Abstract
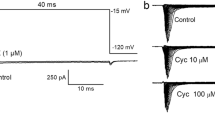
Earlier, we have shown a strong inhibitory effect of donepezil on K+-current of molluscan neurons (Solntseva et al., Comp Biochem Physiol 144, 319–326, 2007). In the present work, a possible interaction of donepezil with the external mouth of the channel was examined using, as a tool, tetraethylammonium (TEA), a classical antagonist of potassium channels. Experiments were conducted in isolated neurons of snail Helix aspersa using the two-microelectrode voltage-clamp technique. A high-threshold slow-inactivating K+-current involving Ca2+-dependent (I C) and Ca2+-independent (I K) components was recorded. The I C was estimated at 30 mV, and I K at 100 mV. The IC50 values for blocking effect of donepezil on I C varied from 5.0 to 8.9 μM in different cells. Corresponding values for I K varied from 4.9 to 9.9 μM. The IC50 values for blocking effect of TEA on I C lied in the range of 200 to 910 μM, and on I K lied in the range of 100 to 990 μM. The comparison of the effects of donepezil and TEA on the same cells revealed significant correlation between IC50 values of these effects. The value of Spearman coefficient of correlation (r) was 0.77 for I C (P < 0.05), and 0.82 for I K (P < 0.05). In the presence of TEA, the effect of donepezil, both on I C and I K, appears significantly weaker than in control solution. Dose–response curves of donepezil effect both on I C and I K were shifted right along horizontal axis when donepezil was applied in combination with TEA. Results suggest that TEA interferes with donepezil and precludes the occupation by donepezil of its own site. We suppose that the site for donepezil is situated near the TEA site with possible overlap.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andalib P, Consiglio JF, Trapani JG, Korn SJ (2004) The external TEA binding site and C-type inactivation in voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys J 87:3148–3161. doi:10.1529/biophysj.104.046664
Arias E, Gallego-Sandin S, Villarroya M, Garcia AG, Lopez MG (2005) Unequal neuroprotection afforded by the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors galantamine, donepezil, and rivastigmine in SH- SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: role of nicotinic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:1346–1353. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.090365
Bal R, Janahmadi M, Green GG, Sanders DJ (2001) Two kinds of transient outward currents, I A and I Adepol, in F76 and D1 soma membranes of the subesophageal ganglia of Helix aspersa. J Membr Biol 179:71–78. doi:10.1007/s002320010038
Cheng DH, Ren H, Tang XC (1996) Huperzine A, a novel promising acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Neuroreport 8:97–101. doi:10.1097/00001756-199612200-00020
Chung S, Lee J, Joe EH, Uhm DY (2001) Beta-amyloid peptide induces the expression of voltage dependent outward rectifying K+ channels in rat microglia. Neurosci Lett 300:67–70. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(01)01516-6
Colom LV, Diaz ME, Beers DR, Neely A, Xie W, Appel SH (1998) Role of potassium channels in amyloid-induced cell death. J Neurochem 70:1925–1934
Consiglio JF, Korn SJ (2004) Influence of permeant ions on voltage sensor function in the Kv2.1 potassium channel. J Gen Physiol 123:387–400. doi:10.1085/jgp.200308976
Gutman GA, Chandy KG, Grissmer S, Lazdunski M, McKinnon D, Pardo LA et al (2005) International union of pharmacology. LIII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of voltage-gated potassium channels. Pharmacol Rev 57:473–508. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.10
Hagiwara S, Saito N (1959) Voltage-current relations in nerve cell membrane of Onchidium verruculatum. J Physiol 148:161–179
Hayashi T, Su T (2005) The sigma receptor: evolution of the concept in neuropsychopharmacology. Curr Neuropharmacol 3:267–280. doi:10.2174/157015905774322516
Kimura M, Akasofu S, Ogura H, Sawada K (2005) Protective effect of donepezil against Abeta (1–40) neurotoxicity in rat septal neurons. Brain Res 1047:72–84. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2005.04.014
