Abstract
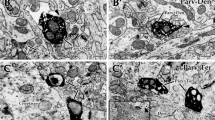
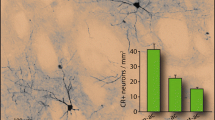
The striatum plays a fundamental role in sensorimotor and cognitive functions of the body, and different sub-regions control different physiological functions. The striatal interneurons play important roles in the striatal function, yet their specific functions are not clearly elucidated so far. The present study aimed to investigate the morphological properties of the GABAergic interneurons expressing neuropeptide Y (NPY), calretinin (Cr), and parvalbumin (Parv) as well as the cholinergic interneurons expressing choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) in the striatal dorsolateral (DL) and ventromedial (VM) regions of rats using immunohistochemistry and Western blot. The present results showed that the somatic size of Cr+ was the smallest, while ChAT+ was the largest among the four types of interneurons. There was no regional difference in neuronal somatic size of all types of interneurons. Cr+ and Parv+ neurons were differentially distributed in the striatum. Moreover, Parv+ had the longest primary dendrites in the DL region, while NPY+ had the longest ones in the VM region of striatum. But there was regional difference in the length of primary dendrites of Parv. The numbers of primary dendrites of Parv+ were the largest in both DL and VM regions of striatum. Both Cr+ and Parv+ primary dendrites displayed regional difference in the striatum. Western blot further confirmed the regional differences in the protein expression level of Cr and Parv. Hence, the present study indicates that GABAergic and cholinergic interneurons might be involved in different physiological functions based on their morphological and distributional diversity in different regions of the rat striatum.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie M (1946) Estimation of nuclear population from microtome sections. Anat Rec 94:239–247
Alexander GE, DeLong MR, Strick PL (1986) Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci 9:357–381
Aoki C, Pickel VM (1988) Neuropeptide Y-containing neurons in the rat striatum: ultrastructure and cellular relations with tyrosine hydroxylase-containing terminals and with astrocytes. Brain Res 459:205–225
Bennett BD, Bolam JP (1993) Characterization of calretinin-immunoreactive structures in the striatum of the rat. Brain Res 609:137–148
Bolam JP, Wainer BH, Smith AD (1984) Characterization of cholinergic neurons in the rat neostriatum. A combination of choline acetyltransferase immunocytochemistry, Golgi-impregnation and electron microscopy. Neuroscience 12:711–718
Centonze D, Gubellini P, Pisani A, Bernardi G, Calabresi P (2003) Dopamine, acetylcholine and nitric oxide systems interact to induce corticostriatal synaptic plasticity. Rev Neurosci 14:207–216
Chuhma N, Tanaka KF, Hen R, Rayport S (2011) Functional connectome of the striatal medium spiny neuron. J Neurosci 31:1183–1192
Cowan RL, Wilson CJ, Emson PC, Heizmann CW (1990) Parvalbumin-containing GABAergic interneurons in the rat neostriatum. J Comp Neurol 302:197–205
Deng YP, Shelby E, Reiner AJ (2010) Immunohistochemical localization of AMPA-type glutamate receptor subunits in the striatum of rhesus monkey. Brain Res 1344:104–123
DiFiglia M, Aronin N (1982) Ultrastructural features of immunoreactive somatostatin neurons in the rat caudate nucleus. J Neurosci 2:1267–1274
Figueredo-Cardenas G, Morello M, Sancesario G, Bernardi G, Reiner A (1996) Colocalization of somatostatin, neuropeptide Y, neuronal nitric oxide synthase and NADPH-diaphorase in striatal interneurons in rats. Brain Res 735:317–324
Fino E, Venance L (2011) Spike-timing dependent plasticity in striatal interneurons. Neuropharmacology 60:780–788
Graveland GA, DiFiglia M (1985) The frequency and distribution of medium-sized neurons with indented nuclei in the primate and rodent neostriatum. Brain Res 327:307–311
Graveland GA, Williams RS, DiFiglia M (1985) A Golgi study of the human neostriatum: neurons and afferent fibers. J Comp Neurol 234:317–333
