Abstract
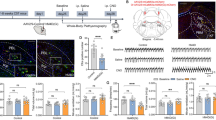
Low concentrations of capsaicin (CAP) stimulate and high concentrations of CAP can be toxic to the primary sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglion (DRG). CAP induces the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) in DRG neurons. The effect of the activation of ERK1/2 by different concentrations of CAP on growth-associated protein 43 (GAP-43) expression and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) depletion in DRG neurons remains unknown. In the present study, organotypic embryonic 15-day-old rat DRG explants were used to determine the effect of different concentrations of CAP on GAP-43 expression and CGRP depletion. The results showed that, compared to unstimulated control cultures, GAP-43 and pERK1/2 protein levels increased at a low concentration (2 μmol/L) of CAP and decreased at a higher concentration (10 μmol/L). The number of CGRP-immunoreactive (IR) migrating neurons also decreased in CAP-treated cultures. The increase in GAP-43 levels and CGRP depletion could be blocked by the administration of ERK1/2 inhibitor PD98059. The results of the present study imply that CAP at different concentrations has different effects on GAP-43 expression and CGRP depletion. These effects were involved in the activation of ERK1/2 in organotypically cultured DRG neurons stimulated with CAP. These data may provide new insights for further development potential therapeutic applications of CAP with moderate dose on neurogenic inflammation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAP:
-
Capsaicin
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CGRP:
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide
- DMEM/F-12:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium with F-12 supplement
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DRG:
-
Dorsal root ganglion
- DRGs:
-
Dorsal root ganglia
- E15:
-
Embryonic day 15
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1/2
- GAP-43:
-
Growth-associated protein-43
- IR:
-
Immunoreactive
- MAP2:
-
Microtubule-associated protein 2
- pERK1/2:
-
Phosphorylated-ERK1/2
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffer saline
- TRPV1:
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1
- VR1:
-
Vanilloid receptor-1
References
Aigner L, Caroni P (1993) Depletion of 43-kD growth-associated protein in primary sensory neurons leads to diminished formation and spreading of growth cones. J Cell Biol 123:417–429
Anand U, Otto WR, Bountra C, Chessell I, Sinisi M, Birch R, Anand P (2008) Cytosine arabinoside affects the heat and capsaicin receptor TRPV1 localisation and sensitivity in human sensory neurons. J Neurooncol 89:1–7
Anderson KD, Merhege MA, Morin M, Bolognani F, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2003) Increased expression and localization of the RNA-binding protein HuD and GAP-43 mRNA to cytoplasmic granules in DRG neurons during nerve regeneration. Exp Neurol 183:100–108
Babbar S, Marier JF, Mouksassi MS, Beliveau M, Vanhove GF, Chanda S, Bley K (2009) Pharmacokinetic analysis of capsaicin after topical administration of a high-concentration capsaicin patch to patients with peripheral neuropathic pain. Ther Drug Monit 31:502–510
Bergman E, Carlsson K, Liljeborg A, Manders E, Hökfelt T, Ulfhake B (1999) Neuropeptides, nitric oxide synthase and GAP-43 in B4-binding and RT97 immunoreactive primary sensory neurons: normal distribution pattern and changes after peripheral nerve transection and aging. Brain Res 832:63–83
Biella G, Panara C, Pecile A, Sotgiu ML (1991) Facilitatory role of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) on excitation induced by substance P (SP) and noxious stimuli in rat spinal dorsal horn neurons: an iontophoretic studio in vivo. Brain Res 559:352–356
Binshtok AM, Bean BP, Woolf CJ (2007) Inhibition of nociceptors by TRPV1-mediated entry of impermeant sodium channel blockers. Nature 449:607–610
Bursova S, Dubovy P, Vlckova-Moravcova E, Nemec M, Klusakova I, Belobradkova J, Bednarik J (2012) Expression of growth-associated protein 43 in the skin nerve fibers of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Neurol Sci 315:60–63
Cady RJ, Glenn JR, Smith KM, Durham PL (2011) Calcitonin gene-related peptide promotes cellular changes in trigeminal neurons and glia implicated in peripheral and central sensitization. Mol Pain 7:94
Chakravarthy B, Rashid A, Brown L, Tessier L, Kelly J, Ménard M (2008) Association of Gap-43 (neuromodulin) with microtubule-associated protein MAP-2 in neuronal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 371:679–683
Cui W, Cui GZ, Li W, Zhang Z, Hu S, Mak S, Zhang H, Carlier PR, Choi CL, Wong YT, Lee SM, Han Y (2011) Bis(12)-hupyridone, a novel multifunctional dimer, promotes neuronal differentiation more potently than its monomeric natural analog huperzine A possibly through alpha7 nAChR. Brain Res 1401:10–17
