Abstract
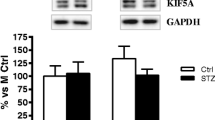
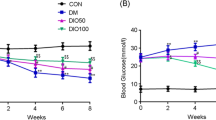
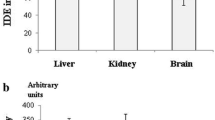
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with increased risk of impaired cognitive function. Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most common and important complications of DM. Estrogens prevent neuronal loss in experimental models of neurodegeneration and accelerate nerve regeneration. Aromatase catalyzes the conversion of androgens to estrogens and expressed in a variety of tissues including neurons. Although insulin is known to regulate the activity of aromatase there is no study about the effects of diabetes on this enzyme. Present study was designed to investigate the effects of experimental diabetes on aromatase expression in nervous system. Gender-based differences were also investigated. Rats were injected with streptozotocin to induce diabetes. At the end of 4 and 12 weeks sciatic nerve and hippocampus homogenates were prepared and evaluated for aromatase proteins. Aromatase expressions in sciatic nerves of both genders were decreased in 4 weeks of diabetes, but in 12 weeks the enzyme levels were increased in females and reached to control levels in male animals. Aromatase levels were not altered in hippocampus at 4 weeks but increased at 12 weeks in female diabetic rats. No significant differences were observed at enzyme levels of hippocampus in male diabetic rats. Insulin therapy prevented all diabetes-induced changes. In conclusion, these results indicated for the first time that, DM altered the expression of aromatase both in central and peripheral nervous systems. Peripheral nervous system is more vulnerable to damage than central nervous system in diabetes. These effects of diabetes differ with gender and compensatory neuroprotective mechanisms are more efficient in female rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaberg ML, Burch DM, Hud ZR, Zacharias MP (2008) Gender differences in the onset of diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Complicat 22:83–87
Alkayed NJ, Harukuni I, Kimes AS, London ED, Traystman RJ, Hurn PD (1998) Gender-linked brain injury in experimental stroke. Stroke 29:159–165, discussion 66
Awad N, Gagnon M, Messier C (2004) The relationship between impaired glucose tolerance, type 2 diabetes, and cognitive function. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 26:1044–1080
Azcoitia I, Sierra A, Veiga S, Honda S, Harada N, Garcia-Segura LM (2001) Brain aromatase is neuroprotective. J Neurobiol 47:318–329
Bicknell RJ (1998) Sex-steroid actions on neurotransmission. Curr Opin Neurol 11:667–671
Bisagno V, Bowman R, Luine V (2003) Functional aspects of estrogen neuroprotection. Endocrine 21:33–41
Brands AM, Biessels GJ, de Haan EH, Kappelle LJ, Kessels RP (2005) The effects of type 1 diabetes on cognitive performance: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 28:726–735
Carrer HF, Cambiasso MJ (2002) Sexual differentiation of the brain: genes, estrogen, and neurotrophic factors. Cell Mol Neurobiol 22:479–500
Faradji V, Sotelo J (1990) Low serum levels of nerve growth factor in diabetic neuropathy. Acta Neurol Scand 81:402–406
Garcia-Ovejero D, Azcoitia I, Doncarlos LL, Melcangi RC, Garcia-Segura LM (2005) Glia-neuron crosstalk in the neuroprotective mechanisms of sex steroid hormones. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 48:273–286
Garcia-Segura LM, Naftolin F, Hutchison JB, Azcoitia I, Chowen JA (1999) Role of astroglia in estrogen regulation of synaptic plasticity and brain repair. J Neurobiol 40:574–584
Garcia-Segura LM, Azcoitia I, DonCarlos LL (2001) Neuroprotection by estradiol. Prog Neurobiol 63:29–60
Garzo VG, Dorrington JH (1984) Aromatase activity in human granulosa cells during follicular development and the modulation by follicle-stimulating hormone and insulin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 148:657–662
Gasparini L, Netzer WJ, Greengard P, Xu H (2002) Does insulin dysfunction play a role in Alzheimer’s disease? Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:288–293
Gorski RA (2002) Hypothalamic imprinting by gonadal steroid hormones. Adv Exp Med Biol 511:57–70, discussion 3
Green PS, Bishop J, Simpkins JW (1997) 17 alpha-estradiol exerts neuroprotective effects on SK-N-SH cells. J Neurosci 17:511–515
Hojo Y, Hattori TA, Enami T, Furukawa A, Suzuki K et al (2004) Adult male rat hippocampus synthesizes estradiol from pregnenolone by cytochromes P45017alpha and P450 aromatase localized in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:865–870
