Abstract
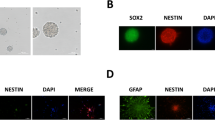
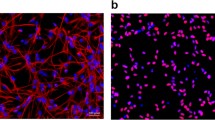
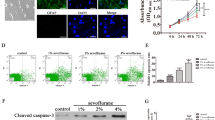
With the increase in fetal surgeries, the effect of maternal anesthesia on progeny has attracted much attention. Our previous studies have demonstrated that 3.5% sevoflurane maternal exposure resulted in over-activated autophagy and cognitive impairment in the offspring. The autophagy activation resulted in increased apoptosis and decreased proliferation. However, the effects of sevoflurane on neural stem cell (NSC) differentiation is unclear. There is evidence that autophagy might participate in anesthesia-induced NSC differentiation. Firstly, we examined the effects of sevoflurane on NSC differentiation and explored possible mechanisms. Then, we investigated whether autophagy was related to differentiation. On gestational day 14 (G14), rats were exposed to 2% or 3.5% sevoflurane for 2 h, then markers of neurons and astrocytes, and the FOXO3 expression was measured in fetal brains 48 h later. The differentiation of NSCs was detected after autophagy inhibition by 3-MA. Changes in NSC differentiation, autophagy level, and FOXO3 were examined after administration of lithium chloride. After 3.5% sevoflurane exposure, the expressions of β-Tubulin III, NeuN, SYP, GFAP and FOXO3 increased. Autophagy inhibition alleviates improper NSC differentiation. Lithium chloride attenuated FOXO3 and autophagy activation, ameliorated NSC differentiation and the decline of Nestin expression. Our results demonstrated that maternal exposure to 3.5% sevoflurane for 2 h during the mid-trimester induced NSC differentiation in the fetal brain through the activation of FOXO3. Autophagy inhibitor or lithium chloride reversed the improper differentiation of NSCs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu M, Aguado D, Benito J, Gomez de Segura IA (2012) Reduction of the sevoflurane minimum alveolar concentration induced by methadone, tramadol, butorphanol and morphine in rats. Lab Anim 46(3):200–206
Asanuma K, Tanida I, Shirato I, Ueno T, Takahara H, Nishitani T, Kominami E, Tomino Y (2003) MAP-LC3, a promising autophagosomal marker, is processed during the differentiation and recovery of podocytes from PAN nephrosis. FASEB J 17(9):1165–1167
Audesse AJ, Dhakal S, Hassell LA, Gardell Z, Nemtsova Y, Webb AE (2019) FOXO3 directly regulates an autophagy network to functionally regulate proteostasis in adult neural stem cells. PLoS Genet 15(4):e1008097
Boya P, Mellen MA, de la Rosa EJ (2008) How autophagy is related to programmed cell death during the development of the nervous system. Biochem Soc Trans 36:813–817
Burgering BM, Kops GJ (2002) Cell cycle and death control: long live Forkheads. Trends Biochem Sci 27(7):352–360
Caballero-Caballero A, Engel T, Martinez-Villarreal J, Sanz-Rodriguez A, Chang P, Dunleavy M, Mooney CM, Jimenez-Mateos EM, Schindler CK, Henshall DC (2013) Mitochondrial localization of the forkhead box class O transcription factor FOXO3a in brain. J Neurochem 124(6):749–756
Dong P, Zhang X, Zhao J, Li D, Li L, Yang B (2018) Anti-microRNA-132 causes sevofluraneinduced neuronal apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/FOXO3a pathway. Int J Mol Med 42(6):3238–3246
Fang F, Xue Z, Cang J (2012) Sevoflurane exposure in 7-day-old rats affects neurogenesis, neurodegeneration and neurocognitive function. Neurosci Bull 28(5):499–508
Filomeni G, De Zio D, Cecconi F (2015) Oxidative stress and autophagy: the clash between damage and metabolic needs. Cell Death Differ 22(3):377–388
Furuyama T, Nakazawa T, Nakano I, Mori N (2000) Identification of the differential distribution patterns of mRNAs and consensus binding sequences for mouse DAF-16 homologues. Biochem J 349(Pt 2):629–634
