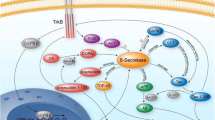
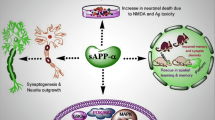
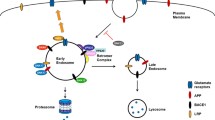
1. Recent research demonstrates the critical importance of neuroproteases for the production of peptide neurotransmitters, and for the production of toxic peptides in major neurodegenerative diseases that include Alzheimer's (AD) and Huntington's diseases. This review describes the strategies utilized to identify the appropriate proteases responsible for producing active peptides for neurotransmission, with application of such approaches for defining protease mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases.
2. Integration of multidisciplinary approaches in neurobiology, biochemistry, chemistry, proteomics, molecular biology, and genetics has been utilized for neuroprotease studies. These investigations have identified secretory vesicle cathepsin L for the production of the enkephalin opioid peptide neurotransmitter and other neuropeptides. Furthermore, new results using these strategies have identified secretory vesicle cathepsin B for the production of β-amyloid (Aβ) in the major regulated secretory pathway that provides activity-dependent secretion of Aβ peptides, which accumulate in AD.
3. CNS neuroproteases that participate in peptide neurotransmission and in neurodegenerative diseases represent new candidate drug targets that may be explored in future research for the development of novel therapeutic agents for neurological conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Allen, R. G., Peng, B., Pellegrino, M. J., Miller, E. D., Grandy, D. K., Lundblad, J. R., Washburn, C. L., and Pintar, J. E. (2001). Altered processing of pro-orphanin FQ/nociceptin and pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides in the brains of mice expressing defective prohormone convertase 2. J. Neurosci. 21:5864–5870.
Anderson, P. L., and Fletcher, C. V. (2004). Updated clinical pharmacologic considerations for HIV-1 protease inhibitors. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 1:33–39.
Bates, G. P., Mangiarini, L., Mahal, A., and Davies, S. W. (1997). Transgenic models of Huntington's disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 6:1633–1637.
Beck, B. (2000). Neuropeptides and obesity. Nutrition 16:916–923.
Berman, Y., Mzhavia, N., Polonskaia, A., Furuta, M., Steiner, D. F., Pintar, J. E., and Devi, L. A. (2000). Defective prodynorphin processing in mice lacking prohormone convertase PC2. J. Neurochem. 75:1763–1770.
Bodnar, R. J., and Klein, G. E. (2005). Endogenous opiates and behavior: 2004. Peptides 26:2629–2711.
Brion, C., Miller, S. G., and Moore, H. P. (1982). Regulated and constitutive secretion, differential effects of protein synthesis arrest on transport of glycosaminoglycan chains to the two secretory pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 267:1477–1483.
Buttle, D. J., Murata, M., Knight, C. G., and Barrett, A. J. (1992). CA074 methyl ester: A proinhibitor for intracellular cathepsin B. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 299:377–380.
Cain, B. M., Connolly, K., Blum, A. C., Vishnuvardhan, D., Marchand, J. E., Zhu, X., Steiner, D. F., and Beinfeld, M. C. (2004). Genetic inactivation of prohormone convertase (PC1) causes a reduction in cholecystokinin (CCK) levels in the hippocampus, amygdala, pons and medulla in mouse brain that correlates with the degree of colocalization of PC1 and CCK mRNA in these structures in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 89:307–313.
Carter, R. J., Lione, L. A., Humby, T., Mangiarini, L., Mahal, A., Bates, G. P., Dunnett, S. B., and Morton, A. J. (1999). Characterization of progressive motor deficits in mice transgenic for the human Huntington's disease mutation. J. Neurosci. 19:3248–3257.
Cool, D. R., Fenger, M., Snell, C. R., and Loh, Y. P. (1995). Indentification of the sorting signal motif within proopeiomelanocortin for the regulated secretory pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 14:8723–8729.
Coulter, C. L., Ross, J. T., Owens, J. A., Bennett, H. P., and McMillen, I. C. (2002). Role of pituitary POMC-peptides and insulin-like growth factor II in the developmental biology of the adrenal gland. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 110:99–105.
