Abstract
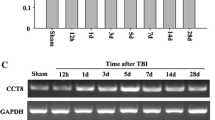
Che-1, a recently identified apoptosis related protein, affects the fate of various cell types when under stress. One attractive biological function of Che-1 is promoting the transcription of p53 after DNA damage; besides, it can also regulate cell cycle via interacting with retinoblastoma protein. Although previous evidence has showed its anti-apoptotic role in cancer cells, some studies point out that Che-1 might play an opposite role in central nervous system (CNS). However, the function of Che-1 in CNS is still with limited acquaintance. To investigate whether Che-1 is involved in CNS lesion, we performed a traumatic brain injury model in adult rats. Up-regulation of Che-1 was observed in the peritrauma brain cortex by performing western blotting and immunohistochemistry. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase deoxy-UTP nick-end labeling and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining suggested that Che-1 was involved in neuronal apoptosis after brain injury. We also investigated co-localization of Che-1 and active-caspase-3 in the ipsilateral brain cortex. In addition, the expression patterns of p53, Bax and PCNA were parallel with that of Che-1. Besides this, neurotrophin receptor-interacting MAGE homolog was found to be associated with Che-1 after brain trauma. Based on our data, we suggested that Che-1 might play an important role in neuronal apoptosis following TBI; and might provide a basis for the further study on its role in regulating the expression of p53 and cell cycle re-entry in traumatic brain injury.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacalini MG, Di Lonardo D, Catizone A, Ciccarone F, Bruno T, Zampieri M, Guastafierro T, Calabrese R, Fanciulli M, Passananti C, Caiafa P, Reale A (2011) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation affects stabilization of Che-1 protein in response to DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst) 10:380–389
Barbato C, Corbi N, Canu N, Fanciulli M, Serafino A, Ciotti M, Libri V, Bruno T, Amadoro G, De Angelis R, Calissano P, Passananti C (2003) Rb binding protein Che-1 interacts with Tau in cerebellar granule neurons. Modulation during neuronal apoptosis. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:1038–1050
Becker EB, Bonni A (2004) Cell cycle regulation of neuronal apoptosis in development and disease. Prog Neurobiol 72:1–25
Bruno T, De Angelis R, De Nicola F, Barbato C, Di Padova M, Corbi N, Libri V, Benassi B, Mattei E, Chersi A, Soddu S, Floridi A, Passananti C, Fanciulli M (2002) Che-1 affects cell growth by interfering with the recruitment of HDAC1 by Rb. Cancer Cell 2:387–399
Bruno T, De Nicola F, Iezzi S, Lecis D, D’Angelo C, Di Padova M, Corbi N, Dimiziani L, Zannini L, Jekimovs C, Scarsella M, Porrello A, Chersi A, Crescenzi M, Leonetti C, Khanna KK, Soddu S, Floridi A, Passananti C, Delia D, Fanciulli M (2006) Che-1 phosphorylation by ATM/ATR and Chk2 kinases activates p53 transcription and the G2/M checkpoint. Cancer Cell 10:473–486
Bruno T, Desantis A, Bossi G, Di Agostino S, Sorino C, De Nicola F, Iezzi S, Franchitto A, Benassi B, Galanti S, La Rosa F, Floridi A, Bellacosa A, Passananti C, Blandino G, Fanciulli M (2010) Che-1 promotes tumor cell survival by sustaining mutant p53 transcription and inhibiting DNA damage response activation. Cancer Cell 18:122–134
Chen AJ, D’Esposito M (2010) Traumatic brain injury: from bench to bedside [corrected] to society. Neuron 66:11–14
Chong ZZ, Li F, Maiese K (2006) Attempted cell cycle induction in post-mitotic neurons occurs in early and late apoptotic programs through Rb, E2F1, and caspase 3. Curr Neurovasc Res 3:25–39
Cregan SP, MacLaurin JG, Craig CG, Robertson GS, Nicholson DW, Park DS, Slack RS (1999) Bax-dependent caspase-3 activation is a key determinant in p53-induced apoptosis in neurons. J Neurosci 19:7860–7869
Dasgupta P, Padmanabhan J, Chellappan S (2006) Rb function in the apoptosis and senescence of non-neuronal and neuronal cells: role in oncogenesis. Curr Mol Med 6:719–729
Di Certo MG, Corbi N, Bruno T, Iezzi S, De Nicola F, Desantis A, Ciotti MT, Mattei E, Floridi A, Fanciulli M, Passananti C (2007) NRAGE associates with the anti-apoptotic factor Che-1 and regulates its degradation to induce cell death. J Cell Sci 120:1852–1858
Di Giovanni S, Movsesyan V, Ahmed F, Cernak I, Schinelli S, Stoica B, Faden AI (2005) Cell cycle inhibition provides neuroprotection and reduces glial proliferation and scar formation after traumatic brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8333–8338
Di Giovanni S, Knights CD, Rao M, Yakovlev A, Beers J, Catania J, Avantaggiati ML, Faden AI (2006) The tumor suppressor protein p53 is required for neurite outgrowth and axon regeneration. EMBO J 25:4084–4096
Floridi A, Fanciulli M (2007) Che-1: a new effector of checkpoints signaling. Cell Cycle 6:804–806
Ghajar J (2000) Traumatic brain injury. Lancet 356:923–929
Greene LA, Liu DX, Troy CM, Biswas SC (2007) Cell cycle molecules define a pathway required for neuron death in development and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:392–401
