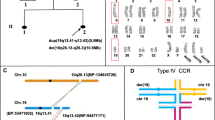
Abstract
Robertsonian translocation (rob) involving chromosomes 1 and 29 represents the most frequent chromosome abnormality observed in cattle breeds intended for meat production. The negative effects of this anomaly on fertility are widely demonstrated, and in many countries, screening programs are being carried out to eliminate carriers from reproduction. Although rob(1;29) was first observed in 1964, the genomic structure of this anomaly is partially unclear. In this work, we demonstrate that, during the fusion process, around 5.4 Mb of the pericentromeric region of BTA29 moves to the q arm, close to the centromere, of rob(1;29). We also clearly show that this fragment is inverted. We find that no deletion/duplication involving sequences reported in the BosTau6 genome assembly occurred during the fusion process which originates this translocation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAC:
-
Bacterial Artificial Chromosome
- BLAST:
-
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
- BTA:
-
Bos Taurus
- C11orf:
-
Chromosome 11 Open Reading Frame
- ESM:
-
Electronic supplementary material
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence In situ Hybridization
- FOLH:
-
folate hydrolase
- HC:
-
heterochromatin
- IDGVA:
-
Istituto Di Genetica e Valorizzazione Animale
- INRA:
-
Institut National Recheche Agronomique
- MIR:
-
microRNA
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- RefSeq:
-
Reference sequence
- SCARNA:
-
small Cajal body-specific RNA
- SLC:
-
solute carrier
- SMORD:
-
small nuclear RNA C/D box non-coding RNA
- SNORA:
-
small nucleolar RNA, H/ACA box
- TRIM:
-
tripartite motif-containing
- TYR:
-
Tyrosine
- UBTFL:
-
upstream binding transcription factor
- UMD:
-
University of Maryland
References
Bickhart DM, Hou Y, Schroeder SG et al. (2012) Copy number variation of individual cattle genomes using next-generation sequencing. Genome Res 22:778–790
Bonnet-Garnier A, Pinton A, Berland HM et al (2006) Sperm nuclei analysis of 1/29 Robertsonian translocation carrier bulls using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Genome Res 112:241–247
Bonnet-Garnier A, Lacaze S, Beckers JF et al (2008) Meiotic segregation analysis in cows carrying the t(1;29) Robertsonian translocation. Cytogenet Genome Res 120:91–96
Chaves R, Adega F, Heslop-Harrison JS et al (2003) Complex satellite DNA reshuffling in the polymorphic t(1;29) Robertsonian translocation and evolutionarily derived chromosomes in cattle. Chromosome Res 11:641–648
De Grouchy J, Roubin M, Passage E (1964) Microtechnique pour l’étude des chromosomes humains a partir d’une culture de leucocytes sanguins. Ann Genet 7:45–46
De Lorenzi L, De Giovanni A, Molteni L et al (2007) Characterization of a balanced reciprocal translocation, rcp(9;11)(q27;q11) in cattle. Cytogenet Genome Res 119:231–234
De Lorenzi L, Kopecna O, Gimelli S et al (2010) Reciprocal translocation t(4;7)(q14;q28) in cattle: molecular characterization. Cytogenet Genome Res 129:298–304
Di Meo GP, Perucatti A, Chaves R et al (2006) Cattle rob(1;29) originating from complex chromosome rearrangements as revealed by both banding and FISH-mapping techniques. Chromosome Res 14:649–655
Douet-Guilbert N, Bris MJ, Amice V et al (2005) Interchromosomal effect in sperm of males with translocations: report of 6 cases and review of the literature. Int J Androl 28:372–379
Ducos A, Revay T, Kovacs A et al (2008) Cytogenetic screening of livestock populations in Europe: an overview. Cytogenet Genome Res 120:26–41
Dyrendahl I, Gustavsson I (1979) Sexual functions, semen characteristics and fertility of bulls carrying the 1/29 chromosome translocation. Hereditas 90:281–289