Dai Y, Iwata K, Fukuoka T, Kondo E, Tokunaga A, Yamanaka H, Tachibana T, Liu Y, Noguchi K (2002) Phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in primary afferent neurons by noxious stimuli and its involvement in peripheral sensitization. J Neurosci 22:7737–7745
Davis JB, Gray J, Gunthorpe MJ, Hatcher JP, Davey PT, Overend P, Harries MH, Latcham J, Clapham C, Atkinson K, Hughes SA, Rance K, Grau E, Harper AJ, Pugh PL, Rogers DC, Bingham S, Randall A, Sheardown SA (2000) Vanilloid receptor-1 is essential for inflammatory thermal hyperalgesia. Nature 405:183–187
Denny JB (2006) Molecular mechanisms, biological actions, and neuropharmacology of the growth-associated protein GAP-43. Curr Neuropharmacol 4:293–304
Di Stefano G, Casoli T, Fattoretti P, Gracciotti N, Solazzi M, Bertoni-Freddari C (2001) Distribution of map2 in hippocampus and cerebellum of young and old rats by quantitative immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 49:1065–1066
Dolly JO, O’Connell MA (2012) Neurotherapeutics to inhibit exocytosis from sensory neurons for the control of chronic pain. Curr Opin Pharmacol 12:100–108
Donnerer J, Liebmann I (2011) A fluorescence-immunohistochemical study on phosphorylation of ERK1/2, p38, and STAT3 in rat dorsal root ganglia following noxious stimulation of hind paw sensory neurons. Tissue Cell 43:178–189
Donnerer J, Liebmann I, Schicho R (2005) ERK and STAT3 phosphorylation in sensory neurons during capsaicin-induced impairment and nerve growth factor treatment. Pharmacology 75:116–121
Donnerer J, Liebmann I, Schuligoi R (2009) Capsaicin- and mustard oil-induced extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase phosphorylation in sensory neurons in vivo: effects of neurokinins 1 and 2 receptor antagonists and of a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 104:11–16
Donoso MV, Hermosilla D, Navarrete C, Alvarez P, Lillo JG, Huidobro-Toro JP (2012) Reciprocal sympatho-sensory control: functional role of nucleotides and calcitonin gene-related peptide in a peripheral neuroeffector junction. Neuroscience 203:216–229
Ebenezer GJ, O’Donnell R, Hauer P, Cimino NP, McArthur JC, Polydefkis M (2011) Impaired neurovascular repair in subjects with diabetes following experimental intracutaneous axotomy. Brain 134:1853–1863
El-Nour H, Lundeberg L, Al-Tawil R, Granlund A, Lonne-Rahm SB, Nordlind K (2006) Upregulation of the axonal growth and the expression of substance P and its NK1 receptor in human allergic contact dermatitis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 28:621–631
Foscarin S, Gianola S, Carulli D, Fazzari P, Mi S, Tamagnone L, Rossi F (2009) Overexpression of GAP-43 modifies the distribution of the receptors for myelin-associated growth-inhibitory proteins in injured Purkinje axons. Eur J Neurosci 30:1837–1848
Fressinaud C, Dubas F (2011) Axon cytoskeleton ultrastructure in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 44:332–339
Furuta A, Suzuki Y, Hayashi N, Egawa S, Yoshimura N (2012) Transient receptor potential A1 receptor-mediated neural cross-talk and afferent sensitization induced by oxidative stress: implication for the pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int J Urol 19:429–436
Goswami C, Schmidt H, Hucho F (2007) TRPV1 at nerve endings regulates growth cone morphology and movement through cytoskeleton reorganization. FEBS J 274:760–772
Gupta SK, Mishra R, Kusum S, Spedding M, Meiri KF, Gressens P, Mani S (2009) GAP-43 is essential for the neurotrophic effects of BDNF and positive AMPA receptor modulator S18986. Cell Death Differ 16:624–637
Hafner A, Obermajer N, Kos J (2012) γ-Enolase C-terminal peptide promotes cell survival and neurite outgrowth by activation of PI3-K/Akt and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways. Biochem J 443:439–450
Ikeuchi M, Wang Q, Izumi M, Tani T (2012) Nociceptive sensory innervation of the posterior cruciate ligament in osteoarthritic knees. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132:891–895
Jaken RJ, van Gorp S, Joosten EA, Losen M, Martínez-Martínez P, De Baets M, Marcus MA, Deumens R (2011) Neuropathy-induced spinal GAP-43 expression is not a main player in the onset of mechanical pain hypersensitivity. J Neurotrauma 28:2463–2473
Jeftinija S, Liu F, Jeftinija K, Urban L (1992) Effect of capsaicin and resiniferatoxin on peptidergic neurons in cultured dorsal root ganglion. Regul Pept 39:123–135
Kato K, Liu H, Kikuchi S, Myers RR, Shubayev VI (2010) Immediate anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha (etanercept) therapy enhances axonal regeneration after sciatic nerve crush. J Neurosci Res 88:360–368
Lai HC, Wu MJ, Chen PY, Sheu TT, Chiu SP, Lin MH, Ho CT, Yen JH (2011) Neurotrophic effect of citrus 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3′,4′-hexamethoxyflavone: promotion of neurite outgrowth via cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway in PC12 cells. PLoS ONE 6:e28280
