Abstract
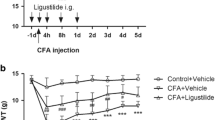
Ligustilide is a major component of Radix Angelica Sinensis and reported to have anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) has been shown to be expressed in the spinal cord and be involved in inflammatory pain and neuropathic pain. Whether ligustilide can inhibit spinal TLR4 expression in inflammatory pain is still unknown. In the present study, we intravenously injected ligustilide daily for 4 days, with the first injection given at 1 h before complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) injection. We tested the analgesic effect of ligustilide by behavioral test and checked the expression and distribution of TLR4 in the spinal cord by real-time quantitative PCR, Western blot, and immunofluorescence. Our data showed that repeated daily intravenous treatment with ligustilide alleviated CFA-induced heat hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia. The same treatment also inhibited CFA-induced TLR4 mRNA and protein increase in the spinal cord. Immunofluorescence double staining showed that TLR4 was predominantly expressed in spinal astrocytes. In primary cultured astrocytes, ligustilide dose-dependently reduced lipopolysaccharide-induced upregulation of TLR4 mRNA expression. These data indicate that ligustilide treatment reduces TLR4 expression in spinal astrocytes and is an effective therapy for inflammatory pain.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- CFA:
-
Complete Freund’s adjuvant
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- qPCR:
-
Real-time quantitative PCR
References
Bettoni I, Comelli F, Rossini C, Granucci F, Giagnoni G, Peri F, Costa B (2008) Glial TLR4 receptor as new target to treat neuropathic pain: efficacy of a new receptor antagonist in a model of peripheral nerve injury in mice. Glia 56(12):1312–1319
Cao H, Zhang YQ (2008) Spinal glial activation contributes to pathological pain states. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32(5):972–983
Casula M, Iyer AM, Spliet WG, Anink JJ, Steentjes K, Sta M, Troost D, Aronica E (2011) Toll-like receptor signaling in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord tissue. Neuroscience 179:233–243
Dixon WJ (1980) Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:441–462
Du J, Yu Y, Ke Y, Wang C, Zhu L, Qian ZM (2007) Ligustilide attenuates pain behavior induced by acetic acid or formalin. J Ethnopharmacol 112(1):211–214
Feng Z, Lu Y, Wu X, Zhao P, Li J, Peng B, Qian Z, Zhu L (2012) Ligustilide alleviates brain damage and improves cognitive function in rats of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J Ethnopharmacol 144(2):313–321
Gao YJ, Ji RR (2010) Targeting astrocyte signaling for chronic pain. Neurotherapeutics 7(4):482–493
Gao YJ, Zhang L, Samad OA, Suter MR, Yasuhiko K, Xu ZZ, Park JY, Lind AL, Ma Q, Ji RR (2009) JNK-induced MCP-1 production in spinal cord astrocytes contributes to central sensitization and neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 29(13):4096–4108
Gao YJ, Xu ZZ, Liu YC, Wen YR, Decosterd I, Ji RR (2010) The c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in spinal astrocytes is required for the maintenance of bilateral mechanical allodynia under a persistent inflammatory pain condition. Pain 148(2):309–319
Gosselin RD, Suter MR, Ji RR, Decosterd I (2010) Glial cells and chronic pain. Neuroscientist 16(5):519–531
Ji RR, Berta T, Nedergaard M (2013) Glia and pain: is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain 154:S10–S28
Kuang X, Wang LF, Yu L, Li YJ, Wang YN, He Q, Chen C, Du JR (2014) Ligustilide ameliorates neuroinflammation and brain injury in focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats: involvement of inhibition of TLR4/peroxiredoxin 6 signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 71:165–175
Lehnardt S, Lachance C, Patrizi S, Lefebvre S, Follett PL, Jensen FE, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ, Vartanian T (2002) The toll-like receptor TLR4 is necessary for lipopolysaccharide-induced oligodendrocyte injury in the CNS. J Neurosci 22(7):2478–2486
Lehnardt S, Massillon L, Follett P, Jensen FE, Ratan R, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ, Vartanian T (2003) Activation of innate immunity in the CNS triggers neurodegeneration through a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(14):8514–8519
