Abstract
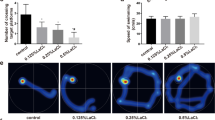
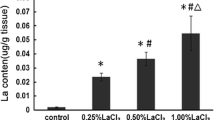
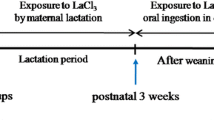
Lanthanum (La) is a natural rare-earth element that can damage the central nervous system and impair learning and memory. However, its neurotoxic mechanism remains unclear. In this study, adult female rats were divided into 4 groups and given distilled water solution containing 0%, 0.125%, 0.25%, and 0.5% LaCl3, respectively, and this was done from conception to the end of the location. Their offspring rats were used to establish animal models to investigate LaCl3 neurotoxicity. Primary neurons cultured in vitro were treated with LaCl3 and infected with LKB1 overexpression lentivirus. The results showed that LaCl3 exposure resulted in abnormal axons in the hippocampus and primary cultured neurons. LaCl3 reduced the expression of LKB1, p-LKB1, STRAD and MO25 proteins, and directly or indirectly affected the expression of LKB1, leading to decreased activity of LKB1-MARK2 and LKB1-STK25-GM130 pathways. This study indicated that LaCl3 exposure could interfere with the normal effects of LKB1 in the brain and downregulate LKB1-MARK2 and LKB1-STK25-GM130 signaling pathways, resulting in abnormal axon in offspring rats.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Change history
21 June 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01244-1
Abbreviations
- Ace:
-
Acetylated α-tubulin
- Dil:
-
1,1'-Dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate
- GM130:
-
Golgi Matrix Protein130
- LaCl3 :
-
Lanthanum chloride
- LKB1:
-
Liver kinase B1
- MARK2:
-
Microtubule affinity-regulating kinases 2
- MO25:
-
Mouse protein 25
- NC:
-
Negative control
- NSE:
-
Neuron-specific enolase
- OE:
-
Over expression
- REEs:
-
Rare-earth elements
- STE20:
-
Sterile twenty
- STK25:
-
Serine/threonine kinase 25
- STRAD:
-
STE20-related adapter
- Tyr:
-
Tyrosinated α-tubulin
References
Antón-Fernández A, León-Espinosa G, DeFelipe J, Muñoz A (2015) Changes in the Golgi apparatus of neocortical and hippocampal neurons in the hibernating hamster. Front Neuroanat 9:157. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2015.00157
Arimura N, Kaibuchi K (2007) Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to intracellular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:194–205. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2056
Asada N, Sanada K (2010) LKB1-mediated spatial control of GSK3beta and adenomatous polyposis coli contributes to centrosomal forward movement and neuronal migration in the developing neocortex. J Neurosci 30:8852–8865. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.6140-09.2010
Baas AF, Boudeau J, Sapkota GP, Smit L, Medema R, Morrice NA, Alessi DR, Clevers HC (2003) Activation of the tumour suppressor kinase LKB1 by the STE20-like pseudokinase STRAD. EMBO J 22:3062–3072. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg292
Barnes AP, Lilley BN, Pan YA, Plummer LJ, Powell AW, Raines AN, Sanes JR, Polleux F (2007) LKB1 and SAD kinases define a pathway required for the polarization of cortical neurons. Cell 129:549–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.025
Binarová P, Tuszynski J (2019) Tubulin: structure, functions and roles in disease. Cells 8:1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101294
Cassimeris L, Guglielmi L, Denis V, Larroque C, Martineau P (2013) Specific in vivo labeling of tyrosinated α-tubulin and measurement of microtubule dynamics using a GFP tagged, cytoplasmically expressed recombinant antibody. PLoS ONE 8:e59812. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059812
Chauhan P, Jethwa K, Rathawa A, Chauhan G, Mehra S (2021) The anatomy of the hippocampus. In: Pluta R (ed) Cerebral ischemia. Exon Publications Brisbane
Drange OK, Smeland OB, Shadrin AA, Finseth PI, Witoelar A, Frei O, Wang Y, Hassani S, Djurovic S, Dale AM, Andreassen OA (2019) Genetic overlap between Alzheimer’s disease and bipolar disorder implicates the MARK2 and VAC14 genes. Front Neurosci 13:220. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00220
Drewes G, Ebneth A, Preuss U, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E (1997) MARK, a novel family of protein kinases that phosphorylate microtubule-associated proteins and trigger microtubule disruption. Cell 89:297–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80208-1