Cuajungco, M. P., Frederickson, C. J., and Bush, A. I. (2005). Amyloid-β metal interaction and metal chelation. Subcell. Biochem. 38:235–254.
Davies, S. W., Turmaine, M., Cozens, B. A., DiFiglia, M., Sharp, A. H., Ross, C. A., Scherzinger, E., Wanker, E. E., Mangiarini, L., and Bates, G. P. (1997). Formation of neuronal intranuclear inclusions underlies the neurological dysfunction in mice transgenic of the HD mutation. Cell 90:537–548.
DiFiglia, M., Sapp, E., Chase, K. O., Davies, S. W., Bates, G. P., Vonsattel, J. P., and Aronin, N. (1997). Aggregation of huntingtin in neuronal intranuclear inclusions and dystrophic neurites in brain. Science 277:1990–1993.
Efthimiopoulos, S., Vassilacopoulou, D., Rippellino, J. A., Tezapsidis, N., and Robakis, N. K. (1996). Cholinergic agonists stimulate secretion of soluble full-length amyloid precursor protein in neuroendocrine cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93:8046–8050.
Farber, S. A., Nitsch, R. M., Schulz, J. G., and Wurtman, R. J. (1995). Regulated secretion of beta-amyloid precursor protein in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 15:7442–7451.
Fugère, M., and Day, R. (2005) Cutting back on pro-protein convertases: The latest approaches to pharmacological inhibition. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 26:294–301.
Furuta, M., Carroll, R., Martin, S., Swift, H. H., Ravazzola, M., Orci, L., and Steiner, D. F. (1998). Incomplete processing of proinsulin to insulin accompanied by elevation of Des-31,32 proinsulin intermediates in islets of mice lacking active PC2. J. Biol. Chem. 273:3431–3437.
Furuta, M., Yano, H., Zhou, A., Rouillé, Y., Holst, J. J., Carroll, R., Ravazzola, M., Orci, L., Furuta, H., and Steiner, D. F. (1997). Defective prohormone processing and altered pancreatic islet morphology in mice lacking active SPC2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94:6646–6651.
Gensberg, K., Jan, S., and Matthews, G. M. (1998). Subtilisin-related serine proteases in the mammalian constitutive secretory pathway. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:11–17.
Gumbiner, G., and Kelly, R. B. (1982). Two distinct intracellular pathways transport secretory and membrane glycoproteins to the surface of pituitary tumor cells. Cell 28:51–55.
Hodgson, J. G., Agopyan, N., Gutekunst, C. A., Leavitt, B. R., LePiane, F., Singaraja, R., Smith, D. J., Bissada, N., McCutcheon, K., Nasir, J., Jamot, L., Li, X.-J., Stevens, M. E., Rosemond, E., Roder, J. C., Phillips, A. G., Rubin, E. M., Hersch, S. M., and Hayden, M. R. (1999). A YAC mouse model for Huntington's disease with full-length mutant huntingtin, cytoplasmic toxicity, and selective striatal neurodegeneration. Neuron 23:181–192.
Holmes, A., Heilig, M., Rupniak, N. M., Steckler, T., and Griebel, G. (2003). Neuropeptide systems as novel therapeutic targets for depression and anxiety disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 24:580–588.
Holsboer, F. (2003). Corticotropin-releasing hormone modulators and depression. Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 4:46–50.
Hook, V. Y. H., Azaryan, A. V., Hwang, S.-R., and Tezapsidis, N. (1994). Proteases and the emerging role of protease inhibitors in prohormone processing. FASEB J. 8:1269–1278.
Hook, V. Y. H., and Reisine, T. D. (2003). Cysteine proteases are the major β-secretase in the regulated secretory pathway that provides most of the β-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease: Role of BACE 1 in the constitutive secretory pathway. J. Neurosci. Res. 74:393–405.
Hook, V. Y. H., Toneff, T., Aaron, W., Yasothornsrikul, S., Bundey, R., and Reisine, T. (2002). β-Amyloid peptide in regulated secretory vesicles of chromaffin cells: Evidence for multiple cysteine proteolytic activities in distinct pathways for β-secretase activity in chromaffin vesicles. J. Neurochem. 81:237–256.