Herrup K, Busser JC (1995) The induction of multiple cell cycle events precedes target-related neuronal death. Development 121:2385–2395
Holloway RG, Quill TE (2010) Treatment decisions after brain injury—tensions among quality, preference, and cost. N Engl J Med 362:1757–1759
Hulsebosch CE, DeWitt DS, Jenkins LW, Prough DS (1998) Traumatic brain injury in rats results in increased expression of Gap-43 that correlates with behavioral recovery. Neurosci Lett 255:83–86
Jurgensmeier JM, Xie Z, Deveraux Q, Ellerby L, Bredesen D, Reed JC (1998) Bax directly induces release of cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4997–5002
Kan EM, Ling EA, Lu J (2012) Microenvironment changes in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Res Bull 87:359–372
Kendall SE, Battelli C, Irwin S, Mitchell JG, Glackin CA, Verdi JM (2005) NRAGE mediates p38 activation and neural progenitor apoptosis via the bone morphogenetic protein signaling cascade. Mol Cell Biol 25:7711–7724
Li X, Yan M, Hu L, Sun L, Zhang F, Ji H, Jiang J, Wang P, Liu H, Gao Y, Tao T, He X, Cheng C, Shen A (2010) Involvement of Src-suppressed C kinase substrate in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: a link between release of astrocyte proinflammatory factor and oligodendrocyte apoptosis. J Neurosci Res 88:1858–1871
Liu DX, Greene LA (2001) Neuronal apoptosis at the G1/S cell cycle checkpoint. Cell Tissue Res 305:217–228
Liu Y, Wang Y, Cheng C, Chen Y, Shi S, Qin J, Xiao F, Zhou D, Lu M, Lu Q, Shen A (2010) A relationship between p27(kip1) and Skp2 after adult brain injury: implications for glial proliferation. J Neurotrauma 27:361–371
Logan A, Frautschy SA, Gonzalez AM, Baird A (1992) A time course for the focal elevation of synthesis of basic fibroblast growth factor and one of its high-affinity receptors (flg) following a localized cortical brain injury. J Neurosci 12:3828–3837
Maas AI, Stocchetti N, Bullock R (2008) Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurol 7:728–741
Martin LJ, Liu Z, Pipino J, Chestnut B, Landek MA (2009) Molecular regulation of DNA damage-induced apoptosis in neurons of cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 19:1273–1293
Martinou JC, Youle RJ (2011) Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 21:92–101
Miller FD, Pozniak CD, Walsh GS (2000) Neuronal life and death: an essential role for the p53 family. Cell Death Differ 7:880–888
Park E, Bell JD, Baker AJ (2008) Traumatic brain injury: can the consequences be stopped? CMAJ 178:1163–1170
Passananti C, Fanciulli M (2007) The anti-apoptotic factor Che-1/AATF links transcriptional regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA damage response. Cell Div 2:21
Plesnila N, von Baumgarten L, Retiounskaia M, Engel D, Ardeshiri A, Zimmermann R, Hoffmann F, Landshamer S, Wagner E, Culmsee C (2007) Delayed neuronal death after brain trauma involves p53-dependent inhibition of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. Cell Death Differ 14:1529–1541
Raghupathi R, Graham DI, McIntosh TK (2000) Apoptosis after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 17:927–938
Slemmer JE, Zhu C, Landshamer S, Trabold R, Grohm J, Ardeshiri A, Wagner E, Sweeney MI, Blomgren K, Culmsee C, Weber JT, Plesnila N (2008) Causal role of apoptosis-inducing factor for neuronal cell death following traumatic brain injury. Am J Pathol 173:1795–1805
Stoica BA, Faden AI (2010) Cell death mechanisms and modulation in traumatic brain injury. Neurotherapeutics 7:3–12
Stoica BA, Byrnes KR, Faden AI (2009) Cell cycle activation and CNS injury. Neurotox Res 16:221–237
Tedeschi A, Nguyen T, Puttagunta R, Gaub P, Di Giovanni S (2009) A p53-CBP/p300 transcription module is required for GAP-43 expression, axon outgrowth, and regeneration. Cell Death Differ 16:543–554
Wang L, Wang R, Herrup K (2007) E2F1 works as a cell cycle suppressor in mature neurons. J Neurosci 27:12555–12564
Wang D, Lu Q, Shao B, Cui G, Wang Y, Liu Y, Wu Q, Zhao J, Cui Z, Xu J, Yang H, Shen A, Gu X (2011) An upregulation of SIAH1 after spinal cord injury in adult rats. J Mol Neurosci 45:134–144
Wong J, Hoe NW, Zhiwei F, Ng I (2005) Apoptosis and traumatic brain injury. Neurocrit Care 3:177–182
Yang Y, Mufson EJ, Herrup K (2003) Neuronal cell death is preceded by cell cycle events at all stages of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 23:2557–2563
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81070992) and funded by Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), Nantong University graduate scientific and technological innovation projects (No. YKC12030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jian Xu and Wei Jin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Jin, W., Wu, X. et al. Up-regulation of Che-1 Relates to Neuronal Apoptosis After Traumatic Brain Injury in Adult Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 85–97 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9874-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9874-7