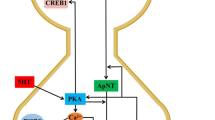
Abstract
The role of kinesin and dynein microtubule-associated molecular motors in the cellular mechanism of depression of acetylcholine-induced inward chloride current (ACh-current) was examined in command neurons of land snails (Helix lucorum) in response to repeated applications of ACh to neuronal soma. This pharmacological stimulation imitated the protocol of tactile stimulation evoking behavioural habituation of the defensive reaction. In this system, a dynein inhibitor (erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)adenine, 50 µM) decreased the ACh-current depression rate. Kinesin Eg5 inhibitors (Eg5 inhibitor III, 10 µM and Eg5 inhibitor V, trans-24, 15 µM) reduced the degree of current depression, and Eg5 inhibitor V also reduced the initial rate of depression. The results of electrophysiological experiments in combination with mathematical modelling provided evidence of the participation of dyneins and kinesin Eg5 proteins in the radial transport of acetylcholine receptors in command neurons of H. lucorum in the cellular analogue of habituation. Furthermore, these results suggest that the reciprocal interaction between dynein and kinesin proteins located on the same vesicle can lead to reverse their usual direction of transport (dyneins—in exocytosis and kinesin Eg5—in endocytosis).





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACh:
-
Acetylcholine
- AChR:
-
Acetylcholine receptor
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- cGMP:
-
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- EHNA:
-
Erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)-adenine
- GPK2:
-
G-Protein kinase 2
- MTOC:
-
Microtubule organising centre
- PDE2:
-
Phosphodiesterase 2
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- PKG:
-
Protein kinase G
References
Abramova MS, Makhnovskii DA, Pivovarov AS (2007) Role of cholinoceptors recycling in short-term potentiation of cholinosensitivity of command neurons in edible snail. Bull Exp Biol Med 144:276–279
Ali MY, Lu H, Bookwalter CS, Warshaw DM, Trybus KM (2008) Myosin V and kinesin act as tethers to enhance each others’ processivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:4691–4696. doi:10.1073/pnas.0711531105
Ally S, Larson AG, Barlan K, Rice SE, Gelfard VI (2009) Opposite-polarity motors activate one another to trigger cargo transport in live cells. J Cell Biol 187:1071–1082. doi:10.1083/jcb.200908075
Barkus RV, Klyachko O, Horiuchi D, Dickson BJ, Saxton WM (2008) Identification of an axonal kinesin-3 motor for fast anterograde vesicle transport that facilitates retrograde transport of neuropeptides. Mol Biol Cell 19:274–283. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-03-0261
Collingridge GL, Isaac JT, Wang YT (2004) Receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:952–962
Gerson-Gurwitz A, Thiede C, Movshovich N, Fridman V, Podolskaya M, Danieli T, Lakämper S, Klopfenstein DR, Schmidt CF, Gheber L (2011) Directionality of individual kinesin-5 Cin8 motors is modulated by loop 8, ionic strength and microtubule geometry. EMBO J 30:4942–4954. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.403
Goldstein LSB, Yang Z (2000) Microtubule-based transport systems in neurons: the roles of kinesins and dyneins. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:39–71. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.23.1.39
Hepp R, Tricoire L, Hu E, Gervasi N, Paupardin-Tritsch D, Lambolez B, Vincent P (2007) Phosphodiesterase type 2 and the homeostasis of cyclic GMP in living thalamic neurons. J Neurochem 102:1875–1886
Holzbaur EL, Goldman YE (2010) Coordination of molecular motors: from in vitro assays to intracellular dynamics. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:4–13. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.12.014
Hoogenraad CC, Bradke F (2009) Control of neuronal polarity and plasticity–a renaissance for microtubules? Trends Cell Biol 19:669–676. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2009.08.006
Ierusalimskii VN, Zakharov IS, Palikhova TA, Balaban PM (1992) The nervous system and the mapping of the neurons in the gastropod Helix lucorum L. Zh Vyssh Nervn Deiat Im IP Pavlova 42:1075–1089
Kimura N, Okabayashi S, Ono F (2012) Dynein dysfunction disrupts intracellular vesicle trafficking bidirectionally and perturbs synaptic vesicle docking via endocytic disturbances. Am J Pathol 180:550–561. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.037
Lee MC, Cahill CM, Vincent JP, Beaudet A (2002) Internalization and trafficking of opioid receptor ligands in rat cortical neurons. Synapse 43:102–111
Lin DT, Fretier P, Jiang C, Vincent SR (2010) Nitric oxide signaling via cGMP-stimulated phosphodiesterase in striatal neurons. Synapse 64:460–466. doi:10.1002/syn.20750
Lux HD, Veselovsky NS (1994) Glutamate-produced long-term potentiation by selective challenge of presynaptic neurons in rat hippocampal cultures. Neurosci Lett 178:231–234
Makhnovskii DA, Tretyakova MS, Murzina GB, Pivovarov AS (2010) Endocytosis of cholinoreceptors in the mechanism of depression of cholinosensitivity in Helix lucorum neurons in a cellular model of habituation. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 60:206–216
Makhnovskii DA, Murzina GB, Tret’iakova MS, Pivovarov AS (2011) The role of serine/threonine and tyrosine protein kinases in the depression of cholinosensitivity Helix lucorum neurons in the cellular correlate of habituation. ZhVyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 61:459–475
Makhnovskiy DA, Murzina GB, Pivovarov AS (2012) Cholinergic receptor exocytosis under conditions of depression of acetylcholine-induced current in edible snail neurons in cellular analogue of habituation. Bull Exp Biol Med 153:424–427. doi:10.1007/s10517-012-1731-7
