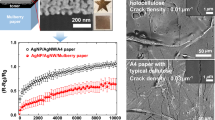
Abstract
Environmental concerns arising from industrial growth, and in particular the accumulation of waste and toxic substances, have prompted the demand for sustainable and ecofriendly solutions. Cellulose, known for its ecological attributes, is a cost-effective and recyclable material that is suitable for replacing silicon substrates, particularly in flexible electronic devices. However, the limitations of 2D techniques, such as inkjet and screen printing, necessitate the adoption of 3D printing technologies in this domain. This study introduces a novel approach utilizing fused deposition modeling printing (FDM) to create a mulberry paper (MP)-graphene filament strain sensor. This process involves the melting and extrusion of multifunctional filaments, which requires a meticulous examination of the bonding between MP and polymers. To optimize the bonding between MP and graphene filaments, adjustments were made to the nozzle and platform temperatures, as well as the printing gap, resulting in a substantial binding strength of 3.85 N, exceeding that of conventional paper by more than 2.5-fold (1.58 N). Leveraging this impressive binding strength, the strain sensor achieved a remarkable gauge factor of approximately 648 and commendable linearity of 0.94. The practical application of the FDM-based MP-graphene filament strain sensor in a household wind speed sensing system showed promising results within a wind range of 8.9–9.4 m/s. The integration of cellulose-based MP and graphene filaments via FDM printing is a pivotal advancement in the development of eco-friendly high-performance strain sensors, offering potential solutions to environmental concerns and application in flexible electronic devices.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confrm that data supporting the fndings of this study are available within the article.
References
Ahmed S, Nauman S, Khan ZM (2021) Development of TPU/CNPs flexible composite strain sensors using additive manufacturing (AM) for structural health monitoring (SHM) of aerospace components. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/IBCAST51254.2021.9393013
Aleeva Y, Pignataro B (2014) Recent advances in upscalable wet methods and ink formulations for printed electronics. J Mater Chem C 2:6436–6453. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC00618F
Boland CS, Khan U, Backes C, O’Neill A, McCauley J, Duane S, Shanker R, Liu Y, Jurewicz I, Dalton AB (2014) Sensitive, high-strain, high-rate bodily motion sensors based on graphene–rubber composites. ACS Nano 8:8819–8830. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn503454h
Borthakur A, Singh P (2021) The journey from products to waste: a pilot study on perception and discarding of electronic waste in contemporary urban India. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:24511–24520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09030-6
Bu Y, Shen T, Yang W, Yang S, Zhao Y, Liu H, Zheng Y, Liu C, Shen C (2021) Ultrasensitive strain sensor based on superhydrophobic microcracked conductive Ti3C2Tx MXene/paper for human-motion monitoring and E-skin. Sci Bull 66:1849–1857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2021.04.041
Cai Y, Shen J, Dai Z, Zang X, Dong Q, Guan G, Li LJ, Huang W, Dong X (2017) Extraordinarily stretchable all-Carbon collaborative nanoarchitectures for epidermal sensors. Adv Mater 29:1606411. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201606411
Camargo JC, Machado ÁR, Almeida EC, Silva EFMS (2019) Mechanical properties of PLA-graphene filament for FDM 3D printing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103:2423–2443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03532-5
Casiraghi C, Macucci M, Parvez K, Worsley R, Shin Y, Bronte F, Borri C, Paggi M, Fiori G (2018) Inkjet printed 2D-crystal based strain gauges on paper. Carbon 129:462–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.12.030
Chen M, Qin X, Zeng G (2017) Biodegradation of carbon nanotubes, graphene, and their derivatives. Trends Biotechnol 35:836–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.12.001
Deiner LJ, Reitz TL (2017) Inkjet and aerosol jet printing of electrochemical devices for energy conversion and storage. Adv Eng Mater 19:1600878. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201600878
Gupta B, Revagade N, Hilborn J (2007) Poly (lactic acid) fiber: an overview. Prog Polym Sci 32:455–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.01.005
