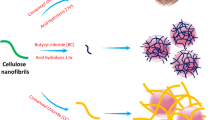
Abstract
As a biological material, cellulose with a low carbon footprint is better for preparing emulsions than traditional surfactant emulsions. However, the high hydrophilicity of nanocellulose is not conducive to its adsorption at the oil–water interface, resulting in a low emulsification capacity of Pickering emulsion. This work applied 2,2,6,6-tetramethy1-1-piperidyloxy(TEMPO)-mediated oxidation and sodium periodate oxidation to prepare nanocellulose with carboxyl and aldehyde groups, and studied the effects of bonding forms on the hydrophilicity of bovine serum albumin (BSA)/nanocellulose composites. Compared with pure components, the composite products prepared by adsorbing or grafting had improved effects in the emulsification by increasing viscosity and reducing surface wettability. With adsorbed BSA, the composite showed a higher hydrophobicity, and the corresponding Pickering emulsion had an extended oil fraction of 60%. Due to the strong chemical bonding, the grafted composite can stabilize the Pickering emulsion of a 70% oil fraction with stable droplets of uniform size. This study provides an idea for improving the emulsification performance of nanocellulose through protein bonding.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Aaen R, Brodin FW, Simon S, Heggset EB, Syverud K (2019) Oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanofibrils—The effects of Ionic strength and pH. Nanomaterials 9:259. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020259
Bergfreund J, Sun QY, Fischer P, Bertsch P (2019) Adsorption of charged anisotropic nanoparticles at oil-water interfaces. Nanoscale Adv 1:4308–4312. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NA00506D
Binks BP (2002) Particles as surfactants—similarities and differences. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 7:21–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-0294(02)00008-0
Brand J, Pecastaings G, Sèbe G (2017) A versatile method for the surface tailoring of cellulose nanocrystal building blocks by acylation with functional vinyl esters. Carbohydr Polym 169:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.03.077
Chen QH, Liu TX, Tang CH (2019) Tuning the stability and microstructure of fine Pickering emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals. Ind Crops Prod 141:111733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111733
Chen Y, Yao M, Peng S, Fang Y, Wan L, Shang W, Xiang D, Zhang W (2023) Development of protein-polyphenol particles to stabilize high internal phase Pickering emulsions by polyphenols’ structure. Food Chem 428:136773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136773
Chevalier Y, Bolzinger MA (2013) Emulsions stabilized with solid nanoparticles: Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf A 439:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.02.054
Dalei G, Das S, Pradhan M (2022) Dialdehyde cellulose as a niche material for versatile applications: an overview. Cellulose 29:5429–5461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04619-1
Fujisawa S, Togawa E, Kuroda K (2017) Nanocellulose-stabilized Pickering emulsions and their applications. Sci Technol Adv Mater 18:959–971. https://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2017.1401423
Goi Y, Fujisawa S, Saito T, Yamane K, Kuroda K, Isogai A (2019) Dual Functions of TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibers in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: A Pickering Emulsifier and a Unique Dispersion Stabilizer. Langmuir 35:10920–10926. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b01977
Gong X, Wang Y, Chen L (2017) Enhanced emulsifying properties of wood-based cellulose nanocrystals as Pickering emulsion stabilizer. Carbohydr Polym 169:295–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.04.024
Guida C, Aguiar AC, Cunha RL (2021) Green techniques for starch modification to stabilize Pickering emulsions: a current review and future perspectives. Curr Opin Food Sci 38:52–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2020.10.017
Hou C, Zhang J, Zhang X, Wang Y, Li T, Xia B, Jiang J, Dong W (2022) High strength chitin nanocrystal/alginate filament prepared by wet-spinning in “green” coagulating bath. Cellulose 29:8611–8621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04814-0
Isogai A (2021) Emerging Nanocellulose Technologies: Recent Developments. Adv Mater 33:2000630. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000630
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NR00583E
Jiang J, Chen H, Liu L, Yu J, Fan Y, Saito T, Isogai A (2020) Influence of Chemical and Enzymatic TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation on Chemical Structure and Nanofibrillation of Lignocellulose. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:14198–14206. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c05291
