NATO Security through Science Series. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 291–296
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York
Jaber JO, Mohsen MS (2001) Evaluation of non-conventional water resources supply in Jordan. Desalination 136:83–92
Kandil HM (2003) Institutional reform vision for the irrigation sector in Egypt. Water Resour Dev 19(2):221–231
Kasinof L (2009) At heart of Yemen’s conflicts: water crisis. Christ Sci Monit, 5 November, p 6
Kassem M (2004) Egyptian politics: the dynamics of authoritarian rule. Lynne Rienner Publishers, Boulder
Khalil M (1998) Azmat al-miyah fi al-Sharq al-Awsat wa-al-amn al-qawmi al-`Arabi wa al-Misri (The water crisis in the Middle East and Arab and Egyptian National Security). al-Tab`ah 1. ed. al-Maktabah al-Akadimiyah, al-Qahirah
Kreimer A, Arnold M, Carlin A (2003) Building safer cities: the future of disaster risk. World Bank, Washington, DC
Kronenberg G (2004) The largest SWRO plant in the world—Ashkelon 100 million m(3)/y BOT project. Desalination 166:457–463
Lahav O, Birnhack L (2007) Quality criteria for desalinated water following post-treatment. Desalination 207:286–303
Lemos MC, Agrawal A (2006) Environmental governance. Annu Rev Environ Resour 31:297–325
Lloyd JW, Pim RH (1990) The hydrogeology and groundwater resources development of the Cambro-Ordovician sandstone aquifer in Saudi Arabia and Jordan. J Hydrol 121:1–20
Marie A, Vengosh A (2001) Sources of salinity in groundwater from Jericho area, Jordan valley. Ground Water 39:240–248
Mashru` al-nahr al-sina`i al-`azim (The Great Man-Made River Project) (1989) [Tripoli]: Jihaz Tanfidh wa-Idarat Mashru` al-nahr al-Sina`i al-`Azim, Amanat al-Lajnah al Sha`biyah al-`Ammah lil-Istislah al Zira`i wa-Ta‘mir al-Aradi, Libya: Tripoli
Miller JE (2003) Review of water resources and desalination technologies. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, NM
Milly PCD, Dunne KA, Vecchia AV (2005) Global pattern of trends in stream flow and water availability in a changing climate. Nature 438:347–350
Mimi Z, Mason M, Zeitoun M (2009) Climate change: impacts, adaptations and policy-making process: Palestine as a case study, Presented at “climate change, water, and the policy-making process in the Levant and North Africa,” American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon, 4 August 2009
Ministry of Public Works and Water Resources, Arab Republic of Egypt (2005) Integrated water resources management plan
Moghadam V (1997) Economic liberalization, women and politics. Middle East Policy September:164–166
Mohorjy AM, Grigg NS (1995) Water-resources management system for Saudi Arabia. Water Resour Plan Manag 121(2):205
Mohsen MS (2007) Water strategies and potential of desalination in Jordan. Desalination 203:27–46
Molle F, Berkhoff J (2006) Cities versus agriculture: revisiting intersectoral water transfers: potential gains and conflicts. Comprehensive Assessment Research Report 10. Comprehensive Assessment Secretariat, Colombo, Sri Lanka
Molle F, Berkhoff J (2006) Cities versus agriculture: revisiting intersectoral water transfers: potential gains and conflicts. Comprehensive Assessment Research Report 10. Comprehensive Assessment Secretariat, Colombo, Sri Lanka
Montero D (2008) Insecurity drives farm purchases abroad. Christ Sci Monit 101(19):1–11
Nelson DR, Adger WN, Brown K (2007) Adaptation to environmental change: contributions of a resilience framework. Annu Rev Environ Resour 32:395–419
Orenstein DE (2004) Population growth and environmental impact: ideology and academic discourse in Israel. Popul Environ 26(1):41–60
Oroud IM (2008) The impacts of climate change on water resources in Jordan. In: Zereini F, Hotzl H (eds) Climate changes and water resources in the Middle East and North Africa. Springer, Environmental Science and Engineering, Berlin
Ostrom E (1990) Governing the commons: the evolution of institutions for collective action. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ostrom E (1992) Crafting institutions for self-governing irrigation systems. ICS Press, San Francisco
Pelling M, High C (2005) Understanding adaptation: what can social capital offer assessments of adaptive capacity? Glob Environ Change 15:308–319
Richards A (2002) Coping with water scarcity: the governance challenge. Institute on Global Conflict and Cooperation, Policy Papers. http://repositories.cdlib.org/igcc/PP/PP54
Richards A, Waterbury J (2008) A political economy of the Middle East, 3rd edn. Westview, Boulder, CO
Rimawi O, Al-Ansari NA (1997) Groundwater degradation in the northeastern part of Mafraq area, Jordan. Freshwater contamination (Proceedings of rabat symposium S4, April–May 1997). IAHS Publ 243:235–243
Ronayne M (2005) The cultural and environmental impacts of large dams in Southeast Turkey. Fact-finding Mission Report. National University of Ireland, Galway, and the Kurdish Human Rights Project, London
Sa`id R (2004) Azmat al-miyah fi al-watan al-`Arabi (The water crisis in the Arab countries). al-Tab`ah 1. ed. Dar al-Amin, al-Qahirah
Salem M (2005) Project Toshka on the edge of failure. Al Masry Al Yom, 23 April
Sánchez E, Gallardoa C, Gaertner MA, Arribas A, Castro M (2004) Future climate extreme events in the Mediterranean simulated by a regional climate model: a first approach. Glob Planet Change 44:163–180
Sauvet-Goichon B (2007) Ashkelon desalination plant—a successful challenge. Desalination 203:75–81
