Abstract
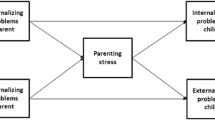
The aim was to examine the potential mediating role of father’s and mother’s parenting styles in the association between parental psychopathology and antisocial behavior in children, and whether this pathway was moderated by child’s sex. Participants included both parents and 338 Spanish outpatient children between 8 and 17 years (56.5% boys). Parenting style had a mediating effect on the studied relationships. Maternal psychopathology was positively associated with antisocial behavior in children, either directly or partially by parenting style, while paternal psychopathology was positively associated with offspring antisocial behavior only through the mediator role of parenting style. Child’s sex did not moderate these relationships. Parenting style could be a target for prevention and intervention of antisocial behavior in the offspring of parents with mental health problems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frick P, Loney B (2002) Understanding the association between parent and child antisocial behaviour. In: McMahon R, Peters R (eds) The effects of parental dysfunction on children. Kluwer, New York, pp 105–126
McMahon R, Frick P (2005) Evidence-based assessment of conduct problems in children and adolescents. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 34:477–505
Vostanis P, Graves A, Meltzer H, Goodman R, Jenkins R, Brugha T (2006) Relationship between parental psychopathology, parenting strategies and child mental health: Findings from the GB national study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 41(7):509–514
Kim-Cohen J, Moffitt T, Taylor A, Pawlby S, Caspi A (2005) Maternal depression and children’s antisocial behavior: nature and nurture effects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62(2):173–181
Kazdin A, Kolko D (1986) Parent psychopathology and family functioning among childhood firesetters. J Abnorm Child Psychol 14(2):315–329
Ohannessian C, Hesselbrock V, Kramer J, Kuperman S, Bucholz K, Schuckit M et al (2005) The relationship between parental psychopathology and adolescent psychopathology: an examination of gender patterns. J Emot Behav Disord 13(2):67–76
Marmorstein N, Iacono W (2004) Major depression and conduct disorder in youth: associations with parental psychopathology and parent-child conflict. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 45(2):377–386
Rhule D, McMahon R, Spieker S (2004) Relation of adolescent mothers’ history of antisocial behavior to child conduct problems and social competence. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 33:524–535
Kuperman S, Schlosser S, Lidral J, Reich W (1999) Relationship of child psychopathology to parental alcoholism and antisocial personality disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 38(6):686–692
Moss H, Baron D, Hardie T, Vanyukov M (2001) Preadolescent children of substance-dependent fathers with antisocial personality disorder: psychiatric disorders and problem behaviors. Am J Addict 10(3):269–278
Frick P, Lahey B, Loeber R, Stouthamer-Loeber M, Christ M, Hanson K (1992) Familial risk factors to oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder: parental psychopathology and maternal parenting. J Consult Clin Psychol 60(1):49–55
Biederman J, Rosenbaum J, Bolduc E, Faraone S, Hirshfeld D (1991) A high risk study of young children of parents with panic disorder and agoraphobia with and without comorbid major depression. Psychiatry Res 37:333–348
Turner S, Beidel D, Costello A (1987) Psychopathology in the offspring of anxiety disorders patients. J Consult Clin Psychol 55:229–235
Burstein M, Ginsburg G, Tein J-T (2010) Parental anxiety and child symptomatology: an examinazation of additive and interactive effects of parent psychopathology. J Abnorm Child Psychol 38:897–909
Berg-Nielsen T, Vikan A, Dahl A (2002) Parenting related to child and parental psychopathology: a descriptive review of the literature. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry 7:529–552
Hirshfeld D, Biederman J, Brody L, Faraone S, Rosenbaum J (1997) Expressed emotion toward children with behavioral inhibition: associations with maternal anxiety disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36:910–917
Thompson A, Hollis C, Richards D (2003) Authoritarian parenting attitudes as a risk for conduct problems: results from a British national cohort study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 12:84–91
Miller S, Loeber R, Hipwell A (2009) Peer deviance, parenting and disruptive behavior among young girls. J Abnorm Child Psychol 37:139–152