Kawaguchi Y, Kubota Y (1993) Correlation of physiological subgroupings of nonpyramidal cells with parvalbumin- and calbindinD28k-immunoreactive neurons in layer V of rat frontal cortex. J Neurophysiol 70:387–396
Kawaguchi Y, Wilson CJ, Augood SJ, Emson PC (1995) Striatal interneurones: chemical, physiological and morphological characterization. Trends Neurosci 18:527–535
Kita H (1993) GABAergic circuits of the striatum. Prog Brain Res 99:51–72
Kreitzer AC, Berke JD (2011) Investigating striatal function through cell-type-specific manipulations. Neuroscience 198:19–26
Kubota Y, Mikawa S, Kawaguchi Y (1993) Neostriatal GABAergic interneurones contain NOS, calretinin or parvalbumin. NeuroReport 5:205–208
Luk KC, Sadikot AF (2001) GABA promotes survival but not proliferation of parvalbumin-immunoreactive interneurons in rodent neostriatum: an in vivo study with stereology. Neuroscience 104:93–103
Ma Y, Feng Q, Ma J, Feng Z, Zhan M, Ouyang L, Mu S, Liu B, Jiang Z, Jia Y, Li Y, Lei W (2013) Melatonin ameliorates injury and specific responses of ischemic striatal neurons in rats. J Histochem Cytochem 61:591–605
Mu S, OuYang L, Liu B, Zhu Y, Li K, Zhan M, Liu Z, Jia Y, Lei W, Reiner A (2011) Preferential interneuron survival in the transition zone of 3-NP-induced striatal injury in rats. J Neurosci Res 89:744–754
Oorschot DE (2013) The percentage of interneurons in the dorsal striatum of the rat, cat, monkey and human: a critique of the evidence. Basal Ganglia 3:19–24
Packard MG, Knowlton BJ (2002) Learning and memory functions of the Basal Ganglia. Annu Rev Neurosci 25:563–593
Rymar VV, Sasseville R, Luk KC, Sadikot AF (2004) Neurogenesis and stereological morphometry of calretinin-immunoreactive GABAergic interneurons of the neostriatum. J Comp Neurol 469:325–339
Schlosser B, Klausa G, Prime G, Ten BG (1999) Postnatal development of calretinin- and parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the rat neostriatum: an immunohistochemical study. J Comp Neurol 405:185–198
Tepper JM, Bolam JP (2004) Functional diversity and specificity of neostriatal interneurons. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:685–692
Tepper JM, Tecuapetla F, Koos T, Ibanez-Sandoval O (2010) Heterogeneity and diversity of striatal GABAergic interneurons. Front Neuroanat 4:150
Vincent SR, Johansson O (1983) Striatal neurons containing both somatostatin- and avian pancreatic polypeptide (APP)-like immunoreactivities and NADPH-diaphorase activity: a light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 217:264–270
Vincent SR, Johansson O, Hokfelt T, Skirboll L, Elde RP, Terenius L, Kimmel J, Goldstein M (1983) NADPH-diaphorase: a selective histochemical marker for striatal neurons containing both somatostatin- and avian pancreatic polypeptide (APP)-like immunoreactivities. J Comp Neurol 217:252–263
Voorn P, Vanderschuren LJ, Groenewegen HJ, Robbins TW, Pennartz CM (2004) Putting a spin on the dorsal-ventral divide of the striatum. Trends Neurosci 27:468–474
Wu Y, Parent A (2000) Striatal interneurons expressing calretinin, parvalbumin or NADPH-diaphorase: a comparative study in the rat, monkey and human. Brain Res 863:182–191
Zaborszky L, Alheid GF, Beinfeld MC, Eiden LE, Heimer L, Palkovits M (1985) Cholecystokinin innervation of the ventral striatum: a morphological and radioimmunological study. Neuroscience 14:427–453
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science Foundations of China (Nos. 31070941, 30770679, 20831006) and the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program, No. 2010CB530004).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yuxin Ma and Qiqi Feng have contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Feng, Q., OuYang, L. et al. Morphological Diversity of GABAergic and Cholinergic Interneurons in the Striatal Dorsolateral and Ventromedial Regions of Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34, 351–359 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-0019-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-0019-4