Abstract
Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots (N, P co-doped CDs) were synthesized using a one-pot hydrothermal carbonization method. The resulting CDs were then applied to fabricate a multilayered coating on cotton fabric through a layer-by-layer self-assembly method, in combination with alginate and polyethyleneimine. When exposed to a 365 nm UV lamp, the coating containing N, P co-doped CDs emitted visible blue light. The cotton treated with these CDs was subsequently evaluated for UV-protection, thermal stability, and flame retardancy. Cotton-1 fabric (110 g/m2) treated with a 6-bilayer CD-containing coating had a significantly higher ultraviolet protection factor (UPF) of 148.4 compared to the pure cotton fabric which had a UPF of 6.65. The cotton-1 fabric treated with CD coating exhibited more char residues at 700 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere in the TGA test. The study also discovered that the CD-containing multilayered coating significantly decreased the peak heat release rate and total heat release rate of cotton-1/(PEI/ACD)6 by 52.8% and 53.8% respectively, in comparison to cotton-1 in the microscale combustion calorimeter test. These findings indicate that N, P co-doped CDs, which have both UV absorption and environmental friendliness, could be potential utilized as a flame retardant on the surface of cotton fibers.
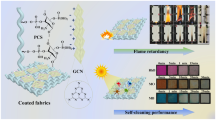
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are included in the manuscript. Data can be available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Cai W, Feng XM, Wang BB et al (2017) A novel strategy to simultaneously electrochemically prepare and functionalize graphene with a multifunctional flame retardant. Chem Eng J 316:514–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.017
Cao CF, Yu B, Guo BF et al (2022) Bio-inspired, sustainable and mechanically robust graphene oxide-based hybrid networks for efficient fire protection and warning. Chem Eng J 439:134516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134516
Du BX, Fang ZP (2011) Effects of carbon nanotubes on the thermal stability and flame retardancy of intumescent flame-retarded polypropylene. Polym Degrad Stabil 96(10):1725–1731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.08.002
Gu WW, Dong ZF, Zhang AY et al (2022a) Functionalization of PET with carbon dots as copolymerizable flame retardants for the excellent smoke suppressants and mechanical properties. Polym Degrad Stabil. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2021.109766
Gu WW, Wei LF, Ma TY et al (2022b) Carbon dots as smoke suppression agents for the reduction of CO release in combustion and improvement of UV resistance towards phosphorus-containing polyester. Eur Polym J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111642
Kausar A (2019) Polymer/carbon-based quantum dot nanocomposite: forthcoming materials for technical application. J Macromol Sci A 56(4):341–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2019.1578614
Lee S, Kim HM, Seong DG et al (2019) Synergistic improvement of flame retardant properties of expandable graphite and multi-walled carbon nanotube reinforced intumescent polyketone nanocomposites. Carbon 143:650–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.11.050
Li YC, Schulz J, Grunlan JC (2009) Polyelectrolyte/Nanosilicate thin-film assemblies: influence of pH on growth, mechanical behavior, and flammability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1(10):2338–2347. https://doi.org/10.1021/am900484q
Liu C, Li HY, Cheng R et al (2022) Facile synthesis, high fluorescence and flame retardancy of carbon dots. J Mater Sci Technol 104:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.06.056
Liu JJ, Li R, Yang B (2020) Carbon dots: a new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Cent Sci 6(12):2179–2195. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.0c01306
Liu QL, Niu XY, Xie KX et al (2021) Fluorescent carbon dots as nanosensors for monitoring and imaging Fe3 + and HPO4 (2-) ions. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4(1):190–197. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c02515
Luo PJG, Yang F, Yang ST et al (2014) Carbon-based quantum dots for fluorescence imaging of cells and tissues. Rsc Adv 4(21):10791–10807
Pan Y, Liu LX, Zhang YP et al (2019) Effect of genipin crosslinked layer-by-layer self-assembled coating on the thermal stability, flammability and wash durability of cotton fabric. Carbohyd Polym 206:396–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.11.037
Rimal V, Shishodia S, Srivastava PK (2020) Novel synthesis of high-thermal stability carbon dots and nanocomposites from oleic acid as an organic substrate. Appl Nanosci 10(2):455–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01178-z
Shishodia S, Rimal V, Srivastava PK (2021) Synthesis of tunable high-thermal stability carbon dots via functionalization for applications in high-temperature environment. Appl Nanosci 11(5):1691–1706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01814-7
Wang X, Kalali EN, Wan JT et al (2017) Carbon-family materials for flame retardant polymeric materials. Prog Polym Sci 69:22–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.02.001
Wang KX, Wu K, Qu ZC et al (2022) Flame-retardant and alarm-sensitive composite films by covalent modification of MWCNT with dopamine. Eur Polym J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2021.110986
Wareing TC, Gentile P, Phan AN (2021) Biomass-based carbon dots: current development and future perspectives. ACS Nano 15(10):15471–15501
Xu Q, Li BF, Ye YC et al (2018) Synthesis, mechanical investigation, and application of nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots with a high photoluminescent quantum yield. Nano Res 11(7):3691–3701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1937-0
Yu ZR, Mao M, Li SN et al (2021) Facile and green synthesis of mechanically fl exible and fl ame-retardant clay/graphene oxide nanoribbon interconnected networks for fi re safety and prevention. Chem Eng J 405:126620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126620
Yu B, Shi YQ, Yuan BH et al (2015) Enhanced thermal and flame retardant properties of flame-retardant-wrapped graphene/epoxy resin nanocomposites. J Mater Chem A 3(15):8034–8044. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta06613h
Zhang ZH, Zhang JW, Cao CF et al (2020) Temperature-responsive resistance sensitivity controlled by L-ascorbic acid and silane co-functionalization in flame-retardant GO network for efficient fire early-warning response. Chem Eng J 386:123894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123894
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (21878064, 41977017), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY21E030009) and Zhejiang Provincial Key Research and Development Program (2022C01174).
Funding
Natural Science Foundation of China: 41977017. Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province: LY21E030009. Zhejiang Provincial Key Research and Development Program: 2022C01174.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YP: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing-original draft. QL and JD: Resources, Writing-review & editing, Supervision. DZ and TL Validation, Formal analysis, Writing-review and editing. HZ and YZ: Validation, Formal analysis, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Human or animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
All the authors consent for the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Y., Wang, W., Liang, Q. et al. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots containing layer-by-layer self-assembled coating on UV resistance and thermal stability of cotton fabric. Cellulose 31, 1957–1966 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05715-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05715-6