Abstract
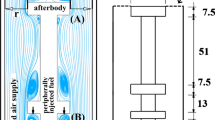
The effects of the fuel concentration gradient and the octane number on the autoignition and knocking phenomena in a stratified mixture were studied experimentally on a using a rapid compression machine using stratified mixtures of air and fuels n-heptane, iso-octane, n-hexane, and n-pentane with different octane numbers (0, 100, 25, and 62, respectively). In the chamber, the lower the vertical location, the richer the fuel concentration of the mixture. The mixture contains no gradient in the horizontal direction. The experimental results show that rapid spread of the flame is caused not by flame propagation but by sequential autoignition. Although ignition delays of a stratified mixture are not dependent on the fuel concentration gradient in the mixture, they are constant as long as mean equivalence ratio is the same, and they decrease with the decreasing mean equivalence ratio. In excess of certain gradient value, the knock intensity is smaller as the gradient becomes larger for all fuels tested regardless of their octane number.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Noda, M. Kubo, S. Kimura, and T. Itoh, “Knocking prediction by using non-dimensional engine cycle simulation with chemical kinetic model,” in: Proc. 17th Int. Combustion Engine Symp., Japan (2002), pp. 95–100.
O. T. Lim, H. Nakano, and N. Iida. “The research of the effects of thermal stratification on n-heptane/iso-octane—air mixture HCCI combustion using a R.C.M,” in: Proc. 2006 JSAE Annual Congress, HCCI I (2006), pp. 1–6.
X. J. Chien, K. Wakai, S. Takahashi, T. Ihara, and K. Shibata. “Resistance wire CT pyrometry used to analyze the knocking problem in direct injection engines” Measur. Sci. Technol., 16, 707–715 (2005).
G. Konig and C. G. W. Sheppard, “End gas autoignition and knock in a spark ignition engine,” SAE Paper No. 902135 (1990), pp. 820–839.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Fizika Goreniya i Vzryva, Vol. 45, No. 4, pp. 93–100, July–August, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ihara, T., Tanaka, T. & Wakai, K. Effects of octane number on autoignition and knocking phenomena in a stratified mixture. Combust Explos Shock Waves 45, 428–434 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10573-009-0053-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10573-009-0053-1