Shahin M (1996) Hydrology and scarcity of water resources in the Arab Region. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Sowers J (2007) Nature reserves and authoritarian rule in Egypt: embedded autonomy revisited. J Environ Dev 16(4):375–397
Sowers J (forthcoming a) Institutional change and environmental governance in the Middle East: water and authority in Egypt. In: VanDeveer S, Steinberg P (eds) Comparative Environmental Politics. MIT Press, Cambridge
Sowers J (forthcoming b) Re-mapping the nation, critiquing the state: narrating land reclamation for Egypt’s New Valley. In: Davis DK, Burke E (eds) Environmental imaginaries of the Middle East: history, policy, power, and practice. Ohio University Press, Athens
Suppan P, Kunstmann H, Heckel A, Rimmer A (2008) Impact of climate change on water availability in the Near East. In: Zereini F, Hotzl H (eds) Climate changes and water resources in the Middle East and North Africa. Springer, Environmental Science and Engineering, Berlin
Steinberger EH, Gazit-Yaari N (1996) Recent changes in the spatial distribution of annual precipitation in Israel. J Climate 9:3328–3336
Stern N (2006) Stern review: the economics of climate change. http://www.hm-treasury.gov.uk/stern_review_report.htm
Tal A (2002) Pollution in a promised land. University of California Press, Berkeley
Tantawi A (1990) Mawarid al-miyah fi Libiya (Water resources in Libya). al-Tab`ah 1. ed. [Cairo]: al-Maktab al-Misri li-Tawzi` al-Matbu`at
Tolba MK, Saab N (2008) Arab public opinion and the environment conference report of 18 country survey. http://www.afedonline.org/en/inner.aspx?contentID=88. Accessed 9 May 2009
Trottier J (2000) Water and the challenge of Palestinian institution building. J Palest Stud 29(2):35–50
United Nations (2009) Syria drought response plan
UNDP (2006) Human development report 2006. Beyond scarcity: power, poverty and the global water crisis. UNDP, New York
UNDP (2007/2008) Human development report 2007/2008, fighting climate change: human solidarity in a divided world. UNDP, New York
UNEP (2003) Desk study on the environment in the occupied Palestinian Territories. UNEP PCDMB, Geneva
Vengosh A (2003) Salinization and saline environments. In: Lollar BS (ed) Environmental geochemistry. Treatise in geochemistry, vol 9. Executive Editors: Holland HD, Turekian KT, Elsevier Science. http://www.TreatiseOnGeochemistry.com
Vengosh A, Rosenthal A (1994) Saline groundwater in Israel: its bearing on the water crisis in the country. J Hydrol 156:389–430
Vengosh A, Heumann KG, Juraske S, Kasher R (1994) Boron isotope application for tracing sources of contamination in groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 28:1968–1974
Vengosh A, Spivack AJ, Artzi Y, Ayalon A (1999) Boron, strontium, and oxygen isotopic and geochemical constraints for the origin of salinity in groundwater from the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Water Resour Res 35:877–1894
Vengosh A, Kloppmann W, Marie A, Livshitz Y, Gutierrez A, Banna M, Guerrot C, Pankratov I, Ranan H (2005) Sources of salinity and boron in the Gaza Strip: natural contaminant flow in the southern Mediterranean Coastal aquifer. Water Resour Res 41:W01013
Vengosh A, Hirschfeld D, Vinson DS, Dwyer GS, Raanan H, Rimawi O, Al-Zoubi A, Akkawi E, Marie A, Haquin G, Zaarur S, Ganor J (2009) High naturally occurring radioactivity in fossil groundwater in the Middle East. Environ Sci Technol 43(6):1769–1775
Vörösmarty CJ, Green P, Salisbury J, Lammers RB (2000) Global water resources: vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 289:284–288
Waldoks EH (2009) A man-made disaster. Jerusalem Post, January 29. http://www.jpost.com/Home/Article.aspx?id=131030
Warner J (2008) Contested hydrohegemony: hydraulic control and security in Turkey. Water Altern 1(2):271–288
Weinthal E (2002) State making and environmental cooperation: linking domestic and international politics in Central Asia. MIT Press, Cambridge
Weinthal E, Marei A (2002) One resource two visions: the prospects for Israeli Palestinian water cooperation. Water Int 27(4):1–8
Weinthal E, Vengosh A, Marie A, Gutierrez A, Kloppmann W (2005) The water crisis in the Gaza strip: prospects for remediation. Ground Water 43:653–660
Wizarat al-Dawla li Shu’un Al-Bi’ah (2007) Al-Taqriir Al-Senawi li Wizarat al-Dawla li Shu’un Al-Bi’ah (Annual report of the ministry of state for environmental affairs). Ministry of State for Environmental Affairs, Egypt, Al-Qahirah
World Bank (2007) Making the most of scarcity: accountability for better water management results in the Middle East and North Africa. World Bank, Washington, DC
Zhang X, Aguilar E, Sensoy S, Melkonyan H, Tagiyeva U, Ahmed N, Kutaladze N, Rahimzadeh F, Taghipour T, Hantosh TH, Albert P, Semawi M, Ali MK, Al Shabibi MHS, Zaid Al-Oulan Z, Zatari T, Khelet IAD, Hamoud S, Sagir R, Demircan M, Eken M, Adiguzel M, Alexander L, Peterson TC, Wallis T (2005) Trends in Middle East climate extreme indices from 1950 to 2003. J Geophys Res 110:D22104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors share equal responsibility for the content and analysis herein.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sowers, J., Vengosh, A. & Weinthal, E. Climate change, water resources, and the politics of adaptation in the Middle East and North Africa. Climatic Change 104, 599–627 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9835-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9835-4