Abstract
The genus Urochloa includes most of the important grasses and hybrids currently used as pastures in the tropical regions. Cytogenetic analyzes have identified some aneuploid hybrids that provide new perspectives for genetic breeding. The objective was to analyze the meiotic behavior in euploid (2n = 4x = 36) and aneuploid (2n = 4x = 36 + 2) hybrids of U. ruziziensis x U. decumbens and U. ruziziensis x U. brizantha. Later, the chromosomes and respective genomes involved in pairing configurations and abnormalities were identified through GISH, with an emphasis on tracking the behavior of the additional chromosomes in the aneuploid hybrid U. ruziziensis x U. decumbens (B1B2B2B2 genomes). The aneuploid U. ruziziensis x U. decumbens shows a higher frequency of univalents, reduction of bivalents, and higher index of irregularities compared with the euploid hybrid. For the aneuploid U. ruziziensis x U. brizantha, there was a reduction in the frequency of univalents, an increase in bivalent and trivalent rates and a lower frequency of abnormalities when compared with the euploid hybrid. The rates of meiotic abnormalities and pairing configurations are parental genotype-dependent and influenced by trisomy. The chromosomes of the B1 and B2 genomes of the aneuploid hybrid (U. ruziziensis x U. decumbens) are involved in the formation of univalents, bivalents, and multivalents in inter-, intra- and inter–intragenomic pairings. In general, the segregation times of chromosomes of the genomes are different, since the chromosomes of the B1 genome segregate more slowly.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GISH:
-
Genomic in situ hybridization
- FISH:
-
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
- gDNA:
-
Genomic DNA
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- SSC:
-
2′ saline sodium citrate
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- rDNA:
-
Ribosomal DNA
References
Adamowski EV, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB do (2008) Meiotic behaviour in three interspecific three-way hybrids between Brachiaria ruziziensis and Brachiaria brizantha (Poaceae: Paniceae). J Genet 87:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-008-0005-7
Alexander MP (1980) A versatile stain for pollen from fungi, yeast and bacteria. Stain Technol 55:13–18. https://doi.org/10.3109/10520298009067890
Alvim MJ, Botrel MA, Xavier DF (2002) As principais espécies de braquiárias utilizadas no país. Comunicado Técnico 22 https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/item/65321/1/COT-22-As-principais-especies-de.pdf. Accessed 10 June 2019
Araújo SAC, Deminicis BB, Campos PRSS (2008) Melhoramento genético de plantas forrageiras tropicais no Brasil. Arch Zootech 57:61–76
Carrillo ARQ, Quiroz JFE, Nieto CRM, Jiménez LM (2010) Apomixis importance for tropical forage grass selection and breeding. Rev Rev Mex Cienc Pecu 1:25–42
Chelysheva LA, Grandont L, Grelon M (2013) Immunolocalization of meiotic proteins in Brassicaceae: method 1. In: Pawlowski WP, Grelon M, Armstrong S (eds) Plant meiosis: methods and protocols. Springer Science+Business Media, New York, pp 93–101
Cho SW, Moritama Y, Ishii T, Kishii M, Tanaka H, Eltayeb AE, Tsujimoto H (2011) Homology of two alien chromosomes during meiosis in wheat. Chromosome Sci 14:45–52. https://doi.org/10.11352/scr.14.45
Choi K (2017) Advances towards controlling meiotic recombination for plant breeding. Mol Cell 40:814–822. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.0171
Euclides VPB, Valle CB do, Macedo MCM, Almeida RGD, Montagner DB, Barbosa RA (2010) Brazilian scientific progress in pasture research during the first decade of XXI century. Rev Bras Zootec 39:151–168. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010001300018
Felismino MF, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB do (2010) Meiotic behavior of interspecific hybrids between artificially tetraploidized sexual Brachiaria ruziziensis and tetraploid apomictic B. brizantha (Poaceae). Sci Agric 67:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162010000200010
Fuzinatto VA, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB do (2007) Microsporogenesis in sexual Brachiaria hybrids (Poaceae). Genet Mol Res 6:1107–1117
Fuzinatto VA, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB do (2012) Meiotic behavior in apomictic Brachiaria ruziziensis × Brachiaria brizantha (Poaceae) progenies. Sci Agric 69:380–385. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162012000600006
Humphreys MW, Canter PJ, Thomas HM (2003) Advances in introgression technologies for precision breeding within the Lolium—Festuca complex. Ann Appl Biol 143:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2003.tb00263.x
Ishigaki G, Gondo T, Suenaga K, Akashi R (2009) Induction of tetraploid ruzigrass (Brachiaria ruziziensis) plants by colchicine treatment of in vitro multiple-shoot clumps and seedlings. Jpn Soc Grassl Sci 5:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-697X.2009.00153.x
