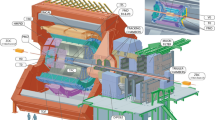
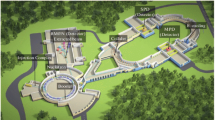
Abstract
In collisions of heavy ions at relativistic energies highly excited nuclear matter is produced. Hadronic and electromagnetic probes are investigated in order to study the composition and the thermodynamical properties of the short-liver interaction volume and its expansion characteristics. The ultimate goal is to identify signals for a phase transition of hadronic matter to the quark-gluon plasma state. Because of the high multiplicity of particles in the final state various experimental techniques and analysis methods have been development in order to study exclusive signals with electromagnetic and hadronic probes. A selection of detector concepts which have been applied in heavy ion reactions at the CERN SPS will be presented here.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Reisdorf and H.G. Ritter: Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 47 (1997) 663.
P. Braun-Munzinger, J. Stachel, J.P. Wessels, N. Xu: Phys. Lett. B 344 (1994) 43.
Recent publications on the web site http://hades.gsi.de/.
A. Kugler: HADES collaboration, lecture presented at the International schoolworkshop RHIP'99, Prague, Czech Republic, Sept. 1999.
Recent publications on the web site http://na49info.cern.ch/.
S. Afansiev et al.: NA49 collaboration, CERN-EP/00-001 and Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 430 (1999) 210.
D. Fancher et al.: Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. 161 (1979) 383.
G. Roland, NA 49 collaboration: Nucl. Phys. A 638 (1998) 91c.
Publications on the web site http://ceres6.physi.uni-heidelberg.de/.
I. Tserruya, CERES collaboration: Nucl. Phys. A 553 (1993) 857c.
P. Holl et al.: Nucl. Inst. Meth. Phys. Res. A 377 (1996) 367.
U. Faschingbauer et al.: Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 377 (1996) 362.
G. Agakichiev et al. Eur. Phys. J. C 4 (1998) 231.
R. Baur et al.: Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 355 (1995) 329.
H. Appelshäuser, CERES collaboration: contribution to the MESON'98 workshop, Cracow, Poland, 1998.
R. Baur et al. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 409 (1998) 278.
Publications on the web site http://pcpig.physik.uni-giessen.de/taps/index.htm.
H. Löhner, Czech. J. of Phys. 47 (1997) 859.
A.R. Gabler et al.: Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 346 (1994) 168.
G. Agakichiev et al.: Eur. Phys. J. C 4 (1998) 249.
Publications on the web site http://www.cern.ch/WA98/.
T. Peitzmann et al., WA98 collaboration: contribution to Quark Matter 99 Conference, Torino, Italy, May 10–15, 1999.
H. Löhner, “Perspectives in the Structure of Hadronic Systems,” ed. by M.N. Harakeh et al., Plenum Press, NY, 1994, p. 213–234, and ref. therein.
D. Bucher, WA98 collaboration: contribution to Quark Matter 99 Conference, Torino, Italy, May 10–15, 1999.
T. Peitzmann et al.: Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 376 (1996) 368.
L. Carlén et al.: Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 413 (1998) 92.
L. Carlén et al.: Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 431 (1999) 123.
L. Carlén et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 412 (1998) 361.
M.M. Aggarwal et al., WA98 collaboration: Phys. Lett. B 469 (1999) 30.
Publications on the web site http://www.cern.ch/NA50/.
R. Arnaldi et al.: Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 411 (1998) 1.
M.C. Abreu et al., NA50 collaboration: CERN-EP/99-13 and Phys. Lett. B 450 (1999) 456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Lectures given at the Indian-Summer School on Relativistic Heavy-Ion Physics-RHIP'99, Prague (Czech Republic), August 30–September 3, 1999.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Löhner, H. Detectors and techniques in relativistic heavy ion physics. Czech J Phys 50 (Suppl 2), 37–51 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10582-000-0030-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10582-000-0030-0