Minton K (2014) Molecular motors: hook-ing up early endosomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:297. doi:10.1038/nrm3795
Mizuno N, Toba S, Edamatsu M, Watai-Nishii J, Hirokawa N, Toyoshima YY, Kikkawa M (2004) Dynein and kinesin share an overlapping microtubule-binding site. EMBO J 23:2459–2467. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600240
Moskvitin AA, Pivovarov AS (2004) An apparatus for recording defensive responses to tactile stimulation in the ground snail. Neurosci Behav Physiol 34:323–326
Nistratova VL, Pivovarov AS (2004) Inositoltriphosphate receptors and ryanodine receptors in regulation of cholinosensitivity of Helix lucorum neurones by Na, K-pump during habituation. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 54:554–564
Palikhova TA, Abramova MS, Pivovarov AS (2006) Cholinergic sensory inputs to command neurons in edible snail. Bull Exp Biol Med 142:275–278
Pavin N, Tolirc-Nørrelykke IM (2013) Dynein, microtubule and cargo: a ménage à trois. Biochem Soc Trans 41:1731–1736. doi:10.1042/BST20130235
Pivovarov AS (1992) Cholinoreceptors of Helix lucorum neurons: their identification and plasticity and its regulation by opioids and second messengers. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 42:1271–1286
Pivovarov AS (1995) Regulation of neuron cholinoreceptor plasticity of Helix lucorum by second messengers and opioids. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 110:229–240
Pivovarov AS (2001) Participation of second messengers in decrease of cholinosensitivity of command Helix neurones in cellular model of habituation. Modulatory effects of opioids. In: Ayrapetyan SN, North ACT (eds) Modern problems of cellular and molecular biophysics. Yerevan, Noyan Tapan, pp 69–81
Pivovarov AS, Drozdova EI (1992) Identification of cholinoreceptors on the soma of RPa3 and LPa3 neurons in Helix lucorum. Neurofiziologiia 24:77–86
Pivovarov AS, Murzina GB, Makhnovsky DA, Tret’yakova MS, Vasil’yeva NA (2013) Mobility of acetylcholine receptors in command Helix lucorum neurons in a cellular analog of habituation. Invert Neurosci 13:135–150. doi:10.1007/s10158-013-0155-z
Puthanveettil SV, Monje FJ, Miniaci MC, Choi YB, Karl KA, Khandros E, Gawinowicz MA, Sheetz MP, Kandel ER (2008) A new component in synaptic plasticity: upregulation of kinesin in the neurons of the gill-withdrawal reflex. Cell 135:960–973. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.003
Rankin CH, Abrams T, Barry RJ, Bhatnagar S, Clayton DF, Colombo J, Coppola G, Geyer MA, Glanzman DL, Marsland S, McSweeney FK, Wilson DA, Wu C-F, Thompson RF (2009) Habituation revisited: an updated and revised description of the behavioral characteristics of habituation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 92:135–138. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2008.09.012
Ratushniak AS, Zapara TA, Zharkikh AA, Ratushniak OA (1996) The effect of changes in the dynamic equilibrium in the microtubular and microfilamentous systems on neuronal plastic reactions. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 46:355–362
Rodionov V, Yi J, Kashina A, Oladipo A, Gross SP (2003) Switching between microtubule- and actin-based transport systems in melanophores is controlled by cAMP levels. Curr Biol 13:1837–1847
Roostalu J, Hentrich C, Bieling P, Telley IA, Schiebel E, Surrey T (2011) Directional switching of the kinesin Cin8 through motor coupling. Science 332:94–99. doi:10.1126/science.1199945
Schlager MA, Hoogenraad CC (2009) Basic mechanisms for recognition and transport of synaptic cargos. Mol Brain 2:25. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-2-25
Schrofner S, Zsombok A, Hermann A, Kerschbaum HH (2004) Nitric oxide decreases a calcium-activated potassium current via activation of phosphodiesterase 2 in Helix U-Cells. Brain Res 999:98–105
Shahpasand K, Ahmadian S, Riazi GH (2008) A possible mechanism for controlling processive transport by microtubule-associated proteins. Neurosci Res 61:347–350. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2008.04.010
Ter-Markaryan AG, Palikhova TA, Sokolov EN (1991) Effect of atropine and d-tubocurarine on the monosynaptic connections between identified neurons in the central nervous system of the edible snail. Neurosci Behav Physiol 21:37–38. doi:10.1007/BF01184236
Tiedge H, Bloom FE, Richter D (2001) Molecular kinesis in cellular function and plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:6997–6998
Tsien JZ (2000) Linking Hebb’s coincidence-detection to memory formation. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10:266–273
Wakana Y, Villeneuve J, van Galen J, Cruz-Garcia D, Tagaya M, Malhotra V (2013) Kinesin-5/Eg5 is important for transport of CARTS from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface. J Cell Biol 202:241–250. doi:10.1083/jcb.201303163
Waterman-Storer CM, Karki SB, Kuznetsov SA, Tabb JS, Weiss DG, Langford GM, Holzbaur EL (1997) The interaction between cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin is required for fast axonal transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:12180–12185. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.22.12180
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by Russian Foundation for Basic Research within the framework of the initiative research Project # 12-04-00209-a.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasil’yeva, N.A., Murzina, G.B. & Pivovarov, A.S. Habituation-Like Decrease of Acetylcholine-Induced Inward Current in Helix Command Neurons: Role of Microtubule Motor Proteins. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35, 703–712 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0165-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0165-y