Henry D, Tolan P, Gorman-Smith D (2001) Longitudinal family and peer group effects on violence and nonviolent delinquency. J Clin Child Psychol 30:172–186
Veenstra R, Lindenberg S, Oldehinkel A, De Winter A, Ormel J (2006) Temperament, environment, and antisocial behavior in a population sample of preadolescent boys and girls. Int J Behav Dev 30:422–432
Snyder J (1991) Discipline as a mediator of the impact of maternal stress and mood on child conduct problems. Dev Psychopathol 3(3):263–276
Harnish J, Dodge K, Valente E (1995) Mother-child interaction quality as a partial mediator of the roles of maternal depressive symptomatology and socioeconomic status in the development of child behavior problems. Child Dev 66(3):739–753
Chang L, Lansford J, Schwartz D, Farver J (2004) Marital quality, maternal depressed affect, harsh parenting, and child externalising in Hong Kong Chinese families. Int J Behav Dev 28:311–318
Miller N, Cowan P, Cowan C, Hetherington E, Clingempeel W (1993) Externalizing in preschoolers and early adolescents: a cross-study replication of a family model. Dev Psychol 29:3–18
McKee L, Forehand R, Rakow A, Reeslund K, Roland E, Hardcastle E, Compas B (2008) Parenting specificity: an examination of the relation between three parenting behaviors and child problem behaviors in the context of a history of caregiver depression. Behav Modif 32:638–658
Trentacosta C, Shaw D (2008) Maternal predictors of rejecting parenting and early adolescent antisocial behavior. J Abnorm Child Psychol 36:247–259
Thornberry T, Freeman-Gallant A, Lovegrove P (2009) Intergenerational linkages in antisocial behaviour. Crim Behav Ment Health 19(2):80–93
Hops H, Davis B, Leve C, Sheeber L (2003) Cross-generational transmission of aggressive parent behavior: a prospective, mediational examination. J Abnorm Child Psychol 31:161–169
Smith C, Farrington D (2004) Continuities in antisocial behavior and parenting across three generations. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 45:230–247
Spieker S, Larson N, Lewis S, Keller T, Gilchrist L (1999) Developmental trajectories of disruptive behavior problems in preschool children of adolescent mothers. Child Dev 70:443–458
Meurs I, Reef J, Verhulst F, van der Ende J (2009) Intergenerational transmission of child problem behavior: a longitudinal, population-based study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 48:138–145
Gryczkowski M, Jordan S, Mercer S (2010) Differential relations between mothers’ and fathers’ parenting practices and child externalizing behavior. J Child Fam Stud 19:539–546
Pajer K, Stein S, Tritt K, Chang C, Wang W, Gardner W (2008) Conduct disorder in girls: neighborhoods, family characteristics, and parenting behaviors. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health 2:28
O’Hara M, Fisher S (2010) Psychopatological states in the father and their impact on parenting. In: Tyano S, Keren M, Herrman H, Cox J (eds) Parenthood and mental health: a bridge between infant and adult psychiatry. Wiley, London, pp 231–240
Meteyer K, Perry-Jenkins M (2009) Dyadic parenting and children’s externalizing symptoms. Fam Relat 58:289–302
van de Molen E, Hipwell A, Vermeiren R, Loeber R (2011) Maternal characteristic predicting young girls’ disruptive behavior. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 40:179–190
Vera J, Ezpeleta L, Granero R, de la Osa N (2010) Antisocial behavior, psychopathology and functional impairment: association with sex and age in clinical children and adolescents. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 41:465–478
O’Connor T (2002) Annotation: the ‘effect’ of parenting reconsidered: findings, challenges, and applications. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 43:555–572
Hollingshead AB (1975) Four factor index of social status. Unpublished manuscript, Yale University, Department of Sociology, New Haven
Derogatis L (1983) SCL-90-R administration, scoring and procedures manual-II. Clinical Psychometric Research, Baltimore
Robles J, Andreu J, Peña M (2002) SCL-90-R: Aplicación y análisis de sus propiedades psicométricas en una muestra de sujetos clínicos españoles. Psicopatología Clínica, Legal y Forense 2:5–19
Perris C, Jacobson L, Lindström H, Von Knorring L, Perris H (1980) Development of a new inventory for assessing memories of parental rearing behaviour. Acta Psychiatr Scand 61:265–274
Castro J, Toro J, Van der Ende J, Arrindell WA (1993) Exploring the feasibility of assessing perceived parental rearing styles in Spanish children with the EMBU. Int J Soc Psychiatry 39:47–57
