Abstract
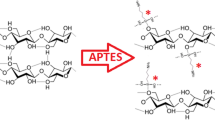
In this study, we have reported an investigation on the three steps preparation of TiO2@SiO2-alkyl-NH2 grafted cellulose, their characterization on the basis of Fourier transforms infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), thermogravimetric analysis-differential scanning calorimetry ((TGA–DSC), scanning electron microscopy-X-ray energy dispersion (SEM–EDX), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analyses, and investigation of thermal stability, mechanical properties, and water adsorption capacity. According to the TGA analysis, the sample shows good and reasonable thermal stability and is stable up to 300 °C. The DSC analysis shows that the decomposition of the sample could occur in two exothermic steps and one endothermic step. The grafted cellulose has 680.23 m2/g, 2.87 nm, and 0.681 cm3/g values for their specific surface area, pore diameter, and pore volume respectively which is higher than those of un-grafted ones. The mechanical properties of the grafted cellulose samples improved to higher values of 78.25 MPa, 3.71 GPa, and 102.36 MPa for flexural strength (FS), flexural modulus (FM), and compressive strength (CS) properties respectively. The water adsorption potential of TiO2@SiO2-alkyl-NH2 grafted cellulose is near 21% which is higher than the un-grafted sample (9%).











Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Abushammala H (2020) Nano-brushes of alcohols grafted onto cellulose nanocrystals for reinforcing poly(butylene succinate): impact of alcohol chain length on interfacial adhesion. Polymer 12:95. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010095
Alamri H, Low IM (2012) Mechanical properties and water absorption behaviour of recycled cellulose fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Polym Test 31:620–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.04.002
Anirudhan TS, Sreekumari SS, Jalajamony S (2012) Preparation of poly(methacrylic acid)-grafted TiO2-densified cellulose as an adsorbent for the removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solutions and industrial effluents. Toxicol Environ Chem 94:1099–1113. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2012.691503
Askar S, Li L, Torkelson JM (2017) Polystyrene-grafted silica nanoparticles: investigating the molecular weight dependence of glass transition and fragility behavior. Macromolecules 50:1589–1598. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.7b00079
Basheer BV, George JJ, Siengchin S, Parameswaranpillai J (2020) Polymer grafted carbon nanotubes—Synthesis, properties, and applications: a review. Nano Struct Nano-Objects 22:100429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2020.100429
Beaumont M, Bacher M, Opietnik M, Gindl-Altmutter W, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2018) A general aqueous silanization protocol to introduce vinyl, mercapto or azido functionalities onto cellulose fibers and nanocelluloses. Molecules 23:1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061427
Beaumont M, Jahn E, Mautner A, Veigel S, Böhmdorfer S, Potthast A, Gindl-Altmutter W, Rosenau T (2022) Facile preparation of mechanically robust and functional silica/cellulose nanofiber gels reinforced with soluble polysaccharides. Nanomaterials 12:895. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060895
Eskandari P, Abousalman-Rezvani Z, Roghani-Mamaqani H, Salami-Kalajahi M, Mardani H (2019) Historical perspective Polymer grafting on graphene layers by controlled radical polymerization. Adv Coll Interface Sci 273:102021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2019.102021
Eyley S, Thielemans W (2014) Surface Modification of Cellulose Nanocrystals. Nanoscale 6:7764–7779. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR01756K
Fallah Z, Nasr Isfahani H, Tajbakhsh M, Tashakkorian H, Amouei A (2018) TiO2-grafted cellulose via click reaction: an efficient heavy metal ions bioadsorbent from aqueous solutions. Cellulose 25:639–660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1563-8
Foruzanmehr MR, Vuillaume PY, Robert M, Elkoun S (2015) The effect of grafting a nano-TiO2 thin film on physical and mechanical properties of cellulosic natural fibers. Mater Des 85:671–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.06.105
Foruzanmehr MR, Vuillaume PY, Elkoun S, Robert M (2016) Physical and mechanical properties of PLA composites reinforced by TiO2 grafted flax fibers. Mater Des 106:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.05.103
Garusinghe UM, Raghuwanshi VS, Batchelor W, Garnier G (2018) Water resistant cellulose-titanium dioxide composites for photocatalysis. Sci Rep 8:2306. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20569-w
Gomri C, Cretin M, Semsarilar M (2022) Recent progress on chemical modification of cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) and its application in nanocomposite films and membranes. Carbohyd Polym 294:119790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119790
Gys N, An R, Pawlak B, Vogelsang D, Wyns K, Baert K, Vansant A, Blockhuys F, Adriaensens P, Hauffman T, Michielsen B, Mullens S, Meynen V (2022) Amino-alkylphosphonate-grafted TiO2: how the alkyl chain length impacts the surface properties and the adsorption efficiency for Pd. ACS Omega 7:45409–45421. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c06020
