Abstract
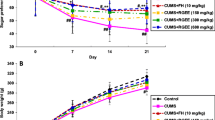
Previous studies in our laboratory have demonstrated that piperine produced antidepressant-like action in various mouse models of behavioral despair, which was related to the serotonergic system. The present study aimed to examine the behavioral and biochemical effects of piperine in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS). The results showed that CUMS caused depression-like behavior in rats, as indicated by the significant decrease in sucrose consumption and increase in immobility time in the forced swim test. In addition, it was found that serotonin (5-HT) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) contents in the hippocampus and frontal cortex were significantly decreased in CUMS-treated rats. Treating the animals with piperine significantly suppressed behavioral and biochemical changes induced by CUMS. The results suggest that piperine produces an antidepressant-like effect in CUMS-treated rats, which is possibly mediated by increasing 5-HT and BDNF contents in selective brain tissues.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chonpathompikunlert P, Wattanathorn J, Muchimapura S (2010) Piperine, the main alkaloid of Thai black pepper, protects against neurodegeneration and cognitive impairment in animal model of cognitive deficit like condition of Alzheimer’s disease. Food Chem Toxicol 48:798–802
Gupta SK, Bansal P, Bhardwaj RK, Velpandian T (2000) Comparative antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory and toxicity profile of nimesulide vs nimesulide and piperine combination. Pharmacol Res 41:657–662
Huang EJ, Reichardt LF (2001) Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:677–736
Ibarguen-Vargas Y, Surget A, Vourc’h P, Leman S, Andres CR, Gardier AM, Belzung C (2009) Deficit in BDNF does not increase vulnerability to stress but dampens antidepressant-like effects in the unpredictable chronic mild stress. Behav Brain Res 202:245–251
Ivy AS, Rodriguez FG, Garcia C, Chen MJ, Russo-Neustadt AA (2003) Noradrenergic and serotonergic blockade inhibits BDNF mRNA activation following exercise and antidepressant. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:81–88
Juric DM, Miklic S, Carman-Krzan M (2006) Monoaminergic neuronal activity up-regulates BDNF synthesis in cultured neonatal rat astrocytes. Brain Res 1108:54–62
Kong LD, Cheng CH, Tan RX (2004) Inhibition of MAO A and B by some plant-derived alkaloids, phenols and anthraquinones. J Ethnopharmacol 91:351–355
Krishnan V, Nestler EJ (2008) The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nature 2008:894–902
Lee SA, Hong SS, Han XH, Hwang JS, Oh GJ, Lee KS, Lee MK, Hwang BY, Ro JS (2005) Piperine from the fruits of Piper longum with inhibitory effect on monoamine oxidase and antidepressant-like activity. Chem Pharm Bull 53:832–835
Li S, Wang C, Li W, Koike K, Nikaido T, Wang MW (2007a) Antidepressant-like effects of piperine and its derivative, antiepilepsirine. J Asian Nat Prod Res 9:421–430
Li S, Wang C, Wang M, Li W, Matsumoto K, Tang Y (2007b) Antidepressant like effects of piperine in chronic mild stress treated mice and its possible mechanisms. Life Sci 80:1373–1381
Mao QQ, Ip SP, Ko KM, Tsai SH, Che CT (2009) Peony glycosides produce antidepressant-like action in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress: effects on hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal function and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:1211–1216
Mao QQ, Huang Z, Zhong XM, Feng CR, Pan AJ, Li ZY, Ip SP, Che CT (2010a) Effects of SYJN, a Chinese herbal formula, on chronic unpredictable stress-induced changes in behavior and brain BDNF in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 128:336–341
Mao QQ, Xian YF, Ip SP, Tsai SH, Che CT (2010b) Long-term treatment with peony glycosides reverses chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behavior via increasing expression of neurotrophins in rat brain. Behav Brain Res 210:171–177
Mao QQ, Huang Z, Ip SP, Xian YF, Che CT (2011a) Role of 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(1B) receptors in the antidepressant-like effect of piperine in the forced swim test. Neurosci Lett 504:181–184
Mao QQ, Xian YF, Ip SP, Che CT (2011b) Involvement of serotonergic system in the antidepressant-like effect of piperine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:1144–1147
Mao QQ, Huang Z, Ip SP, Xian YF, Che CT (2012) Peony glycosides reverse the effects of corticosterone on behavior and brain BDNF expression in rats. Behav Brain Res 227:305–309
Mattson MP, Maudsley S, Martin B (2004) BDNF and 5-HT: a dynamic duo in age-related neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci 27:589–594
Monteggia LM, Luikart B, Barrot M, Theobold D, Malkovska I, Nef S, Parada LF, Nestler EJ (2007) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor conditional knockouts show gender differences in depression-related behaviors. Biol Psychiatry 61:187–197
Porsolt RD, Pichon MLE, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressant. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 229:327–336
Schildkraut JJ (1965) The catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders: a review of supporting evidence. Am J Psychiatry 122:509–522
Selvendiran K, Singh JP, Krishnan KB, Sakthisekaran D (2003) Cytoprotective effect of piperine against benzo[a]pyrene induced lung cancer with reference to lipid peroxidation and antioxidant system in Swiss albino mice. Fitoterapia 74:109–115
Tõnissaar M, Mällo T, Eller M, Häidkind R, Kõiv K, Harro J (2008) Rat behavior after chronic variable stress and partial lesioning of 5-HT-ergic neurotransmission: effects of citalopram. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:164–177
Willner P (1997) Validity, reliability and utility of the chronic mild stress model of depression: a 10-year review and evaluation. Psychopharmacology 134:319–329
Willner P (2005) Chronic mild stress (CMS) revisited: consistency and behavioural–neurobiological concordance in the effects of CMS. Neuropsychobiology 52:90–110
Zhou J, Li L, Tang S, Cao X, Li Z, Li W, Li C, Zhang X (2008) Effects of serotonin depletion on the hippocampal GR/MR and BDNF expression during the stress adaptation. Behav Brain Res 195:129–138
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Y2110307).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, QQ., Huang, Z., Zhong, XM. et al. Piperine Reverses Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Behavioral and Biochemical Alterations in Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34, 403–408 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0025-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0025-1