Castro J, de Pablo J, Gómez J, Arrindell WA, Toro J (1997) Assessing rearing behaviour from the perspective of the parents: a new form of the EMBU. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 32:230–235
Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA (2001) Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms and Profiles. University of Vermont, Research Center for Children Youth and Families, Burlington
Sardinero E, Pedreira JL, Muñiz J (1997) El cuestionario CBCL de Achenbach: Adaptación española y aplicaciones clínico-epidemiológicas. Clínica y Salud 8:447–480
Reich W (2000) Diagnostic interview for children and adolescents (DICA). J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39:59–66
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
de la Osa N, Ezpeleta L, Domènech JM, Navarro JB, Losilla JM (1996) Fiabilidad entre entrevistadores de la entrevista diagnóstica estructurada para niños y adolescentes (DICA-R). Psicothema 8:359–368
Ezpeleta L, de la Osa N, Júdez J, Doménech JM, Navarro JB, Losilla JM (1997) Diagnostic agreement between clinician and the diagnostic interview for children and adolescents—DICA-R in a Spanish outpatient sample. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 38:431–440
Ezpeleta L, de la Osa N, Domenech JM, Navarro JB, Losilla JM (1997) Fiabilidad test-retest de la adaptación española de la diagnostic interview for children and adolescents (DICA-R). Psicothema 9:529–539
Baron R, Kenny D (1986) The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol 51:1173–1182
Kenny D, Kashy D, Bolger N (1998) Data analysis in social psychology. In: Gilbert D, Fiske S, Lindzey G (eds) The handbook of social psychology. McGraw-Hill, Boston, pp 233–265
Bollen K, Long J (eds) (1993) Testing structural equations models. Newbury Park, CA
Browne M, Cudeck R (1993) Alternative ways of assessing model fix. In: Bollen K, Long J (eds) Testing structural equations models. Newbury Park, CA, pp 136–162
Holmbeck G, Johnson S, Wills K, McKernon W, Rose B, Erklin S et al (2002) Observed and perceived parental overprotection in relation to psychosocial adjustment in preadolescents with a physical disability: the mediational role of behavioral autonomy. J Consult Clin Psychol 70:96–110
Kendler K, Sham P, MacLean C (1997) The determinants of parenting: an epidemiological, multi-informant, retrospective study. Psychol Med 27:549–563
Thornberry T, Freeman-Gallant A, Lovegrove P (2009) The impact of parental stressors on the intergenerational transmission of antisocial behavior. J Youth Adolesc 38:312–322
Jaffee S, Moffitt T, Caspi A, Taylor A (2003) Life with (or without) father: the benefits of living with two biological parents depend on the father’s antisocial behavior. Child Dev 74:109–126
Gerdes A, Hoza B, Arnold L, Pelham W, Swanson J, Wigal T et al (2007) Maternal depressive symptomatology and parenting behavior: exploration of possible mediators. J Abnorm Child Psychol 35:705–714
Zahn-Waxler C, Shirtcliff E, Marceau K (2008) Disorder of childhood and adolescence: gender and psychopathology. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 4:275–303
Loeber R, Burke J, Lahey B, Winters A, Zera M (2000) Oppositional defiant and conduct disorder: a review of the past 10 years, Part I. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39:1468–1484
Rey J, Plapp J (1990) Quality of perceived parenting in oppositional and conduct disordered adolescents. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 29:382–385
Kjobli J, Hagen K (2009) A mediational model of interparental collaboration, parenting practices, and child externalizing behavior in a clinical sample. Fam Relat 58:275–288
Sanders M, Dittman C, Keown L, Farruggia S, Rose D (2010) What are the parenting experiences of fathers? The use of household survey data to inform decisions about the delivery of evidence-based parenting interventions to fathers. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 41:562–581
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Innovation (Spain) [grant number PSI2009-07542].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vera, J., Granero, R. & Ezpeleta, L. Father’s and Mother’s Perceptions of Parenting Styles as Mediators of the Effects of Parental Psychopathology on Antisocial Behavior in Outpatient Children and Adolescents. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 43, 376–392 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-011-0272-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-011-0272-z