Greer EL, Brunet A (2005) FOXO transcription factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression. Oncogene 24(50):7410–7425
Heras-Sandoval D, Perez-Rojas JM, Hernandez-Damian J, Pedraza-Chaverri J (2014) The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cell Signal 26(12):2694–2701
Hoekman MF, Jacobs FM, Smidt MP, Burbach JP (2006) Spatial and temporal expression of FoxO transcription factors in the developing and adult murine brain. Gene Expr Patterns 6(2):134–140
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y, Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorumski CF, Olney JW, Wozniak DF (2003) Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. J Neurosci 23(3):876–882
Lee JW, Nam H, Kim LE, Jeon Y, Min H, Ha S, Lee Y, Kim SY, Lee SJ, Kim EK, Yu SW (2019) TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) activation suppresses autophagy through inhibition of FOXO3 and impairs phagocytic capacity of microglia. Autophagy 15(5):753–770
Li G, Yu B (2014) Elevation of protective autophagy as a potential way for preventing developmental neurotoxicity of general anesthetics. Med Hypotheses 82(2):177–180
Li Q, Li H, Roughton K, Wang X, Kroemer G, Blomgren K, Zhu C (2010) Lithium reduces apoptosis and autophagy after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Cell Death Dis 1:e56
Li X, Wu Z, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Han G, Zhao P (2017) Activation of autophagy contributes to sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in fetal rats. Front Mol Neurosci 10:432
Mao Z, Liu L, Zhang R, Li X (2007) Lithium reduces FoxO3a transcriptional activity by decreasing its intracellular content. Biol Psychiatry 62(12):1423–1430
Miyamoto K, Araki KY, Naka K, Arai F, Takubo K, Yamazaki S, Matsuoka S, Miyamoto T, Ito K, Ohmura M, Chen C, Hosokawa K, Nakauchi H, Nakayama K, Nakayama KI, Harada M, Motoyama N, Suda T, Hirao A (2007) Foxo3a is essential for maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool. Cell Stem Cell 1(1):101–112
Paik JH, Ding Z, Narurkar R, Ramkissoon S, Muller F, Kamoun WS, Chae SS, Zheng H, Ying H, Mahoney J, Hiller D, Jiang S, Protopopov A, Wong WH, Chin L, Ligon KL, DePinho RA (2009) FoxOs cooperatively regulate diverse pathways governing neural stem cell homeostasis. Cell Stem Cell 5(5):540–553
Palanisamy A (2012) Maternal anesthesia and fetal neurodevelopment. Int J Obstet Anesth 21(2):152–162
Pan H, Cai N, Li M, Liu GH, Izpisua Belmonte JC (2013) Autophagic control of cell “stemness.” EMBO Mol Med 5(3):327–331
Perna RB, Loughan AR, Le JA, Hertza J (2015) Prenatal and perinatal anesthesia and the long-term cognitive sequelae: a review. Appl Neuropsychol Child 4(1):65–71
Qian X, Shen Q, Goderie SK, He W, Capela A, Davis AA, Temple S (2000) Timing of CNS cell generation: a programmed sequence of neuron and glial cell production from isolated murine cortical stem cells. Neuron 28(1):69–80
Renault VM, Rafalski VA, Morgan AA, Salih DA, Brett JO, Webb AE, Villeda SA, Thekkat PU, Guillerey C, Denko NC, Palmer TD, Butte AJ, Brunet A (2009) FoxO3 regulates neural stem cell homeostasis. Cell Stem Cell 5(5):527–539
Salih DA, Brunet A (2008) FoxO transcription factors in the maintenance of cellular homeostasis during aging. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20(2):126–136
Sanes DH, Reh TA, Harris WA (2006) Development of the nervous system. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Schmidt-Strassburger U, Schips TG, Maier HJ, Kloiber K, Mannella F, Braunstein KE, Holzmann K, Ushmorov A, Liebau S, Boeckers TM, Wirth T (2012) Expression of constitutively active FoxO3 in murine forebrain leads to a loss of neural progenitors. FASEB J 26(12):4990–5001