Hook, V., Toneff, T., Bogyo, M., Greenbaum, D., Medzihradszky, K. F., Neveu, J., Lane, W., Hook, G., and Reisine, T. (2005). Inhibition of cathepsin B reduces β-amyloid production in regulated secretory vesicles of neuronal chromaffin cells: Evidence for cathepsin B as a candidate β-secretase of Alzheimer's disease. Biol. Chem. 386:931–940.
Hook, V., Yasothornsrikul, S., Greenbaum, D., Medzihradszky, K. F., Troutner, K., Toneff, T., Bundey, R., Reinheckel, T., Peters, C., and Bogyo, M. (2004). Cathepsin L and Arg/Lys aminopeptidase: A distinct prohormone processing pathway for the biosynthesis of peptide neurotransmitters and hormones. Biol. Chem. 385:473–480.
Hoozemans, J. J. M., and O’Banion, M. K. (2005). The role of COX-1 and COX-2 in Alzheimer's disease pathology and the therapeutic potentials of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 4:307–315.
Hosaka, M., Nagahama, M., Kim, W. S., Watanabe, T., Hatsuzawa, K., Ikemizu, J., Murakami, K., and Nakayama, K. (1991). Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 266:12127–12130.
Hughes, D. B., and Britton, M. L. (2005). Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers for prevention and treatment of nephropathy associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacotherapy 25:1602–1620.
Hussain, I., Powell, D., Howlett, D. R., Tew, D. G., Meek, T. D., Chapman, C., Gloger, I. S., Murphy, K. E., Southan, C. D., Ryan, D. M., Smith, T. S., Simmons, D. L., Walsha, F. S., Dingwall, C., and Christie, G. (1999). Identification of a novel aspartic protease (Asp 2) as β-Secretase. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 14:419–427.
Ishidoh, K., and Kominami, E. (2002). Processing and activation of lysosomal proteinases. Biol. Chem. 383:1827–1831.
Iverson, L. L., Mortishire-Smith, R. J., Pollack, S. J., and Shearman, M. S. (1995). The toxicity in vitro of β-amyloid protein. Biochem. J. 311:1–16.
Jacobson, L. (2005). Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical axis regulation. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 34:271–292.
Jolly-Tornetta, C., Gao, Z. Y., Lee, V. M., and Wolf, B. A. (1998). Regulation of amyloid precursor protein secretion by glutamate receptors in human Ntera 2 neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 272:140015–140021.
Kanjhan, R. (1995). Opioids and pain. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 22:397–403.
Landles, C., and Bates, G. P. (2004). Huntingtin and the molecular pathogenesis of Huntington's disease. Fourth in molecular medicine review series. EMBO Rep. 5:958–963.
Law, P. Y., and Loh, H. H. (1999). Regulation of opioid receptor activities. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 289:607–624.
Lin, L., and Achermann, J. C. (2004). The adrenal. Horm. Res. 62(Suppl. 3):22–29.
Lin, X., Koelsch, G., Wu, S., Downs, D., Dashti, A., and Tang, J. (2000). Human aspartic protease memapsin 2 cleaves the β-secretase site of β-amyloid precursor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97:1456–1460.
Lipton, S. A. (2005). The molecular basis of memantine action in Alzheimer's disease and other neurologic disorders: Low-affinity, uncompetitive antagonism. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2:155–165.
Lodish, H., Berk, A., Zipursky, S. L., Matsudaira, P., Baltimore, D., and Darnell, J. (1999). Molecular Cell Biology, 4th edn., W.H. Freeman, New York.
Loh, Y. P., Kim, T., Rodriguez, Y. M., and Cawley, N. X. (2004). Secretory granule biogenesis and neuropeptide sorting to the regulated secretory pathway in neuroendocrine cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 22:63–71.