Habibi Y, Dufresne A (2008) Highly filled bionanocomposites from functionalized polysaccharide nanocrystals. Biomacromol 9:1974–1980. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm8001717
Hettegger H, Sumerskii I, Sortino S, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2015) Silane meets click chemistry: towards the functionalization of wet bacterial cellulose sheets. Chemsuschem 8:680–687. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201402991
Kang H, Liu R, Huang Y (2015) Graft modification of cellulose: methods, properties and applications. Polymer 70:A1–A16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2015.05.041
Kedzior SA, Zoppe JO, Berry RM, Cranston ED (2019) Recent advances and an industrial perspective of cellulose nanocrystal functionalization through polymer grafting. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 23:74–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2018.11.005
Khalid A, Ullah H, Ul-Islam M, Khan R, Khan S, Ahmad F, Khan T, Wahid F (2017) Bacterial cellulose-TiO2 nanocomposites promote healing and tissue regeneration in burn mice model. RSC Adv 7:47662–47668. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA06699F
Kumar R, Sharma RK, Singh AP (2018) Grafted cellulose: a bio-based polymer for durable applications. Polym Bull 75:2213–2242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-017-2136-6
Labet M, Thielemans W, Dufresne A (2007) Polymer grafting onto starch nanocrystals. Biomacromol 8:2916–2927. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm700468f
Li M, Qiu J, Xu J, Yao J (2020) Cellulose/TiO2-based carbonaceous composite film and aerogel for highly efficient photocatalysis under visible light. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:13997–14003. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c01682
Liang H, Yin D, Shi L, Liu Y, Hu X, Zhu N, Guo K (2023) Surface modification of cellulose via photo-induced click reaction. Carbohyd Polym 301:120321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120321
Liu R, Gong T, Zhang K, Lee C (2017) Graphene oxide papers with high water adsorption capacity for air dehumidification. Sci Rep 7:9761. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09777-y
Loosli F, Le Coustumer P, Stoll S (2015) Effect of electrolyte valency, alginate concentration and pH on engineered TiO2 nanoparticle stability in aqueous solution. Sci Total Environ 535:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.037
Marcinko S, Fadeev AY (2004) Hydrolytic stability of organic monolayers supported on TiO2 and ZrO2. Langmuir 20:2270–2273. https://doi.org/10.1021/la034914l
Naghdi S, Moheb Shahrestani M, Zendehbad M, Djahaniani H, Kazemian H, Eder D (2023) Recent advances in application of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as adsorbent and catalyst in removal of persistent organic pollutants (POPs). J Hazard Mater 442:130127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130127
Poliah R, Sreekantan S (2011) Characterization and photocatalytic activity of enhanced copper-silica-loaded titania prepared via hydrothermal method. J Nanomater 2011:239289. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/239289
Soliman AIA, Díaz Baca JA, Fatehi P (2023) One-pot synthesis of magnetic cellulose nanocrystal and its post-functionalization for doxycycline adsorption. Carbohyd Polym 308:120619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120619
Thielemans W, Naceur Belgacem M, Dufresne A (2006) Starch nanocrystals with large chain surface modifications. Langmuir 22:4804–4810. https://doi.org/10.1021/la053394m
Tiwari N, Nawale L, Sarkar D, Badiger MV (2017) Carboxymethyl cellulose-grafted mesoporous silica hybrid nanogels for enhanced cellular uptake and release of curcumin. Gels 3:8. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels3010008
Yang Z, Lin Z, Huang J (2023) Hierarchically structured NH2-MIL-125/TiO2/cellulose composite membranes with enhanced photocatalytic performance. ChemNanoMat 9:e202200504. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.202200504
Yun T, Tao Y, Li Q, Cheng Y, Lu J, Lv Y, Du J, Wang H (2023) Superhydrophobic modification of cellulosic paper-based materials: fabrication, properties, and versatile applications. Carbohyd Polym 305:120570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120570
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the Najafabad Branch, Islamic Azad University research council and Lodz University of Technology (Poland) for partial support of this research. The article was completed while the second author (SayedMohsen Mortazavi Najafabadi), it’s a doctoral candidate in the interdisciplinary Doctoral School at the Lodz University of Technology, Poland.
Funding
There are no funding reports to be declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PT: methodology, perform experiments, formal analysis, SMN: formal analysis, writing—original draft. DG: formal analysis, writing—original draft. MG: Supervisor, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Torkian, P., Mortazavi Najafabadi, S., Grzelczyk, D. et al. TiO2 bonded SiO2-alkyl-NH2 grafted cellulose for improving thermal stability, mechanical strength characteristics, and water adsorption capacity. Cellulose 31, 1801–1812 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05718-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05718-3