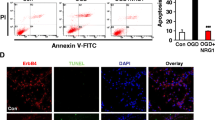
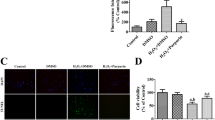
Abstract
Following endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, cerebral infarctions have been reported to involve an apoptotic process, including the activation of the caspase cascade. To confirm whether fragmented caspase-12, which is activated by cleavage and is detectable during ER stress, is also involved in embolic cerebral infarctions in rats, we adopted an autologous blood clot model for the analysis of cerebral infarctions. We performed experiments in rats with brain infarctions, which are closely related to embolic cerebral infarctions. We utilized a homologous blood clot, i.e., natural materials, to form the infarct area. Our findings reveal that caspase-12 is fragmented when infarct areas form in cerebral cortical neurons. Interestingly, we observed that these fragments translocated to the nuclei of not only cerebral cortical neurons but hippocampal neurons. We further found that glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), a marker of ER stress, is up-regulated in both cerebral cortical and hippocampal neurons during cerebral infarction. This result suggests that the fragmentation of caspase-12 and the subsequent nuclear translocation of these fragments are involved in the brain infarction process in rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- GRP78:
-
Glucose-regulated protein 78
- Bcl-2:
-
B cell/lymphoma-2
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- HE:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick end labeling
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
References
Back SH, Schroder M, Lee K, Zhang K, Kaufman RJ (2005) ER stress signaling by regulated splicing: IRE1/HAC1/XBP1. Methods 35:395–416
Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2:326–332
DeGracia DJ, Montie HL (2004) Cerebral ischemia and the unfolded protein response. J Neurochem 91:1–8
Di Sano F, Ferraro E, Tufi R, Achsel T, Piacentini M, Cecconi F (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces apoptosis by an apoptosome-dependent but caspase 12-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem 281:2693–2700
Feng Y, Kudo M, Shimoke K, Ikeuchi T, Ebihara Y, Takasaki M (2002) Suppression of angiogenesis causes a significant delay of repair process in rat thromboembolic cerebral infarction. J Tokyo Med Univ 60:489–500
Fujita E, Kouroku Y, Jimbo A, Isoai A, Maruyama K, Momoi T (2002) Caspase-12 processing and fragment translocation into nuclei of tunicamycin-treated cells. Cell Death Differ 9:1108–1114
Imaizumi K, Miyoshi K, Katayama T, Yoneda T, Taniguchi M, Kudo T, Tohyama M (2001) The unfolded protein response and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1536:85–96
Ito D, Tanaka K, Suzuki S, Dembo T, Kosakai A, Fukuuchi Y (2001) Up-regulation of the Ire1-mediated signaling molecule, Bip, in ischemic rat brain. Neuroreport 12:4023–4028
Kalai M, Lamkanfi M, Denecker G, Boogmans M, Lippens S, Meeus A, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P (2003) Regulation of the expression and processing of caspase-12. J Cell Biol 162:457–467
Kishi S, Shimoke K, Nakatani Y, Shimada T, Okumura N, Nagai K, Shin-Ya K, Ikeuchi T (2010) Nerve growth factor attenuates 2-deoxy-d-glucose-triggered endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis via enhanced expression of GRP78. Neurosci Res 66:14–21
Kudo M, Aoyama A, Ichimori S, Fukunaga N (1982) An animal model of cerebral infarction. Homologous blood clot emboli in rats. Stroke 13:505–508
Lee AS (2005) The ER chaperone and signaling regulator GRP78/BiP as a monitor of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Methods 35:373–381
Morimoto N, Oida Y, Shimazawa M, Miura M, Kudo T, Imaizumi K, Hara H (2007) Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Neuroscience 147:957–967
Murakami Y, Aizu-Yokota E, Sonoda Y, Ohta S, Kasahara T (2007) Suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase activation and cell death by the overexpression of Bcl-xL or Bcl-2. J Biochem 141:401–410
Nakagawa T, Yuan J (2000) Cross-talk between two cysteine protease families. Activation of caspase-12 by calpain in apoptosis. J Cell Biol 150:887–894
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature 403:98–103
Nakano T, Watanabe H, Ozeki M, Asai M, Katoh H, Satoh H, Hayashi H (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ depletion induces endothelial cell apoptosis independently of caspase-12. Cardiovasc Res 69:908–915
Obeng EA, Boise LH (2005) Caspase-12 and caspase-4 are not required for caspase-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 280:29578–29587
Paschen W, Aufenberg C, Hotop S, Mengesdorf T (2003) Transient cerebral ischemia activates processing of xbp1 messenger RNA indicative of endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:449–461
Pennington R, Gatenbee C, Kennedy B, Harpending H, Cochran G (2009) Group differences in proneness to inflammation. Infect Genet Evol 9:1371–1380
Rao RV, Peel A, Logvinova A, del Rio G, Hermel E, Yokota T, Goldsmith PC, Ellerby LM, Ellerby HM, Bredesen DE (2002) Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program: role of the ER chaperone GRP78. FEBS Lett 514:122–128
Rojas-Rivera D, Caballero B, Zamorano S, Lisbona F, Hetz C (2010) Alternative functions of the BCL-2 protein family at the endoplasmic reticulum. Adv Exp Med Biol 687:33–47
Ruiz-Vela A, Opferman JT, Cheng EH, Korsmeyer SJ (2005) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK control multiple initiator caspases. EMBO Rep 6:379–385
Schroder M, Kaufman RJ (2005) ER stress and the unfolded protein response. Mutat Res 569:29–63
Shen X, Zhang K, Kaufman RJ (2004) The unfolded protein response–a stress signaling pathway of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Chem Neuroanat 28:79–92
Shibata M, Hattori H, Sasaki T, Gotoh J, Hamada J, Fukuuchi Y (2003) Activation of caspase-12 by endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Neuroscience 118:491–499
Shimoke K, Amano H, Kishi S, Uchida H, Kudo M, Ikeuchi T (2004a) Nerve growth factor attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis via suppression of caspase-12 activity. J Biochem 135:439–446
Shimoke K, Utsumi T, Kishi S, Nishimura M, Sasaya H, Kudo M, Ikeuchi T (2004b) Prevention of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. Brain Res 1028:105–111
Shimoke K, Kishi S, Utsumi T, Shimamura Y, Sasaya H, Oikawa T, Uesato S, Ikeuchi T (2005) NGF-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway prevents thapsigargin-triggered ER stress-mediated apoptosis in PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 389:124–128
Urano F, Bertolotti A, Ron D (2000) IRE1 and efferent signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 21):3697–3702
Wootz H, Hansson I, Korhonen L, Napankangas U, Lindholm D (2004) Caspase-12 cleavage and increased oxidative stress during motoneuron degeneration in transgenic mouse model of ALS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322:281–286
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107:881–891
Zong WX, Li C, Hatzivassiliou G, Lindsten T, Yu QC, Yuan J, Thompson CB (2003) Bax and Bak can localize to the endoplasmic reticulum to initiate apoptosis. J Cell Biol 162:59–69
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants-in-aid for scientific research (KAKENHI 21570152) and the “Strategic Project to Support the Formation of Research Bases at Private Universities (SENRYAKU)” (2008–2012) from MEXT (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan). This work was also supported by the Kansai University Special Research Fund, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimoke, K., Matsuki, Y., Fukunaga, K. et al. Appearance of Nuclear-sorted Caspase-12 Fragments in Cerebral Cortical and Hippocampal Neurons in Rats Damaged by Autologous Blood Clot Embolic Brain Infarctions. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31, 795–802 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9687-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9687-0