Abstract
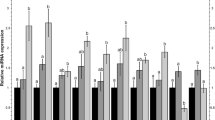
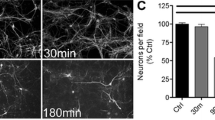
The mechanism of sevoflurane preconditioning-induced neuroprotection is poorly understood. This study was aimed at identifying microRNAs (miRNAs) involved in the protective effect of sevoflurane preconditioning against hypoxic injury using the miRCURYTM LNA Array. The screened differentially expressed miRNAs were further validated using qRT-PCR. Finally, after transfection of miRNA (miR-101a or miR-34b) mimics or inhibitor, MTT and flow cytometry assays were used to evaluate cell survival and apoptosis in sevoflurane preconditioning. qRT-PCR confirmed the changes in expression of differentially expressed miRNAs that were screened by the microarray: down-regulation of rno-miR-101a, rno-miR-106b, and rno-miR-294 and up-regulation of rno-miR-883, rno-miR-16, and rno-miR-34b. MiR-101a and miR-34b were the most differentially expressed miRNAs. Sevoflurane preconditioning-inhibited apoptosis and preconditioning-enhanced cell viability of PC12 cells were significantly attenuated by transfection of miR-101a mimetic or miR-34b inhibitors, but were significantly enhanced by transfection of miR-34b mimetic. Therefore, a number of miRNAs, including miR-101a and miR-34b, might play important roles in the neuroprotection induced by sevoflurane preconditioning. Such miRNAs might provide novel targets for preventive and therapeutic strategies against cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Beitner-Johnson D, Rust RT, Hsieh T, Millhorn DE (2000) Regulation of CREB by moderate hypoxia in PC12 cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 475:143–152
Boutros A, Wang J, Capuano C (1997) Isoflurane and halothane increase adenosine triphosphate preservation, but do not provide additive recovery of function after ischemia, in preconditioned rat hearts. Anesthesiology 86:109–117
Clarkson AN (2007) Anesthetic-mediated protection/preconditioning during cerebral ischemia. Life Sci 80:1157–1175
Codaccioni JL, Velly LJ, Moubarik C, Bruder NJ, Pisano PS, Guillet BA (2009) Sevoflurane preconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia: inhibition of apoptosis in the face of transient improvement of neurological outcome. Anesthesiology 110:1271–1278
Cope DK, Impastato WK, Cohen MV, Downey JM (1997) Volatile anesthetics protect the ischemic rabbit myocardium from infarction. Anesthesiology 86:699–709
Das KP, Freudenrich TM, Mundy WR (2004) Assessment of PC12 cell differentiation and neurite growth: a comparison of morphological and neurochemical measures. Neurotoxicol Teratol 26:397–406
Gozal E, Sachleben LR Jr, Rane MJ, Vega C, Gozal D (2005) Mild sustained and intermittent hypoxia induce apoptosis in PC-12 cells via different mechanisms. Am J Physiol 288:C535–542
Heiss WD, Graf R (1994) The ischemic penumbra. Curr Opin Neurol 7:11–19
Hermeking H (2010) The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 17:193–199
Hu K, Xie YY, Zhang C, Ouyang DS, Long HY, Sun DN et al (2012) MicroRNA expression profile of the hippocampus in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy and miR-34a-targeted neuroprotection against hippocampal neurone cell apoptosis post-status epilepticus. BMC Neurosci 13:115
Kamiya T, Kwon AH, Kanemaki T, Matsui Y, Uetsuji S, Okumura T, Kamiyama Y (1998) A simplified model of hypoxic injury in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 34:131–137
Kaneko T, Yokoyama K, Makita K (2005) Late preconditioning with isoflurane in cultured rat cortical neurones. Br J Anaesth 95:662–668
Kawaguchi M, Drummond JC, Cole DJ, Kelly PJ, Spurlock MP, Patel PM (2004) Effect of isoflurane on neuronal apoptosis in rats subjected to focal cerebral ischemia. Anesth Analg 98:798–805
Kitano H, Kirsch JR, Hurn PD, Murphy SJ (2007) Inhalational anesthetics as neuroprotectants or chemical preconditioning agents in ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1108–1128
Kosik KS (2006) The neuronal microRNA system. Nat Rev 7:911–920
Lehane C, Guelzow T, Zenker S, Erxleben A, Schwer CI, Heimrich B et al (2013) Carbimazole is an inhibitor of protein synthesis and protects from neuronal hypoxic damage in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 347:781–793
Li X, Luo P, Wang F, Yang Q, Li Y, Zhao M et al (2014) Inhibition of N-myc downstream-regulated gene-2 is involved in an astrocyte-specific neuroprotection induced by sevoflurane preconditioning. Anesthesiology 121:549–562
Liu Z, Yang D, Xie P, Ren G, Sun G, Zeng X, Sun X (2012) MiR-106b and MiR-15b modulate apoptosis and angiogenesis in myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem 29:851–862
Pompili M, Venturini P, Campi S, Seretti ME, Montebovi F, Lamis DA et al (2012) Do stroke patients have an increased risk of developing suicidal ideation or dying by suicide? An overview of the current literature. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:711–721
Serafini G, Pompili M, Innamorati M, Giordano G, Montebovi F, Sher L et al (2012) The role of microRNAs in synaptic plasticity, major affective disorders and suicidal behavior. Neurosci Res 73:179–190
Shukla GC, Singh J, Barik S (2011) MicroRNAs: processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol 3:83–92
Toner CC, Connelly K, Whelpton R, Bains S, Michael-Titus AT, McLaughlin DP, Stamford JA (2001) Effects of sevoflurane on dopamine, glutamate and aspartate release in an in vitro model of cerebral ischaemia. Br J Anaesth 86:550–554
Wang H, Lu S, Yu Q, Liang W, Gao H, Li P et al (2011) Sevoflurane preconditioning confers neuroprotection via anti-inflammatory effects. Front Biosci 3:604–615
Wang L, Li L, Guo R, Li X, Lu Y, Guan X et al (2014) miR-101 promotes breast cancer cell apoptosis by targeting Janus kinase 2. Cell Physiol Biochem 34:413–422
Wolf PA (1998) Prevention of stroke. Lancet 352(Suppl 3):SIII15–18
Xu Y, An Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Zhang H, Huang C et al (2013) miR-101 inhibits autophagy and enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 29:2019–2024
Yang Q, Dong H, Deng J, Wang Q, Ye R, Li X et al (2011) Sevoflurane preconditioning induces neuroprotection through reactive oxygen species-mediated up-regulation of antioxidant enzymes in rats. Anesth Analg 112:931–937
Yang Q, Yan W, Li X, Hou L, Dong H, Wang Q et al (2012) Activation of canonical notch signaling pathway is involved in the ischemic tolerance induced by sevoflurane preconditioning in mice. Anesthesiology 117:996–1005
Yellon DM, Dana A (2000) The preconditioning phenomenon: a tool for the scientist or a clinical reality? Circ Res 87:543–550
Zhong X, Lin R, Li Z, Mao J, Chen L (2014) Effects of Salidroside on cobalt chloride-induced hypoxia damage and mTOR signaling repression in PC12 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 37:1199–1206
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript.
Ethical standards
No Human Participants and/or Animals were involved in this research, and we have read and have abided by the statement of ethical standards for manuscript submitted to Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Li, Y., Liu, L. et al. Identification of miRNAs Involved in the Protective Effect of Sevoflurane Preconditioning Against Hypoxic Injury in PC12 Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 1117–1125 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0205-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0205-7