Ha H, Müller S, Baumann R-P, Hwang B (2023) PeakForce quantitative nanomechanical mapping for surface energy characterization on the nanoscale: a mini-review. Facta Univ Ser Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.22190/FUME221126001H
Ha H, Qaiser N, Yun TG, Cheong JY, Lim S, Hwang B (2023) Sensing mechanism and application of mechanical strain sensor: a mini-review. Facta Univ Ser: Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.22190/FUME230925043H
Hazra A, Das S, Ganguly A, Das P, Chatterjee P, Murmu N, Banerjee P (2019) Plasma arc technology: a potential solution toward waste to energy conversion and of GHGs mitigation. Waste Manag Res 2:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2784-1_19
Hu G, Kang J, Ng LW, Zhu X, Howe RC, Jones CG, Hersam MC, Hasan T (2018) Functional inks and printing of two-dimensional materials. Chem Soc Rev 47:3265–3300. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CS00084K
Hwang B, Han Y, Matteini P (2022) Bending fatigue behavior of Ag nanowire/Cu thin-film hybrid interconnects for wearable electronics. Facta Univ Ser: Mech Eng 20:553–560. https://doi.org/10.22190/FUME220730040H
Islam A, Ahmed T, Awual MR, Rahman A, Sultana M, Aziz AA, Monir MU, Teo SH, Hasan M (2020) Advances in sustainable approaches to recover metals from e-waste-A review. J Clean Prod 244:118815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118815
Jabari E, Toyserkani E (2015) Micro-scale aerosol-jet printing of graphene interconnects. Carbon 91:321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.04.094
Kalita NK, Damare NA, Hazarika D, Bhagabati P, Kalamdhad A, Katiyar V (2021) Biodegradation and characterization study of compostable PLA bioplastic containing algae biomass as potential degradation accelerator. Environ Chall 3:100067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100067
Kantaros A, Karalekas D (2013) Fiber Bragg grating based investigation of residual strains in ABS parts fabricated by fused deposition modeling process. Mater Des 50:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.02.067
Kantaros A, Karalekas D (2014) FBG based in situ characterization of residual strains in FDM process. Residual Stress 8:333–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-00876-9_41
Ke SH, Guo PW, Pang CY, Tian B, Luo CS, Zhu HP, Wu W (2020) Screen-printed flexible strain sensors with ag nanowires for intelligent and tamper‐evident packaging applications. Adv Mater Technol 5:1901097. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.201901097
Kim S, Lee H, Kim D, Ha H, Qaiser N, Yi H, Hwang B (2020) Ethylcellulose/Ag nanowire composites as multifunctional patchable transparent electrodes. Surf Coat Technol 394:125898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125898
Kim H, Qaiser N, Hwang B (2023) Electro-Mechanical response of stretchable PDMS composites with a hybrid Filler System. Facta Univ Ser Mech Eng 21:51–61. https://doi.org/10.22190/FUME221205002K
Kim K, Yankowitz M, Fallahazad B, Kang S, Movva HCP, Huang S, Larentis S, Corbet CM, Taniguchi T, Watanabe K, Banerjee SK, LeRoy BJ, Tutuc E (2016) Van der waals heterostructures with high accuracy rotational alignment. Nano Lett 16:1989–1995. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b05263
Kurapati R, Martìn C, Palermo V, Nishina Y, Bianco A (2021) Biodegradation of graphene materials catalyzed by human eosinophil peroxidase. Faraday Discuss 227:189–203. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FD00094A
Li T, Chen C, Brozena AH, Zhu JY, Xu L, Driemeier C, Dai J, Rojas OJ, Isogai A, Wagberg L, Hu L (2021) Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material. Nature 590:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03167-7
Li Q, Liu H, Zhang S, Zhang D, Liu X, He Y, Mi L, Zhang J, Liu C, Shen C (2019) Superhydrophobic electrically conductive paper for ultrasensitive strain sensor with excellent anticorrosion and self-cleaning property. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:21904–21914. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b03421
Li B, Zhang S, Zhang L, Gao Y, Xuan F (2022) Strain sensing behavior of FDM 3D printed carbon black filled TPU with periodic configurations and flexible substrates. J Manuf Process 74:283–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.12.020
Liao X, Zhang Z, Liao Q, Liang Q, Ou Y, Xu M, Li M, Zhang G, Zhang Y (2016) Flexible and printable paper-based strain sensors for wearable and large-area green electronics. Nanoscale 8:13025–13032. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR02172G