MacDonald, M. E., Ambrose, C. M., Duyao, M. P., Myers, R. H., Lin, C., Srinidhi, L., Barnes, G., Taylor, S. A., James, M., Groot, N., MacFarlane, H., Jenkins, B., Anderson, M. A., Wexler, N. S., Gusella, J. F., Bates, G. P., Baxendale, S., Hummerich, H., Kirby, S., North, M., Youngman, S., Mott, R., Zehetner, G., Sedlacek, Z., Poustka, A., Frischauf, A.-M., Lehrach, H., Buckler, A. J., Church, D., Doucette-Stamm, L., O’Donovan, M. C., Riba-Ramirez, L., Shah, M., Stanton, V. P., Strobel, S. A., Draths, K. M., Wales, J. L., Dervan, P., Housman, D. E., Altherr, M., Shiang, R., Thompson, L., Fielder, T., Wasmuth, J. J., Tagle, D., Valdes, J., Elmer, L., Allard, M., Castilla, L., Swaroop, M., Blanchard, K., Collins, F. S., Snell, R., Holloway, T., Gillespie, K., Datson, N., Shaw, D., and Harper, P. S. (1993). A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Cell 72:971–983.
Matsumoto, K., Mizoue, K., Kitamura, K., Tse, W.-C., Huber, C. P., and Ishida, T. (1999). Structural basis of inhibition of cysteine proteases by E-64 and its derivatives. Biopolymers 51:99–107.
Mende-Mueller, L. M., Toneff, T., Hwang, S.-R., Chesselet, M.-F., and Hook, V. Y. H. (2001). Tissue-specific proteolysis of huntingtin (htt) in human brain: Evidence of enhanced levels of N- and C-terminal htt fragments in Huntington's disease striatum. J. Neurosci. 21:1830–1837.
Mielniczuk, L., and Stevenson, L. W. (2005). Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type I receptor blockers in the management of congestive heart failure patients. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 20:250–255.
Miller, R., Aaron, W., Toneff, T., Vishnuvardhan, D., Beinfeld, M., and Hook, V. Y. H. (2003a). Obliteration of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone derived from POMC in pituitary and brains of PC2-deficient mice. J. Neurochem. 86:556–563.
Miller, R., Toneff, T., Vishnuvardhan, D., Beinfeld, M., and Hook, V. Y. H. (2003b). Selective roles for the PC2 processing enzyme in the regulation of peptide neurotransmitter levels in brain and peripheral neuroendocrine tissues of PC2 deficient mice. Neuropeptides 37:140–148.
Mukerjee, A., and Hersh, L. B. (2002). Regulation of amyloid β-peptide levels by enzymatic degradation. J. Alzheimers Dis. 4:341–348.
Munglani, R., Hudspith, M. J., and Hunt, S. P. (1996). The therapeutic potential of neuropeptide Y. Analgesic, anxiolytic and antihypertensive. Drugs 52:371–389.
Muñoz-Ruiz, P., Rubio, L., García-Palomero, E., Dorronsoro, I., del Monte-Millán, M., Valenzuela, R., Usán, P., de Austria, C., Bartolini, M., Andrisano, V., Bidon-Chanal, A., Orozco, M., Luque, F. J., Medina, M., and Martínez, A. (2005). Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: New disease-modifying agents for Alzheimer's disease. J. Med. Chem. 48:7223–7233.
Musial, B. L., Chojnacki, J. K., and Coleman, C. I. (2004). Atazanavir: A new protease inhibitor to treat HIV infection. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 61:1365–1374.
Nitsch, R. J., Farber, S. A., Growdon, J. H., and Wurtman, R. J. (1993). Release of amyloid beta-protein precursor derivatives by electrical depolarization of rat hippocampal slices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90:5191–5193.
Nitsch, R. M., Slack, B. E., Wurtman, R. J., and Growdon, J. H. (1992). Release of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor derivatives by activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Science 258:304–307.
Pan, H., Nanno, D., Che, F. Y., Zhu, X., Salton, S. R., Steiner, D. F., Fricker, L. D., and Devi, L. A. (2005). Neuropeptide processing profile in mice lacking prohormone convertase-1. Biochemistry 44:4939–4948.
Randolph, J. T., and Degoey, D. A. (2004). Peptidomimetic inhibitors of HIV protease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 4:1079–1095.
Richardson, D. E. (1990). Central stimulation-induced analgesia in humans—Modulation by endogenous opioid peptides. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 6:33–37.
Rubinsztein, D. C., Leggo, J., Chiano, M., Korn, S., Dodge, A., Norbury, G., Rosser, E., and Craufurd, D. (1997). Homozygotes and heterozygotes for ciliary neurotrophic factor null alleles do not show earlier onset of Huntington's disease. Neurology 49:890–892.