Li Y, Zhang H, Kosturakis AK, Jawad AB, Dougherty PM (2014) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling contributes to paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Pain 15(7):712–725
Liu J, Burdette JE, Xu H, Gu C, van Breemen RB, Bhat KP, Booth N, Constantinou AI, Pezzuto JM, Fong HH et al (2001) Evaluation of estrogenic activity of plant extracts for the potential treatment of menopausal symptoms. J Agric Food Chem 49(5):2472–2479
Mika J, Zychowska M, Popiolek-Barczyk K, Rojewska E, Przewlocka B (2013) Importance of glial activation in neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 716:106–119
Miyoshi K, Obata K, Kondo T, Okamura H, Noguchi K (2008) Interleukin-18-mediated microglia/astrocyte interaction in the spinal cord enhances neuropathic pain processing after nerve injury. J Neurosci 28(48):12775–12787
Nakagawa T, Kaneko S (2010) Spinal astrocytes as therapeutic targets for pathological pain. J Pharmacol Sci 114(4):347–353
Peng HY, Du JR, Zhang GY, Kuang X, Liu YX, Qian ZM, Wang CY (2007) Neuroprotective effect of Z-ligustilide against permanent focal ischemic damage in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 30(2):309–312
Peng B, Zhao P, Lu YP, Chen MM, Sun H, Wu XM, Zhu L (2013) Z-ligustilide activates the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Brain Res 1520:168–177
Ren K, Dubner R (2008) Neuron-glia crosstalk gets serious: role in pain hypersensitivity. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 21(5):570–579
Sorge RE, LaCroix-Fralish ML, Tuttle AH, Sotocinal SG, Austin JS, Ritchie J, Chanda ML, Graham AC, Topham L, Beggs S et al (2011) Spinal cord Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory and neuropathic hypersensitivity in male but not female mice. J Neurosci 31(43):15450–15454
Su YW, Chiou WF, Chao SH, Lee MH, Chen CC, Tsai YC (2011) Ligustilide prevents LPS-induced iNOS expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages by preventing ROS production and down-regulating the MAPK, NF-kappaB and AP-1 signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 11(9):1166–1172
Tanga FY, Nutile-McMenemy N, DeLeo JA (2005) The CNS role of Toll-like receptor 4 in innate neuroimmunity and painful neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(16):5856–5861
Vallejo R, Tilley DM, Vogel L, Benyamin R (2010) The role of glia and the immune system in the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain. Pain Pract 10(3):167–184
van Noort JM, Bsibsi M (2009) Toll-like receptors in the CNS: implications for neurodegeneration and repair. Prog Brain Res 175:139–148
Wang J, Du JR, Wang Y, Kuang X, Wang CY (2010) Z-ligustilide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory response via inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway in primary rat microglia. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31(7):791–797
Watkins LR, Hutchinson MR, Milligan ED, Maier SF (2007) “Listening” and “talking” to neurons: implications of immune activation for pain control and increasing the efficacy of opioids. Brain Res Rev 56(1):148–169
White FA, Wilson NM (2008) Chemokines as pain mediators and modulators. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 21(5):580–585
Wieseler-Frank J, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2004) Glial activation and pathological pain. Neurochem Int 45(2–3):389–395
Wu XM, Qian ZM, Zhu L, Du F, Yung WH, Gong Q, Ke Y (2011) Neuroprotective effect of ligustilide against ischaemia-reperfusion injury via up-regulation of erythropoietin and down-regulation of RTP801. Br J Pharmacol 164(2):332–343
Yim TK, Wu WK, Pak WF, Mak DH, Liang SM, Ko KM (2000) Myocardial protection against ischaemia-reperfusion injury by a Polygonum multiflorum extract supplemented ‘Dang-Gui decoction for enriching blood’, a compound formulation, ex vivo. Phytother Res 14(3):195–199
Zhao LX, Jiang BC, Wu XB, Cao DL, Gao YJ (2014) Ligustilide attenuates inflammatory pain via inhibition of NFkappaB-mediated chemokines production in spinal astrocytes. Eur J Neurosci 39(8):1391–1402
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, B., Li, F., Zhao, LX. et al. Ligustilide Ameliorates Inflammatory Pain and Inhibits TLR4 Upregulation in Spinal Astrocytes Following Complete Freund’s Adjuvant Peripheral Injection. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36, 143–149 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0228-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0228-0