Abstract
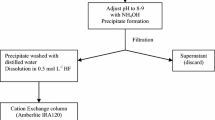
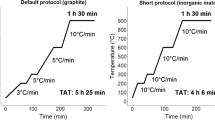
The radioactive chlorine isotope, 36Cl, decays with a half-life of 3×105 years by emitting a beta particle (98 %) and by electron capture. The aim of this paper is to propose a radiochemical separation method of 36Cl from the other beta-gamma emitters present in low and medium radioactive wastes such as spent ion exchange resins and evaporator concentrates, that arise from Nuclear Power Plants and particularly in the wastes that come from decommissioning activities of graphite reactors, in order to provide data for 36Cl inventory calculations. The separation method proposed is based on an oxidation technique where chlorine is trapped by NaOH. 36Cl beta emissions are measured by liquid scintillation counting by the dual label technique in order to avoid the contamination produced by 14C which is also trapped by NaOH and which is the main contaminant present in graphite samples. The sensitivity of this method is sufficient to achieve the needed thresholds for the radiological characterization of the radioactive materials to which this method can be applied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xinqi, L. et al.: “Determination of the 36Cl Content in Reactor Cooling Water and Active Resins from Swiss Nuclear Power Plants”, Technical Report 91-07, National Cooperative for the Disposal of Radioactive Waste, Switzerland, April 1991.
Lepel, E.A. et al.: “Radiological Characterization of Spent Control Rod Assemblies”, PNL-SA-23417. In: Methods and Applications of Radioanalytical Chemistry-III, Kailua-Kona, Hawaii, April 1994.
Kleinberg, J.: “Collected Radiochemical and Geochemical Procedures”, LA-1721, 5th Edition, Los Alamos National Laboratory, New Mexico, May 1990
Kramer, G. H., and Joseph, S.: Canadian Journal of Chemistry 62 (1984) 23.
Cecil, L.D. et al.: Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, B 172 (1–4) (2000) 679.
Piña, G. et al.: “Characterisation of radioactive graphite from NPP dismantling”, In: ENTRAP Papers, Wûrzburg 2002, (Eds. J. Botte and M. Bruggeman), 2002, p.55.
Kessler, M. J.: “Liquid Scintillation Analysis: Science and Technology”, Publication No. 169-3052 Packard Instrument Company. 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, M., Piña, G. & Lara, E. Radiochemical analysis of chlorine-36. Czech J Phys 56, D211–D217 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10582-006-1019-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10582-006-1019-0