Lievens H (1995) Wide web coating of complex materials. Surf Coat Technol 76:744–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/0257-8972(95)02612-6
Liu H, Jiang H, Du F, Zhang D, Li Z, Zhou H (2017) Flexible and degradable paper-based strain sensor with low cost. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:10538–10543. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02540
Liu L, Jiao Z, Zhang J, Wang Y, Zhang C, Meng X, Jiang X, Niu S, Han Z, Ren L (2020) Bioinspired, superhydrophobic, and paper-based strain sensors for wearable and underwater applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:1967–1978. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c18818
Liu H, Xiang H, Wang Y, Li Z, Qian L, Li P, Ma Y, Zhou H, Huang W (2019) A flexible multimodal sensor that detects strain, humidity, temperature, and pressure with carbon black and reduced graphene oxide hierarchical composite on paper. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:40613–40619. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b13349
Long Y, He P, Xu R, Hayasaka T, Shao Z, Zhong J, Lin L (2020) Molybdenum-carbide-graphene composites for paper-based strain and acoustic pressure sensors. Carbon 157:594–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.10.083
Mahajan A, Frisbie CD, Francis LF (2013) Optimization of aerosol jet printing for high-resolution, high-aspect ratio silver lines. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:4856–4864. https://doi.org/10.1021/am400606y
Maurizi M, Cianetti F, Slavič J, Zucca G, Palmieri M (2019) Piezoresistive dynamic simulations of FDM 3D-printed embedded strain sensors: a new modal approach. Procedia Struct Integr 24:390–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostr.2020.02.036
Maurizi M, Slavič J, Cianetti F, Jerman M, Valentinčič J, Lebar A, Boltežar M (2019) Dynamic measurements using FDM 3D-printed embedded strain sensors. Sensors 19:2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122661
Milić P, Marinković D, Klinge S, Ćojbašić Ž (2023) Reissner-Mindlin based Isogeometric finite element formulation for piezoelectric active laminated shells. Tehnicki Vjesn 30:416–425. https://doi.org/10.17559/TV-20230128000280
Milić P, Marinković D, Klinge S, Ćojbašić Ž (2023) Geometrically nonlinear analysis of piezoelectric active laminated shells by means of Isogeometric FE Formulation. Facta Univ Ser Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.22190/FUME050123059M
Natarajan S, Jayaraj J, Prazeres DMF (2021) A cellulose paper-based fluorescent lateral flow immunoassay for the quantitative detection of cardiac troponin I. Biosensors 11:49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11020049
Ong KJ, Ede JD, Pomeroy-Carter CA, Sayes CM, Mulenos MR, Shatkin JA (2020) A 90-day dietary study with fibrillated cellulose in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Rep 7:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.01.003
Qaiser N, Al-Modaf F, Khan SM, Shaikh SF, El‐Atab N, Hussain MM (2021) A robust wearable point‐of‐care CNT‐based strain sensor for wirelessly monitoring throat‐related illnesses. Adv Funct Mater 31:2103375. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202103375
Qi X, Ha H, Hwang B, Lim S (2020) Printability of the screen-printed strain sensor with carbon black/silver paste for sensitive wearable electronics. Appl Sci 10:6983. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196983
Qi X, Li X, Jo H, Bhat KS, Kim S, An J, Kang J-W, Lim S (2020) Mulberry paper-based graphene strain sensor for wearable electronics with high mechanical strength. Sens Actuators A: Phys 301:111697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2019.111697
Qi X, Matteini P, Hwang B, Lim S (2023) Roll stamped Ni/MWCNT composites for highly reliable cellulose paper-based strain sensor. Cellulose 30:1543–1552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04970-3
Qian Q, Wang Y, Zhang M, Chen L, Feng J, Wang Y, Zhou Y (2019) Ultrasensitive paper-based polyaniline/graphene composite strain sensor for sign language expression. Compos Sci Technol 181:107660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.05.017
Sardana S, Kaur H, Arora B, Aswal DK, Mahajan A (2022) Self-powered monitoring of ammonia using an MXene/TiO2/cellulose nanofiber heterojunction-based sensor driven by an electrospun triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Sens 7:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.1c02388