Li X, Ding L, Zhang Y, Wang B, Jiang Y, Feng X, Mao Z, Sui X (2019) Oil-in-water Pickering emulsions from three plant-derived regenerated celluloses. Carbohydr Polym 207:755–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.037
Liu F, Tang CH (2014) Emulsifying Properties of Soy Protein Nanoparticles: Influence of the Protein Concentration and/or Emulsification Process. J Agric Food Chem 62:2644–2654. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf405348k
Liu F, Zheng J, Huang CH, Tang CH, Ou SY (2018) Pickering high internal phase emulsions stabilized by protein-covered cellulose nanocrystals. Food Hydrocolloids 82:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.03.047
Liu Y, Shi Z, Zou Y, Yu J, Liu L, Fan Y (2023) Comparison of cellulose and chitin nanofibers on Pickering emulsion stability—Investigation of size and surface wettability contribution. Int J Biol Macromol 235:123754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123754
Lu Y, Li J, Ge L, Xie W, Wu D (2021) Pickering emulsion stabilized with fibrous nanocelluloses: Insight into fiber flexibility-emulsifying capacity relations. Carbohydr Polym 255:117483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117483
Meng Y, Sun W, Yang H, Wang W, Jin N, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Lü H (2020) Fine tuning of surface properties of SiO2 nanoparticles for the regulation of Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf A 592:124603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124603
Miao C, Atifi S, Hamad WY (2020) Properties and stabilization mechanism of oil-in-water Pickering emulsions stabilized by cellulose filaments. Carbohydr Polym 248:116775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116775
Pang B, Liu H, Liu P, Peng X, Zhang K (2018) Water-in-oil Pickering emulsions stabilized by stearoylated microcrystalline cellulose. J Colloid and Interface Sci 513:629–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.11.079
Pang B, Liu H, Zhang K (2021) Recent progress on Pickering emulsions stabilized by polysaccharides-based micro/nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 296:102522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102522
Sarkar A, Dickinson E (2020) Sustainable food-grade Pickering emulsions stabilized by plant-based particles. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 49:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2020.04.004
Soni R, Asoh TA, Hsu YI, Uyama H (2022) Freshwater-durable and marine-degradable cellulose nanofiber reinforced starch film. Cellulose 29:1667–1678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04410-8
Wang J, Yu M, Yang C (2019) Colloidal TiO2 nanoparticles with near-neutral wettability: An efficient Pickering emulsifier. Colloids Surf A 570:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.03.035
Wang Y, Li X, Li T, Wang Y, Jiang J, Zhang X, Huang J, Xia B, Shum HC, Yang Z, Dong W (2023) Ultra-stable pickering emulsions stabilized by zein-cellulose conjugate particles with tunable interfacial affinity. Food Hydrocolloids 134:108055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.108055
Yan X, Ma C, Cui F, McClements DJ, Liu X, Liu F (2020) Protein-stabilized Pickering emulsions: Formation, stability, properties, and applications in foods. Trends Food Sci Technol 103:293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.07.005
Zhang L, Zhang Q, Zheng Y, He Z, Guan P, He X, Hui L, Dai Y (2018) Study of Schiff base formation between dialdehyde cellulose and proteins, and its application for the deproteinization of crude polysaccharide extracts. Ind Crops Prod 112:532–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.12.056
Zhou Y, Saito T, Bergström L, Isogai A (2018) Acid-Free Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals by TEMPO Oxidation and Subsequent Cavitation. Biomacromol 19:633–639. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.7b01730
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21975108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mengzhang Ke: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft.Yijie Wang: Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation.Ting Li: Formal analysis, Investigation.Jie Jiang: Validation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.Weifu Dong: Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This work is unapplicable for both human and animal studies.
Consent to publication
This work is original and has not been published elsewhere, nor is it under consideration by another journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ke, M., Wang, Y., Li, T. et al. Comparison of Pickering emulsion stabilized by nanocellulose-protein composite particles through adsorption and grafting. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05897-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05897-7