Mendes–Bonato AB, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB do (2004) Abnormal pollen mitoses (PM I and PM II) in an interspecific hybrid of Brachiaria ruziziensis and Brachiaria decumbens (Gramineae). J Genet 83:279–283
Mendes–Bonato AB, Pagliarini MS, do Valle CB do (2006a) Abnormal spindle orientation during microsporogenesis in an interspecific Brachiaria (Gramineae) hybrid. Genet Mol 29:122–125. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572006000100023
Mendes–Bonato AB, Risso-Pascotto C, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB do (2006b) Cytogenetic evidence for genome elimination during microsporogenesis in interspecific hybrid between Brachiaria ruziziensis and B. brizantha (Poaceae). Genet Mol Biol 29:711–714. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572006000400021
Mendes–Bonato AB, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB do (2007) Meiotic arrest compromises pollen fertility in an interspecific hybrid between Brachiaria ruziziensis x Brachiaria decumbens (Poaceae: Paniceae). Braz Arch Biol Technol 50:831–837. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132007000500011
Molnár-Láng M, Ceoloni C, Doležel J (2015) Alien introgression in wheat—cytogenetics, molecular biology, and genomics. Springer, Switzerland
Moraes IC, Rume GC, Souza Sobrinho F, Techio VH (2019) Characterization of aneuploidy in interspecific hybrid between Urochloa ruziziensis (R. germ. & Evrard) Crins and Urochloa decumbens (Stapf) R. D. Webster. Mol Biol Rep 46:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04643-8
Nani TF, Pereira DL, Souza Sobrinho F, Techio VH (2016) Physical map of repetitive DNA sites in Brachiaria spp.: intravarietal and interspecific hybrids. Crop Sci 56:1769–1783. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2015.12.0760
Papp I, Iglesias VA, Moscone EA, Michalowski S, Spiker S, Park YD, Matzke MA, Matzke AJM (1996) Structural instability of a transgene locus in tobacco is associated with aneuploidy. Plant J 10:469–478. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1996.10030469.x
Paula CMP, Sobrinho FS, Techio VH (2017) Genomic constitution and relationship in Urochloa (Poaceae) species and hybrids. Crop Sci 57:2605–2616. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2017.05.0307
Rocha LC, Ferreira MTM, Cunha IMF, Mittelmann A, Techio VH (2018) 45S rDNA sites in meiosis of Lolium multiflorum Lam.: variability, non-homologous associations and lack of fragility. Protoplasma 256:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-018-1292-3
Santos YS (2018). Avaliação de marcas epigenéticas com a análise da expressão gênica de rDNA45S em Urochloa ruziziensis, Urochloa brizantha e seu híbrido. Dissertation, Universidade de Federal de Lavras
Singh RJ (2017) Plant cytogenetics, 3rd edn. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Sybenga J (1992) Cytogenetics in plant breeding. Springer-Verlag, New York
Techio VH, Davide LC (2007) Análise genômica em cromossomos de plantas com base no pareamento meiótico. Biotemas 20:7–18.
Timbó AL de O, Souza PN da C, Pereira RC, Nunes JD, Pinto JEBP, Souza Sobrinho F, Davide LC (2014) Obtaining tetraploid plants of ruzigrass (Brachiaria ruziziensis). R Bras Zootec 43:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982014000300004
Valle CB do, Pagliarini MS (2009) Biology, cytogenetics, and breeding of Brachiaria In: Singh RJ (ed) Genetic resources, chromosome engineering, and crop improvement. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 103–151
Valle CB do, Savidan Y (1996) Genetics, cytogenetics and reproductive biology of Brachiaria. In: Miles JW, Maass BL, Valle CB (eds) Brachiaria: biology, agronomy, and improvement. CIAT, Cali, pp 147–163
Worthington M, Heffelfinger C, Bernal D, Quintero C, Zapata YP, Perez JG, De Vega J, Miles J, Dellaporta S, Tohme J (2016) A parthenogenesis gene candidate and evidence for segmental allopolyploidy in apomictic Brachiaria decumbens. Genetics 203:1117–1132. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.116.190314
Funding
The authors thank the support of the Foundation for Research Support of the State of Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for financial support for the development of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans De Jong
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
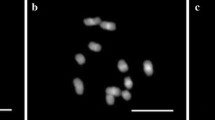
Mitotic metaphases of the EGL RxD#01 hybrid between U. ruziziensis x U. decumbens with 36 chromosomes (a) and the hybrid 10.6-168 between U. ruziziensis x U. brizantha with 36 + 2 chromosomes (b). The bar represents 10 μm. (PNG 503 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Rocha, M.J., Chiavegatto, R.B., Damasceno, A.G. et al. Comparative meiosis and cytogenomic analysis in euploid and aneuploid hybrids of Urochloa P. Beauv. Chromosome Res 27, 333–344 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-019-09616-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-019-09616-y