Erck C, Peris L, Andrieux A, Meissirel C, Gruber AD, Vernet M, Schweitzer A, Saoudi Y, Pointu H, Bosc C, Salin PA, Job D, Wehland J (2005) A vital role of tubulin-tyrosine-ligase for neuronal organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:7853–7858. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409626102
Fan G, Yuan Z, Zheng H, Liu Z (2004) Study on the effects of exposure to rare earth elements and health-responses in children aged 7–10 years. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 33:23–28
Ferraro L, Tomasini MC, Tanganelli S, Mazza R, Coluccia A, Carratù MR, Gaetani S, Cuomo V, Antonelli T (2009) Developmental exposure to methylmercury elicits early cell death in the cerebral cortex and long-term memory deficits in the rat. Int J Dev Neurosci 27:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2008.11.004
Han GC, Jing HM, Zhang WJ, Zhang N, Li ZN, Zhang GY, Gao S, Ning JY, Li GJ (2021) Effects of lanthanum nitrate on behavioral disorder, neuronal damage and gene expression in different developmental stages of Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicology 465:153012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2021.153012
Hasegawa R, Ebina T, Tanaka YR, Kobayashi K, Matsuzaki M (2020) Structural dynamics and stability of corticocortical and thalamocortical axon terminals during motor learning. PLoS ONE 15:e0234930. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0234930
Howes SC, Alushin GM, Shida T, Nachury MV, Nogales E (2014) Effects of tubulin acetylation and tubulin acetyltransferase binding on microtubule structure. Mol Biol Cell 25:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E13-07-0387
Hu X, Yang J, Sun Y, Gao X, Zhang L, Li Y, Yu M, Liu S, Lu X, Jin C, Wu S, Cai Y (2018) Lanthanum chloride impairs memory in rats by disturbing the glutamate-glutamine cycle and over-activating NMDA receptors. Food Chem Toxicol 113:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.01.023
Ichinose S, Ogawa T, Jiang X, Hirokawa N (2019) The spatiotemporal construction of the axon initial segment via KIF3/KAP3/TRIM46 transport under MARK2 signaling. Cell Rep 28:2413–2426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.093
Jin C, Gao L, Li Y, Wu S, Lu X, Yang J, Cai Y (2017) Lanthanum damages learning and memory and suppresses astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle in rat hippocampus. Exp Brain Res 235:3817–3832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-017-5102-5
Kennedy MB (2013) Synaptic signaling in learning and memory. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8:a016824. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016824
Knierim JJ (2015) The hippocampus. Curr Biol 25:R1116-1121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.10.049
Kuwako KI, Okano H (2018) Versatile roles of LKB1 kinase signaling in neural development and homeostasis. Front Mol Neurosci 11:354. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00354
Liu H, Yang J, Liu Q, Jin C, Wu S, Lu X, Zheng L, Xi Q, Cai Y (2014) Lanthanum chloride impairs spatial memory through ERK/MSK1 signaling pathway of hippocampus in rats. Neurochem Res 39:2479–2491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1452-6
Liu T, He F, Yan J, Kuang W, Yu C (2019) Icariside II affects hippocampal neuron axon regeneration and improves learning and memory in a chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rat model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 12:826–834
Lizcano JM, Göransson O, Toth R, Deak M, Morrice NA, Boudeau J, Hawley SA, Udd L, Mäkelä TP, Hardie DG, Alessi DR (2004) LKB1 is a master kinase that activates 13 kinases of the AMPK subfamily, including MARK/PAR-1. EMBO J 23:833–843. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600110
Malhotra N, Hsu HS, Liang ST, Roldan MJM, Lee JS, Ger TR, Hsiao CD (2020) An updated review of toxicity effect of the rare earth elements (REEs) on aquatic organisms. Animals (Basel) 10:1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091663
