Abstract
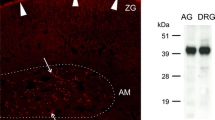
To clarify the role of angiotensin II (Ang II) in the regulation of sensory signaling, we studied the effect of subpressor dose (150 ng/kg/min) of Ang II on pain-related behavior in relation with neuronal injury and activation of satellite glial cells (SGCs) in the dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) after chronic constriction injury (CCI). Systemic continuous delivery of Ang II induced the tactile, heat and cold hyperlagesia, when measured at 7 days ofpost-injury. Blockade of the AT1 receptor with losartan (2.5 mg/kg/day) prevented tactile hyperalgesia and attenuated cold hyperalgesia, but did not affect the response to noxious heat stimulus. A marked increase of large-sized injured primary afferent neurons, detected by ATF3 immunolabeling, was seen in lower lumbar DRGs on ipsilateral side after Ang II treatment. Subpressor dose of Ang II induced an increase of activated SGCs (detected by GFAP immunolabeling) enveloping large-diameter neurons. Our results suggested that Ang II through the AT1 receptor activation is an important regulatory factor in neuropathic pain perception and plays an important role in the injury of large-sized primary afferent neurons and activation of SGCs elicited by the CCI.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almasi R, Pethö G, Bölcskei K, Szolcsanyi J (2003) Effect of resiniferatoxin on the noxious heat threshold temperature in the rat: a novel heat allodynia model sensitive to analgesics. Br J Pharmacol 139:49–58
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Bölcskei K, Horvath D, Szolcsanyi J, Pethö G (2007) Heat injury-induced drop of the noxious heat threshold measured with and increasing-temperature water bath: a novel rat thermal hyperalgesia model. Europ J Pharmacol 564:80–87
Cassis L, Marshall DE, Fettinger MJ, Rosenbluth B, Lodder RA (1998) Mechanisms contributing to angiotensin II regulation of body weight. Am J Physiol 274:E867–E876
Cizkova D, Lukacova N, Marsala M, Marsala J (2002) Neuropathic pain is associated with alteration of nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity and catalytic activity in dorsal root ganglia and spinal dorsal horn. Brain Res Bull 58:161–171
De Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger T (2000) International Union of Pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev 52:415–472
Hanani M (2005) Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: from form to function. Brain Res Rev 48:457–476
Kazama K, Wang G, Frys K, Anrather J, Iadecola C (2003) Angiotensin II attenuates functional hyperemia in the mouse somatosensory cortex. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H1890–H1899
Kim DS, Figueroa KW, Li KW, Boroujerdi A, Yolo T, Luo ZD (2009) Profiling of dynamically changed gene expression in dorsal root ganglia post peripheral nerve injury and critical role of injury-induced glial fibrillary acetic protein in maintenance of pain behaviors. Pain 143:114–122
Le Bars D, Gozariu M, Cadden SW (2001) Animal models of nociception. Pharmacol Rev 53:597–652
Liu FY, Sun YN, Wang FT, Li Q, Su L, Zhao ZF, Meng XL, Zhao H, Wu X, Sun Q, Xin GG, Wan Y (2011) Activation of satellite glial cells in lumbar dorsal root ganglia contributes to neuropathic pain after spinal nerve ligation. Brain Res 1427:65–77
Marques-Lopes J, Pinto M, Pinho D, Morato M, Patinha D, Albino-Teixeira A, Tavares I (2009) Microinjection of angiotensin II in the caudal ventrolateral medulla induces hyperalgesia. Neuroscience 158:1301–1310
McManis PG, Schmelzer JD, Zollman PJ, Low PA (1997) Blood flow and autoregulation on somatic and autonomic ganglia. Comparison with sciatic nerve. Brain 120:445449
Obata K, Yamanaka H, Fukuoka T, Yi D, Tokunaga A, Hashimoto N, Yoshikawa H, Noguchi K (2003) Contribution of injured and uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons to pain behavior and the changes in gene expression following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats. Pain 101:65–77
Ohara PT, Vit JP, Bhargava A, Romero M, Sundberg C, Charles AC, Jasmin L (2009) Gliopathic pain: when satellite glial cells go bad. Neuroscientist 15:450–463
Pannese E (2010) The structure of the perineuronal sheath of satellite glial cells (SGCs) in sensory ganglia. Neuron Glia Biol 6:3–10
Pavel J, Tang H, Brimijoin S, Moughamian A, Nishioku T, Benicky J, Saavedra JM (2008) Expression and transport of angiotensin II AT1 receptors in spinal cord, dorsal root ganglia and sciatic nerve of the rat. Brain Res 1246:111–122
Pavel J, Hricova L, Jergova S, Lukacova N (2011) The impact of short-lasting repeated vibrations on retrograde axonal transport, the expression of CGRP and parvalbumin in lower lumbar dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res 1396:1–10
Pelegrini-da-Silva A, Martins AR, Prado WA (2005) A new role for the rennin–angiotensin system in the rat periaqueductal gray matter: angiotensin receptor-mediated modulation of nociception. Neuroscience 132:453–463
Saavedra JM (2012) Angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockers as treatment for inflammatory brain disorders. Clin Sci (Lond) 123:567–590
Sakagawa T, Okuyama S, Kawashima N, Hozumi S, Nakagawasai O, Tadano T, Kisara K, Ichiki T, Inagami T (2000) Pain threshold, learning and formation of brain edema in mice lacking the angiotensin II type 2 receptor. Life Sci 67:2577–2585
Sapunar D, Kostic S, Banozic A, Puljak L (2012) Dorsal root ganglion—a potential new therapeutic target for neuropathic pain. J Pain Res 5:31–38
Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2007) The neuropathic pain triad: neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat Neurosci 10:1361–1368
Takeda M, Takahashi M, Matsumoto S (2009) Contribution of the activation of satellite glia in sensory ganglia to pathological pain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33:784–792
Tang H, Pavel J, Saavedra JM, Brimijoin S (2008) Angiotensin II type 1 receptors may not influence response of spinal autonomic neurons to axonal damage. Neurol Res 30:751–760
Yoshizawa H, Kobayashi S, Hachiya Y (1991) Blood supply of nerve roots and dorsal root ganglia. Orthop Clin North Am 22:195–211
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. I. Vrabelova for technical assistance. The study was supported by the VEGA Grants No. 2/0203/10 and No. 2/0191/13, APVV Grant No. 0314-06 and CE NOREG from the Slovak Academy of Sciences, and by ITMS 26220220127 supported by the Research & Development Operational Programme funded by the ERDF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavel, J., Oroszova, Z., Hricova, L. et al. Effect of Subpressor Dose of Angiotensin II on Pain-Related Behavior in Relation with Neuronal Injury and Activation of Satellite Glial Cells in the Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 681–688 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9934-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9934-7