Hoyer S (2002) The brain insulin signal transduction system and sporadic (type II) Alzheimer disease: an update. J Neural Transm 109:341–360
Islamov RR, Hendricks WA, Jones RJ, Lyall GJ, Spanier NS, Murashov AK (2002) 17Beta-estradiol stimulates regeneration of sciatic nerve in female mice. Brain Res 943:283–286
Islamov RR, Hendricks WA, Katwa LC, McMurray RJ, Pak ES et al (2003) Effect of 17 beta-estradiol on gene expression in lumbar spinal cord following sciatic nerve crush injury in ovariectomized mice. Brain Res 966:65–75
Lee SJ, McEwen BS (2001) Neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions of estrogens and their therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:569–591
Leinninger GM, Edwards JL, Lipshaw MJ, Feldman EL (2006) Mechanisms of disease: mitochondria as new therapeutic targets in diabetic neuropathy. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:620–628
McRobie DJ, Korzekwa KR, Glover DD, Tracy TS (1997) The effects of diabetes on placental aromatase activity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 63:147–153
Moreira PI, Santos MS, Seica R, Oliveira CR (2007) Brain mitochondrial dysfunction as a link between Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. J Neurol Sci 257:206–214
Nachemson AK, Lundborg G, Myrhage R, Rank F (1985) Nerve regeneration and pharmacological suppression of the scar reaction at the suture site. An experimental study on the effect of estrogen-progesterone, methylprednisoloneacetate and cis-hydroxyproline in rat sciatic nerve. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 19:255–260
Nestler JE (1993) Regulation of the aromatase activity of human placental cytotrophoblasts by insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I, and -II. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 44:449–457
Pasquier F, Boulogne A, Leys D, Fontaine P (2006) Diabetes mellitus and dementia. Diabetes Metab 32:403–414
Roglio I, Bianchi R, Giatti S, Cavaletti G, Caruso D et al (2007) Testosterone derivatives are neuroprotective agents in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1158–1168
Roglio I, Giatti S, Pesaresi M, Bianchi R, Cavaletti G et al (2008) Neuroactive steroids and peripheral neuropathy. Brain Res Rev 57:460–469
Roof RL, Hall ED (2000) Gender differences in acute CNS trauma and stroke: neuroprotective effects of estrogen and progesterone. J Neurotrauma 17:367–388
Rune GM, Frotscher M (2005) Neurosteroid synthesis in the hippocampus: role in synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience 136:833–842
Ryan CM, Williams TM, Orchard TJ, Finegold DN (1992) Psychomotor slowing is associated with distal symmetrical polyneuropathy in adults with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 41:107–113
Ryan CM, Geckle MO, Orchard TJ (2003) Cognitive efficiency declines over time in adults with type 1 diabetes: effects of micro- and macrovascular complications. Diabetologia 46:940–948
Said G (2007) Diabetic neuropathy—a review. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 3:331–340
Simpson ER (2003) Sources of estrogen and their importance. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 86:225–230
Simpson ER, Zhao Y, Agarwal VR, Michael MD, Bulun SE et al (1997) Aromatase expression in health and disease. Recent Prog Horm Res 52:185–213, discussion 4
Stamataki KE, Spina J, Rangou DB, Chlouverakis CS, Piaditis GP (1996) Ovarian function in women with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 45:615–621
Stoffel-Wagner B (2001) Neurosteroid metabolism in the human brain. Eur J Endocrinol 145:669–679
Veiga S, Garcia-Segura LM, Azcoitia I (2003) Neuroprotection by the steroids pregnenolone and dehydroepiandrosterone is mediated by the enzyme aromatase. J Neurobiol 56:398–406
Wessels AM, Scheltens P, Barkhof F, Heine RJ (2008) Hyperglycaemia as a determinant of cognitive decline in patients with type 1 diabetes. Eur J Pharmacol 585:88–96
Wise PM (2002) Estrogens and neuroprotection. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13:229–230
Acknowledgment
This study was funded by Hacettepe University Research Foundation (Project No: 06D05301001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burul-Bozkurt, N., Pekiner, C. & Kelicen, P. Diabetes Alters Aromatase Enzyme Levels in Sciatic Nerve and Hippocampus Tissues of Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 445–451 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9469-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9469-0