Schiller, M. R., Mende-Mueller, L., Moran, K., Meng, M., Miller, K. W., and Hook, V. Y. H. (1995). “Prohormone thiol protease” (PTP) processing of recombinant proenkephalin. Biochemistry 34:7988–7995.
Schott, P. A., Hokfelt, T., and Ogren, S. O. (2000). Galanin and spatial learning in the rat. Evidence for a differential role for galanin in subregions of the hippocampal formation. Neuropharmacology 39:1386–1403.
Seidah, N. G., and Prat, A. (2002). Precursor convertases in the secretory pathway, cytosol and extracellular milieu. Essays Biochem. 38:79–94.
Selkoe, D. J. (2001). Alzheimer's disease: Genes, proteins, therapy. Physiol. Rev. 81:741–761.
Sica, D. A. (2005). Pharmacotherapy review: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. J. Clin. Hypertens. 7:485–488.
Sinha, S., Anderson, J. P., Barbour, R., Basi, G. S., Caccavello, R., Davis, D., Doan, M., Dovey, H. F., Frigon, N., Hong, J., Jacobson-Croak, K., Jewett, N., Keim, P., Knops, J., Lieberburg, I., Power, M., Tan, H., Tatsuno, G., Tung, J., Schenk, D., Seubert, P., Suomensaari, S. M., Wang, S., Walker, D., Zhao, J., Mcconlogue, L., and John, V. (1999). Purification and cloning of amyloid precursor protein β-secretase from human brain. Nature 402:537–540.
Sisodia, S. S. (1999). Alzheimer's disease: Perspectives for the new millennium. J. Clin. Invest. 104:1169–1170.
Smith, J. D., and Levin-Allerhand, J. A. (2003). Potential use of estrogen-like drugs for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 20:277–282.
Song, E.-S., Juliano, M. A., Juliano, L., and Hersh, L. B. (2003). Substrate activation of insulin-degrading enzyme (insulysin). A potential target for drug development. J. Biol. Chem. 278:49789–49794.
Steiner, D. F. (1998). The proprotein convertases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2:31–39.
Steiner, R. A., Hohmann, J. G., Holmes, A., Wrenn, C. C., Cadd, G., Juréus, A., Clifton, D. K., Luo, M., Gutshall, M., Ma, S. Y., Mufson, E. J., and Crawley, J. N. (2001). Galanin transgenic mice display cognitive and neurochemical deficits characteristic of Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98:4184–4189.
Stuve, O., Youssef, S., Steinman, L., and Zamvil, S. S. (2003). Statins as potential therapeutic agents in neuroinflammatory disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 16:393–401.
Tezapsidis, N., Li, H.-G., Rippellino, J. A., Efthimiopoulos, S., Vassilacopoulou, D., Sambamurti, K., Toneff, T., Yasothornsrikul, S., Hook, V. Y. H., and Robakis, N. K. (1998). Release of nontransmembrane, full-length Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein from the lumenar surface of chromaffin granule membranes. Biochemistry 37:1274–1282.
Turk, B., Turk, D., and Turk, V. (2000). Lysosomal cysteine proteases: More than scavengers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1477:98–111.
Ugleholdt, R., Zhu, X., Deacon, C. F., Ørskov, C., Steiner, D. F., and Holst, J. J. (2004). Impaired intestinal proglucagon processing in mice lacking prohormone convertase 1. Endocrinology 145:1349–1355.
Vassar, R., Bennet, B. D., Babu-Khan, S., Kahn, S., Mendiaz, E. A., Denis, P., Teplow, D. B., Ross, S., Amarante, P., Loeloff, R., Luo, Y., Fisher, S., Fuller, J., Edenson, S., Lile, J., Jarosinski, M. A., Biere, A. L., Curran, E., Burgess, T., Louis, J.-C., Collins, F., Treanor, J., Rogers, G., and Citron, M. (1999). β-Secretase cleavage of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 286:735–741.
Vassilacopoulou, D., Ripellino, J. A., Tezapsidis, N., Hook, V. Y. H., and Robakis, N. K. (1995). Full-length and truncated Alzheimer amyloid precursors in chromaffin granules: Solubilization of membrane amyloid precursor is mediated by an enzymatic mechanism. J. Neurochem. 64:2140–2146.