Lee KB, Choi JH, Byun K, Chung KH, Ahn JH, Jeong GB, Hwang IK, Kim S, Won MH, Lee B (2012) Recovery of CNS pathway innervating the sciatic nerve following transplantation of human neural stem cells in rat spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:149–157
Liao KK, Wu MJ, Chen PY, Huang SW, Chiu SJ, Ho CT, Yen JH (2012) Curcuminoids promote neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells through MAPK/ERK- and PKC-dependent pathways. J Agric Food Chem 60:433–443
Liu Y, Saad RS, Shen SS, Silverman JF (2003) Diagnostic value of microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP-2) for neuroendocrine neoplasms. Adv Anat Pathol 10:101–106
Liu Z, Cai H, Zhang P, Li H, Liu H, Li Z (2012) Activation of ERK1/2 and PI3 K/Akt by IGF-1 on GAP-43 expression in DRG neurons with excitotoxicity induced by glutamate in vitro. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:191–200
Marinelli S, Luvisetto S, Cobianchi S, Makuch W, Obara I, Mezzaroma E, Caruso M, Straface E, Przewlocka B, Pavone F (2010) Botulinum neurotoxin type A counteracts neuropathic pain and facilitates functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury in animal models. Neuroscience 171:316–328
Mechsner S, Schwarz J, Thode J, Loddenkemper C, Salomon DS, Ebert AD (2007) Growth-associated protein 43-positive sensory nerve fibers accompanied by immature vessels are located in or near peritoneal endometriotic lesions. Fertil Steril 88:581–587
Nagamoto-Combs K, Morecraft RJ, Darling WG, Combs CK (2010) Long-term gliosis and molecular changes in the cervical spinal cord of the rhesus monkey after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 27:565–585
Noto C, Pappagallo M, Szallasi A (2009) NGX-4010, a high-concentration capsaicin dermal patch for lasting relief of peripheral neuropathic pain. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 10:702–710
Orita S, Ishikawa T, Miyagi M, Ochiai N, Inoue G, Eguchi Y, Kamoda H, Arai G, Aoki Y, Toyone T, Kubo T, Takahashi K, Ohtori S (2011) Pain-related sensory innervation in monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rat knees that gradually develops neuronal injury in addition to inflammatory pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 12:134
Passmore GM (2005) Dorsal root ganglion neurones in culture: a model system for identifying novel analgesic targets. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 51:201–208
Schumacher MA (2010) Transient receptor potential channels in pain and inflammation: therapeutic opportunities. Pain Pract 10:185–200
Snider WD, McMahon SB (1998) Tackling pain at the source: new ideas about nociceptors. Neuron 20:629–632
Tabernero A, Granda B, Medina A, Sánchez-Abarca LI, Lavado E, Medina JM (2002) Albumin promotes neuronal survival by increasing the synthesis and release of glutamate. J Neurochem 81:881–891
Tominaga M, Tominaga T (2005) Structure and function of TRPV1. Pflugers Arch 451:143–150
Tsai SY, Chiu PY, Yang CP, Lee YH (2002) Synergistic effects of corticosterone and kainic acid on neurite outgrowth in axotomized dorsal root ganglion. Neuroscience 114:55–67
Tsai SY, Yang LY, Wu CH, Chang SF, Hsu CY, Wei CP, Leu SJ, Liaw J, Lee YH, Tsai MD (2007) Injury-induced Janus kinase/protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation of growth-associated protein 43 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 for neurite growth in dorsal root ganglion. J Neurosci Res 85:321–331
Winston J, Toma H, Shenoy M, Pasricha PJ (2001) Nerve growth factor regulates VR-1 mRNA levels in cultures of adult dorsal root ganglion neurons. Pain 89:181–186
Yang X, Gong H, Liu Z, Liu H, Wang H, Li Z (2010) Similar and different effects of capsaicin and resiniferatoxin on substance P release and transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 expression of cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 32:3–11
Zhang X, Daugherty SL, de Groat WC (2011) Activation of CaMKII and ERK1/2 contributes to the time-dependent potentiation of Ca2 + response elicited by repeated application of capsaicin in rat DRG neurons. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300:R644–R654
Zhao JC, Zhang LX, Zhang Y, Shen YF (2012) The differential regulation of Gap43 gene in the neuronal differentiation of P19 cells. J Cell Physiol 227:2645–2653
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81000517), the Foundation for the Doctoral Program New Teacher of State Education Ministry of China (No. 20090131120013), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 200904501203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Liu, G., Li, H. et al. Capsaicin-Induced Activation of ERK1/2 and Its Involvement in GAP-43 Expression and CGRP Depletion in Organotypically Cultured DRG Neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 433–441 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9909-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9909-8