Sengupta A, Molkentin JD, Yutzey KE (2009) FoxO transcription factors promote autophagy in cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem 284(41):28319–28331
van der Vos KE, Eliasson P, Proikas-Cezanne T, Vervoort SJ, van Boxtel R, Putker M, van Zutphen IJ, Mauthe M, Zellmer S, Pals C, Verhagen LP, Groot Koerkamp MJ, Braat AK, Dansen TB, Holstege FC, Gebhardt R, Burgering BM, Coffer PJ (2012) Modulation of glutamine metabolism by the PI(3)K-PKB-FOXO network regulates autophagy. Nat Cell Biol 14(8):829–837
Vazquez P, Arroba AI, Cecconi F, de la Rosa EJ, Boya P, de Pablo F (2012) Atg5 and Ambra1 differentially modulate neurogenesis in neural stem cells. Autophagy 8(2):187–199
Wang H, Ma J, Tan Y, Wang Z, Sheng C, Chen S, Ding J (2010) Amyloid-beta1-42 induces reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagic cell death in U87 and SH-SY5Y cells. J Alzheimers Dis 21(2):597–610
Wang Y, Tian C, Zheng JC (2013) FoxO3a contributes to the reprogramming process and the differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 22(22):2954–2963
Wang Y, Yin S, Xue H, Yang Y, Zhang N, Zhao P (2018) Mid-gestational sevoflurane exposure inhibits fetal neural stem cell proliferation and impairs postnatal learning and memory function in a dose-dependent manner. Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.01.022
Warner DO, Zaccariello MJ, Katusic SK, Schroeder DR, Hanson AC, Schulte PJ, Buenvenida SL, Gleich SJ, Wilder RT, Sprung J, Hu D, Voigt RG, Paule MG, Chelonis JJ, Flick RP (2018) Neuropsychological and behavioral outcomes after exposure of young children to procedures requiring general anesthesia: The Mayo Anesthesia Safety in Kids (MASK) study. Anesthesiology 129(1):89–105
Webb AE, Brunet A (2014) FOXO transcription factors: key regulators of cellular quality control. Trends Biochem Sci 39(4):159–169
Woodward TJ, Timic Stamenic T, Todorovic SM (2019) Neonatal general anesthesia causes lasting alterations in excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission in the ventrobasal thalamus of adolescent female rats. Neurobiol Dis 127:472–481
Yalcin S, Marinkovic D, Mungamuri SK, Zhang X, Tong W, Sellers R, Ghaffari S (2010) ROS-mediated amplification of AKT/mTOR signalling pathway leads to myeloproliferative syndrome in Foxo3(-/-) mice. EMBO J 29(24):4118–4131
Zhang DX, Jiang S, Yu LN, Zhang FJ, Zhuang Q, Yan M (2015) The effect of sevoflurane on the cognitive function of rats and its association with the inhibition of synaptic transmission. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(11):20853–20860
Zhao Y, Huang Q, Yang J, Lou M, Wang A, Dong J, Qin Z, Zhang T (2010) Autophagy impairment inhibits differentiation of glioma stem/progenitor cells. Brain Res 1313:250–258
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Numbers 81870838; Liaoning Province Distinguished Professor Support Program [Grant Numbers XLYC1802096]; Shenyang Clinical Medicine Research Center of Anesthesiology [Grant Numbers 19-110-4-24, 20-204-4-44]; Outstanding Scientific Fund of Shengjing Hospital [Grant Number 201708].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL: study conception and design, experimental operation, data analysis, and writing-original draft. XJ: experimental operation and data collection. QG: writing-reviewing and editing. PZ: supervision and guidance.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No author claims competing interests or relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Jiang, X., Gao, Q. et al. FOXO3 Regulates Sevoflurane-Induced Neural Stem Cell Differentiation in Fetal Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 1777–1786 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01055-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01055-w