Villeneuve, P., Feliciangeli, S., Croissandeau, G., Seidah, N. G., Mbikay, M., Kitabgi, P., and Beaudet, A. (2002). Altered processing of the neurotensin/neuromedin N precursor in PC2 knock down mice: A biochemical and immunohistochemical study. J. Neurochem. 82:783–793.
Vonsattel, J. P., and DiFiglia, M. (1998). Huntington disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 57:369–384.
Walker, P., Grouzmann, E., Burnier, M., and Waeber, B. (1991). The role of neuropeptide Y in cardiovascular regulation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 12:111–115.
Wieland, H. A., Hamilton, B. S., Krist, B., and Doods, H. N. (2000). The role of NPY in metabolic homeostasis: Implications for obesity therapy. Expert Opin. Invest. Drugs 9:1327–1346.
Wolf, B. A., Wertkin, A. M., Jolly, Y. C., Yasukda, R. P., Wolfe, B. B., Konrad, R. J., Manning, D., Ravi, S., Williamson, J. R., and Lee, V. M. (1995). Muscarinic regulation of Alzheimer's disease amyloid precursor protein secretion and amyloid β-protein production in human neuronal NT2N cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270:4916–4922.
Yamamoto, A., Hara, T., Tomoo, K., Ishida, T., Fujii, T., Hata, Y., Murata, M., and Kitamura, K. (1997). Binding mode of CA074, a specific irreversible inhibitor, to bovine cathepsin B as determined by X-ray crystal analysis of the complex. J. Biochem. 121:974–977.
Yan, R., Bienkowski, M. J., Shuck, M. E., Miao, H., Tory, M. C., Pauley, A. M., Brashler, J. R., Stratman, N. C., Mathews, W. R., Buhl, A. E., Carter, D. B., Tomasselli, A. G., Parodi, L. A., Heinrikson, R. L., and Gurney, M. E. (1999). Membrane-anchored aspartyl protease with Alzheimer's disease β-secretase activity. Nature 402:533–537.
Yasothornsrikul, S., Aaron, W., Toneff, T., and Hook, V. Y. H. (1999). Evidence for the proenkephalin processing enzyme prohormone thiol protease (PTP) as a multicatalytic cysteine protease complex: Activation by glutathione localized to secretory vesicles. Biochemistry 38:7421–7430.
Yasothornsrikul, S., Greenbaum, D., Medzihradszky, K. F., Toneff, T., Bundey, R., Miller, R., Schilling, B., Petermann, I., Dehnert, J., Logvinova, A., Goldsmith, P., Neveu, J. M., Lane, W. S., Gibson, B., Reinheckel, T., Peters, C., Bogyo, M., and Hook, V. (2003). Cathepsin L in secretory vesicles functions as a prohormone-processing enzyme for production of the enkephalin peptide neurotransmitter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100:9590–9595.
Zhou, A., Webb, G., Zhu, X., and Steiner, D. F. (1999). Proteolytic processing in the secretory pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 274:20745–20748.
Zhu, X., Orci, L., Carroll, R., Norrbom, C., Ravazzola, M., and Steiner, D. F. (2002a). Severe block in processing of proinsulin to insulin accompanied by elevation of des-64,65 proinsulin intermediates in islets of mice lacking prohormone convertase 1/3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99:10299–10304.
Zhu, X., Zhou, A., Dey, A., Norrbom, C., Carroll, R., Zhang, C., Laurent, V., Lindberg, I., Ugleholdt, R., Holst, J. J., and Steiner, D. F. (2002b). Disruption of PC1/3 expression in mice causes dwarfism and multiple neuroendocrine peptide processing defects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99:10293–10298.
Zimanyi, I. A., Fathi, Z., and Poindexter, G. S. (1998). Central control of feeding behavior by neuropeptide Y. Curr. Pharm. Des. 4:349–366.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author appreciates support of this research from the National Institutes of Health, American Life Science Pharmaceuticals (ALSP) Inc., and the Hereditary Disease Foundation. Dr. V. Hook holds equity in ALSP Inc., and serves on the Scientific Advisory Board of ALSP. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California, San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hook, V.Y.H. Protease Pathways in Peptide Neurotransmission and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 447–467 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9047-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9047-7