Abstract
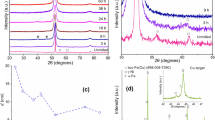
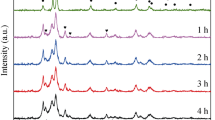
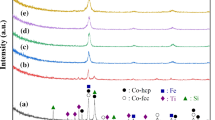
The melt-spun Co- and Fe-based amorphous alloys have been investigated extensively for applications in magnetic devices, which require magnetically soft materials. Although these alloys exhibit excellent soft magnetic properties, their thin sheet shape, which is a consequence of the low glass forming ability, limits significantly their engineering applications. A powder metallurgy is thus an alternative way of producing bulk and, at the same time, soft magnetic materials, having desired shape. In our case, Co56Fe16Zr8B20 and Co70.3Fe4.7Si10B15 amorphous ribbons have been ball-milled for a short time and subsequently compacted (by hot pressing) into disc-shaped specimens with the aim to achieve samll values of resulting coercivity. This work is focused only on the first preparation step i.e. on structural and magnetic properties of ball-milled powders obtained by ball-milling of Co-based melt-spun ribbons at different conditions. Two different ways of milling were employed in order to obtain a powder form of the material: the ribbons were either continuously ball-milled for up to 12 hours or, after each half an hour of ball-milling, the vials were cooled in liquid nitrogen bath for half an hour. Mössbauer spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry were employed to compare and to present the differences between these two different ways of milling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.E. McHenry, M.A. Willard, and D.E. Laughlin: Progress in Materials Science44 (1999) 291.
A. Makino, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto: Mater Trans. JIM36 (1995) 924
T. Mizushima, K. Iskarashi, S. Yoshida, A. Makino, and A. Inoue: Mat. Trans. JIM40 (1999) 1019.
A. Inoue, T. Zhang, and A. Takeuchi: Appl. Phys. Lett.71 (1997) 464.
J. Eckert, N. Schlorke, C.A.R.T. Miranda, and L. Schultz: inSynthesis and Processing of Light Weight Metallic Materials II (Editors C. M. Ward-Close et al.). The Minerals Metals and Materials Society, Warendale, 1997, p. 383.
M. Seidel, J. Eckert, H.-D. Bauer, and L. Schultz: Mater. Sci. Forum119 (1996) 225.
R.A. Brand: NORMOS program 1997 version, unpublished.
Y.-S. Kwon, K. B. Gerasimov, and A.-K. Yoon: J. Alloys Compounds346 (2002) 276.
H. Chen, Y. He, G.J. Shiflat, and S.J. Poon: Nature367 (1994) 99.
M.L. Trudeau, R. Schultz, D. Dussault, and A. van Neste: Phys. Rev. Lett.64 (1990) 99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grants Vega 1/1014/04, Vega 1/0284/03, VEGA 1/1021/04 and SK/CZ/057.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Degmová, J., Tóth, I., Bednarčík, J. et al. The influence of ball-milling on structural and magnetic properties of Co-based powders. Czech J Phys 55, 791–801 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10582-005-0081-3
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10582-005-0081-3