Marra P, Salvatore L, Mironov A Jr, Di Campli A, Di Tullio G, Trucco A, Beznoussenko G, Mironov A, De Matteis MA (2007) The biogenesis of the Golgi ribbon: the roles of membrane input from the ER and of GM130. Mol Biol Cell 18:1595–1608. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e06-10-0886
Matsuki T, Matthews RT, Cooper JA, van der Brug MP, Cookson MR, Hardy JA, Olson EC, Howell BW (2010) Reelin and stk25 have opposing roles in neuronal polarization and dendritic Golgi deployment. Cell 143:826–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.10.029
McRae R, Lapierre LA, Manning EH, Goldenring JR (2017) Rab11-FIP1 phosphorylation by MARK2 regulates polarity in MDCK cells. Cell Logist 7:e1271498. https://doi.org/10.1080/21592799.2016.1271498
Mehenni H, Gehrig C, Nezu J, Oku A, Shimane M, Rossier C, Guex N, Blouin JL, Scott HS, Antonarakis SE (1998) Loss of LKB1 kinase activity in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and evidence for allelic and locus heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet 63:1641–1650. https://doi.org/10.1086/302159
Mencarelli C, Nitarska J, Kroecher T, Ferraro F, Massey K, Riccio A, Pichaud F (2018) RanBP1 couples nuclear export and Golgi regulation through LKB1 to promote cortical neuron polarity. Cell Rep 24:2529–2539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.107
Milburn CC, Boudeau J, Deak M, Alessi DR, van Aalten DM (2004) Crystal structure of MO25 alpha in complex with the C terminus of the pseudo kinase STE20-related adaptor. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb716
Moss KR, Bopp TS, Johnson AE, Höke A (2021) New evidence for secondary axonal degeneration in demyelinating neuropathies. Neurosci Lett 744:135595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135595
Mukherjee A, Brooks PS, Bernard F, Guichet A, Conduit PT (2020) Microtubules originate asymmetrically at the somatic golgi and are guided via Kinesin2 to maintain polarity within neurons. Elife 9:e58943. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.58943
Muzio MR, Cascella M (2021) Histology, axon (ed). StatPearls, Treasure Island
Nakamura N, Rabouille C, Watson R, Nilsson T, Hui N, Slusarewicz P, Kreis TE, Warren G (1995) Characterization of a cis-Golgi matrix protein, GM130. J Cell Biol 131:1715–1726. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.131.6.1715
Peng RL, Pan XC, Xie Q (2003) Relationship of the hair content of rare earth elements in young children aged 0 to 3 years to that in their mothers living in a rare earth mining area of Jiangxi. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 37:20–22
Peris L, Wagenbach M, Lafanechère L, Brocard J, Moore AT, Kozielski F, Job D, Wordeman L, Andrieux A (2009) Motor-dependent microtubule disassembly driven by tubulin tyrosination. J Cell Biol 185:1159–1166. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200902142
Rao S, Kirschen GW, Szczurkowska J, Di Antonio A, Wang J, Ge S, Shelly M (2018) Repositioning of somatic Golgi apparatus is essential for the dendritic establishment of adult-born hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 38:631–647. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1217-17.2017
Saw G, Tang FR (2020) Epigenetic regulation of the hippocampus, with special reference to radiation exposure. Int J Mol Sci 21:9514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249514
Shelly M, Poo MM (2011) Role of LKB1-SAD/MARK pathway in neuronal polarization. Dev Neurobiol 71:508–527. https://doi.org/10.1002/dneu.20884
Shelly M, Cancedda L, Heilshorn S, Sumbre G, Poo MM (2007) LKB1/STRAD promotes axon initiation during neuronal polarization. Cell 129:565–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.012
Shen YA, Chen Y, Dao DQ, Mayoral SR, Wu L, Meijer D, Ullian EM, Chan JR, Lu QR (2014) Phosphorylation of LKB1/Par-4 establishes Schwann cell polarity to initiate and control myelin extent. Nat Commun 5:4991. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5991
Sleigh JN, Rossor AM, Fellows AD, Tosolini AP, Schiavo G (2019) Axonal transport and neurological disease. Nat Rev Neurol 15:691–703. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0257-2
Squire LR, Genzel L, Wixted JT, Morris RG (2015) Memory consolidation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a021766. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a021766