Selamneni V, Bs A, Sahatiya P (2020) Highly air-stabilized black phosphorus on disposable paper substrate as a tunnelling effect‐based highly sensitive piezoresistive strain sensor. Med Devices Sens 3:e10099. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds3.10099
Seo Y, Hwang B (2019) Mulberry-paper-based composites for flexible electronics and energy storage devices. Cellulose 26:8867–8875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02686-5
Shen L, Zhou S, Gu B, Wang S, Wang S (2023) Highly sensitive strain sensor fabricated by direct laser writing on lignin paper with strain Engineering. Adv Eng Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202201882
Singh M, Haverinen HM, Dhagat P, Jabbour GE (2010) Inkjet printing—process and its applications. Adv Mater 22:673–685. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200901141
Tang F, Li Y, Huang J, Tang J, Chen X, Yu H-Y, Zhou Y, Tang D (2021) An environmentally friendly and economical strategy to cyclically produce cellulose nanocrystals with high thermal stability and high yield. Green Chem 23:4866–4872. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC01392K
Tian X, Jin J, Yuan S, Chua CK, Tor SB, Zhou K (2017) Emerging 3D-printed electrochemical energy storage devices: a critical review. Adv Eng Mater 7:1700127. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201700127
Tobjörk D, Österbacka R (2011) Paper electronics. Adv Mater 23:1935–1961. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201004692
Tsuji H, Suzuyoshi K (2002) Environmental degradation of biodegradable polyesters 1. Poly (ε-caprolactone), poly [(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], and poly (L-lactide) films in controlled static seawater. Polym Degrad Stab 75:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(01)00240-3
Veeralingam S, Sahatiya P, Badhulika S (2021) Papertronics: hand-written MoS2 on paper based highly sensitive and recoverable pressure and strain sensors. IEEE Sens J 21:8943–8949. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3052814
Wisitsoraat A, Mensing JP, Karuwan C, Sriprachuabwong C, Jaruwongrungsee K, Phokharatkul D, Daniels T, Liewhiran C, Tuantranont A (2017) Printed organo-functionalized graphene for biosensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 87:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.116
Xia K, Chen X, Shen X, Li S, Yin Z, Zhang M, Liang X, Zhang Y (2019) Carbonized Chinese art paper-based high-performance wearable strain sensor for human activity monitoring. ACS Appl Electron Mater 1:2415–2421. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.9b00564
Yan T, Wu Y, Yi W, Pan Z (2021) Recent progress on fabrication of carbon nanotube-based flexible conductive networks for resistive-type strain sensors. Sens Actuators A Phys 327:112755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.112755
Yun T, Du J, Ji X, Tao Y, Cheng Y, Lv Y, Lu J, Wang H (2023) Waterproof and ultrasensitive paper-based wearable strain/pressure sensor from carbon black/multilayer graphene/carboxymethyl cellulose composite. Carbohydr Polym 313:120898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120898
Zhang F, Wei M, Viswanathan VV, Swart B, Shao Y, Wu G, Zhou C (2017) 3D printing technologies for electrochemical energy storage. Nano Energy 40:418–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.08.037
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2021R1A2C1011248).
Funding
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2021R1A2C1011248).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OP, HH: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing—original draft. HH: Investigation, Review and editing. BH: Investigation, Review and editing. SK: Investigation, Review and editing. SL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Supervision, Investigation, review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
None.
Consent for publication
We, the undersigned, give consent for the publication of identifable details, which can include photographs (s) and details within the text to be published in this journal.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pawar, O.Y., Ha, H., Qaiser, N. et al. The effect of printing parameters on the bonding strength and electric performance of FDM-printed graphene filaments to mulberry paper for paper electronics. Cellulose 31, 1741–1754 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05730-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05730-7