Korn SJ, Trapani JG (2005) Potassium channels. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 4:21–33. doi:10.1109/TNB.2004.842466
Maurice T, Meunier J, Feng B, Ieni J, Monaghan DT (2006) Interaction with {sigma}1 protein, but not NMDA receptor, is involved in the pharmacological activity of donepezil. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:606–614. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.097394
Miller LJ (2007) The use of cognitive enhancers in behavioral disturbances of Alzheimer’s disease. Consult Pharm 22:754–762
Pan Y, Xu X, Tong X, Wang X (2004) Messenger RNA and protein expression analysis of voltage-gated potassium channels in the brain of Abeta(25–35)-treated rats. J Neurosci Res 77:94–99. doi:10.1002/jnr.20134
Pannaccione A, Boscia F, Scorziello A, Adornetto A, Castaldo P, Sirabella R et al (2007) Up-regulation and increased activity of KV3.4 channels and their accessory subunit MinK-related peptide 2 induced by amyloid peptide are involved in apoptotic neuronal death. Mol Pharmacol 72:665–673. doi:10.1124/mol.107.034868
Rogers SL, Doody RS, Mohs RS, Friedhoff LT (1998) Donepezil improves cognition and global function in Alzheimer disease: a 15-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Donepezil Study Group. Arch Intern Med 158:1021–1031. doi:10.1001/archinte.158.9.1021
Seltzer B (2007) Donepezil: an update. Expert Opin Pharmacother 8:1011–1023. doi:10.1517/14656566.8.7.1011
Snape MF, Misra A, Murray TK, De Sousa RJ, Williams JL, Cross AJ et al (1999) A comparative study in rats of the in vitro and in vivo pharmacology of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors tacrine, donepezil and NXX-066. Neuropharmacology 38:181–193. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(98)00164-6
Solntseva EI, Bukanova JV, Marchenko E, Skrebitsky VG (2007) Donepezil is a strong antagonist of voltage-gated calcium and potassium channels in molluscan neurons. Comp Biochem Physiol 144(Part C):319–326
Trapani JG, Andalib P, Consiglio JF, Korn SJ (2006) Control of single channel conductance in the outer vestibule of the Kv2.1 potassium channel. J Gen Physiol 128:231–246. doi:10.1085/jgp.200509465
Vilner BJ, Bowen WD (2000) Modulation of cellular calcium by sigma-2 receptors: release from intracellular stores in human SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells. (2000). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292:900–911
Watanabe T, Iwasaki K, Ishikane S, Naitou T, Yoshimitsu Y, Yamagata N et al (2008) Spatial memory impairment without apoptosis induced by the combination of beta-amyloid oligomers and cerebral ischemia is related to decreased acetylcholine release in rats. J Pharmacol Sci 106:84–91. doi:10.1254/jphs.FP0071648
Wei AD, Gutman GA, Aldrich R, Chandy KG, Grissmer S, Wulff H (2005) International union of pharmacology. LII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of calcium-activated potassium channels. Pharmacol Rev 57:463–472. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.9
Yu SP (2003) Regulation and critical role of potassium homeostasis in apoptosis. Prog Neurobiol 70:363–386. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(03)00090-X
Yu B, Hu G-Y (2005) Donepezil blocks voltage-gated ion channels in rat dissociated hippocampal neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 508:15–21. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.12.004
Yu SP, Farhangrazi ZS, Ying HS, Yeh CH, Choi DW (1998) Enhancement of outward potassium current may participate in beta-amyloid peptide-induced cortical neurons death. Neurobiol Dis 5:81–88. doi:10.1006/nbdi.1998.0186
Zhang H, Cuevas J (2002) Sigma receptors inhibit high-voltage-activated calcium channels in rat sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons. J Neurophysiol 87:2867–2879
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Grant 07-04-00636 from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solntseva, E.I., Bukanova, J.V., Marchenko, E.V. et al. The Binding of Donepezil with External Mouth of K+-Channels of Molluscan Neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29, 219–224 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-008-9314-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-008-9314-x