Eggen A, Oustry A, Vaiman D et al (1994) Bovine synteny group U7, previously assigned to G-banded chromosome 25 in the ISCNDA nomenclature, assigns to R-banded chromosome 29. Hereditas 121:295–300
Guichaoua MR, Quack B, Speed RM et al (1990) Infertility in human males with autosomal translocations: meiotic study of a 14;22 Robertsonian translocation. Hum Genet 86:162–166
Gustavsson I, Rockborn G (1964) Chromosome abnormality in three cases of lymphatic leukemia in cattle. Nature 203:990
Hayes BJ, Chamberlain AJ, Maceachern S et al (2009) A genome map of divergent artificial selection between Bos taurus dairy cattle and Bos taurus beef cattle. Anim Genet 40:176–184
Holmberg M, Andersson-Eklund L (2006) Quantitative trait loci affecting fertility and calving traits in Swedish dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci 89:3664–3671
Hou Y, Liu GE, Bickhart DM, Cardone MF et al (2011) Genomic characteristics of cattle copy number variations. BMC Genomics 12:127
Iannuzzi A, Di Meo GP, Caputi-Jambrenghi A et al (2008) Frequency and distribution of rob(1;29) in eight Portuguese cattle breeds. Cytogenet Genome Res 120:147–149
Iannuzzi L, King WA, Di Berardino D (2009) Chromosome evolution in domestic bovids as revealed by chromosome banding and FISH-mapping techniques. Cytogenet Genome Res 126:49–62
Liu GE, Hou Y, Zhu B et al (2010) Analysis of copy number variations among diverse cattle breeds. Genome Res 20:693–703
Lonergan P, Kommisrud E, Andresen O et al (1994) Use of semen from a bull heterozygous for the 1;29 translocation in an IVF program. Theriogenology 41:1379–1384
Mahjoub M, Mehdi M, Brahem S et al (2011) Chromosomal segregation in spermatozoa of five Robertsonian translocation carriers t(13;14). J Assist Reprod Genet 28:607–613
Ogur G, Van Assche E, Vegetti W et al (2006) Chromosomal segregation in spermatozoa of 14 Robertsonian translocation carriers. Mol Hum Reprod 12:209–215
Popescu CP, Pech A (1991) Une bibliographie sur la translocation 1/29 de bovines dans le monde (1964–1990). Ann Zootech 40:271–305
Schmutz SM, Moker JS, Barth AD, Mapletoft RJ (1991) Embryonic loss in superovulated cattle caused by the 1;29 Robertsonian translocation. Theriogenology 35:705–714
Schulman NF, Sahana G, Lund MS et al (2008) Quantitative trait loci for fertility traits in Finnish Ayrshire cattle. Genet Sel Evol 40:195–214
Switoński M, Gustavsson I, Plöen L (1987) The nature of the 1;29 translocation in cattle as revealed by synaptonemal complex analysis using electron microscopy. Cytogenet Cell Genet 44:103–111
Vozdova M, Kubickova S, Cernohorska H, Rubes J (2008) Detection of translocation rob(1;29) in bull sperm using a specific DNA probe. Cytogenet Genome Res 120:102–105
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the CRB GADIE (INRA, Jouy-en-Josas, France) for providing cattle-specific BACs and to Prof. Mariano Rocchi (Di.Ge.Mi, Bari, Italy) for providing human-specific BACs. We are also grateful to ANABIC employers for providing fresh blood from subjects carrying rob(1;29) and Domenico Incarnato, CNR-ISPAAM of Naples, for his excellent technical assistance. This study was partially supported by PSR, Misura 214, e2 of Campania Region, Project “Razze Autoctone a Rischio di Estinzione della Regione Campania–RARECa.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Herbert Macgregor.
Lisa De Lorenzi and Viviana Genualdo contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Lorenzi, L., Genualdo, V., Gimelli, S. et al. Genomic analysis of cattle rob(1;29). Chromosome Res 20, 815–823 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-012-9315-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-012-9315-y