Sun X, Gao L, Chien HY, Li WC, Zhao J (2013) The regulation and function of the NUAK family. J Mol Endocrinol 51:R15-22. https://doi.org/10.1530/jme-13-0063
Sun W, Yang J, Hong Y, Yuan H, Wang J, Zhang Y, Lu X, Jin C, Wu S, Cai Y (2020) Lanthanum chloride impairs learning and memory and induces dendritic spine abnormality by down-regulating Rac1/PAK signaling pathway in hippocampus of offspring rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40:459–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00748-7
Tomasini MC, Beggiato S, Ferraro L, Tanganelli S, Marani L, Lorenzini L, Antonelli T (2012) Prenatal exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin produces alterations in cortical neuron development and a long-term dysfunction of glutamate transmission in rat cerebral cortex. Neurochem Int 61:759–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.07.004
Trivisano M, Specchio N (2020) What are the epileptic encephalopathies? Curr Opin Neurol 33:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1097/wco.0000000000000793
Turra C (2018) Sustainability of rare earth elements chain: from production to food—a review. Int J Environ Health Res 28:23–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2017.1415307
Vakilna YS, Tang WC, Wheeler BC, Brewer GJ (2021) The flow of axonal information among hippocampal subregions: 1. Feed-forward and feedback network spatial dynamics underpinning emergent information processing. Front Neural Circuits 15:660837. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2021.660837
Veleva-Rotse BO, Smart JL, Baas AF, Edmonds B, Zhao ZM, Brown A, Klug LR, Hansen K, Reilly G, Gardner AP, Subbiah K, Gaucher EA, Clevers H, Barnes AP (2014) STRAD pseudokinases regulate axogenesis and LKB1 stability. Neural Dev 9:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8104-9-5
Wang J, Wu T, Ma L, Guo Y, Huang Y, Zheng L (2020) Action of Akt pathway on La-induced hippocampal neuron apoptosis of rats in the growth stage. Neurotox Res 38:434–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00206-z
Yu M, Yang J, Gao X, Sun W, Liu S, Han Y, Lu X, Jin C, Wu S, Cai Y (2020) Lanthanum chloride impairs spatial learning and memory by inducing [Ca(2+)](m) overload, mitochondrial fission-fusion disorder and excessive mitophagy in hippocampal nerve cells of rats. Metallomics 12:592–606. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9mt00291j
Zeqiraj E, Filippi BM, Deak M, Alessi DR, van Aalten DM (2009) Structure of the LKB1-STRAD-MO25 complex reveals an allosteric mechanism of kinase activation. Science 326:1707–1711. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1178377
Zheng L, Yang J, Liu Q, Yu F, Wu S, Jin C, Lu X, Zhang L, Du Y, Xi Q, Cai Y (2013) Lanthanum chloride impairs spatial learning and memory and downregulates NF-κB signalling pathway in rats. Arch Toxicol 87:2105–2117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1076-7
Zhu W, Xu S, Zhang H, Shao P, Wu D, Yang W, Feng J (1996) Investigation of children intelligence quotient in REE mining area: bio-effect study of REE mining area in South Jiangxi. Chin Sci Bull 41:914–916
Zuo YC, Xiong NX, Shen JY, Yu H, Huang YZ, Zhao HY (2016) MARK2 rescues Nogo-66-induced inhibition of neurite outgrowth via regulating microtubule-associated proteins in neurons in vitro. Neurochem Res 41:2958–2968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2016-8
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81773469).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JY was responsible for the experimental design and revised the paper. ZS performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. HM, JL and WS created the models. SW, XL and CJ provided technical support.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Fig. 6 has been updated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Mao, H., Liu, J. et al. Lanthanum Chloride Induces Axon Abnormality Through LKB1-MARK2 and LKB1-STK25-GM130 Signaling Pathways. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 1181–1196 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01237-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01237-0