Abstract
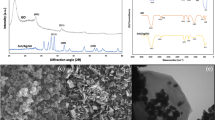
The main purpose of this study is to design and manufacture a water treatment filter using a metal–organic framework to remove pollutants from aqueous solutions with high efficiency. A uniform layer of the metal–organic framework was placed on cellulose filter paper. Cellulose filter paper is biodegradable and economical and its surface can be easily modifiable due to its high hydroxyl groups. HKUST-1, a kind of MOF with a porous and adjustable structure as well as having many active sites was selected for modification of cellulose filter paper for increasing the removal efficiency. The important point of this research is using a very easy method to synthesize the filter in a short time and at room temperature. Synthesized HKUST-1@Filter paper was characterized by SEM, FTIR, and XRD analysis. This filter was used to remove meloxicam from the aqueous solution with a removal percentage of more than 87%. To study the stability and reusability of the synthesized filter, an organic solvent was used for desorption, and it was found that the filter remains stable and had high efficiency to remove contaminants several times after desorption. Langmuir and Freundlich’s isotherms were used to investigate the adsorption mechanism. With the equilibrium adsorption isotherm, it was found that the absorption of meloxicam followed the Langmuir model, and the maximum adsorption capacity was 2500 mg g−1.
Graphical abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdelhameed RM, Abdel-Gawad H, Elshahat M, Emam HE (2016) Cu–BTC@ cotton composite: design and removal of ethion insecticide from water. RSC Adv 6(48):42324–42333
Ahmaruzzaman M (2008) Adsorption of phenolic compounds on low-cost adsorbents: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 143(1–2):48–67
Ali I, Asim M, Khan TA (2012) Low cost adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J Environ Manag 113:170–183
Álvarez-Torrellas S, Peres J, Gil-Álvarez V, Ovejero G, García J (2017) Effective adsorption of non-biodegradable pharmaceuticals from hospital wastewater with different carbon materials. J Chem Eng 320:319–329
Azhar MR, Abid HR, Sun H, Periasamy V, Tadé MO, Wang S (2016) Excellent performance of copper based metal organic framework in adsorptive removal of toxic sulfonamide antibiotics from wastewater. J Colloid Interface Sci 478:344–352
Breitbach M, Bathen D, Schmidt-Traub H (2003) Effect of ultrasound on adsorption and desorption processes. Ind Eng Chem 42(22):5635–5646
Choudalakis G, Gotsis A (2009) Permeability of polymer/clay nanocomposites: a review. Eur Polym J 45(4):967–984
Chui S-Y, Lo S-F, Charmant JPH, Orpen AG, Williams ID (1999) A chemically functionalizable nanoporous material [Cu3(TMA)2(H2O)3]n. Science 5405(283):1148–1150
D’Halluin M, Rull-Barrull J, Bretel G, Labrugère C, Le Grognec E, Felpin F-X (2017) Chemically modified cellulose filter paper for heavy metal remediation in water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(2):1965–1973
Da Silva Pinto M, Sierra-Avila CA, Hinestroza JP (2012) In situ synthesis of a Cu-BTC metal–organic framework (MOF 199) onto cellulosic fibrous substrates: cotton. Cellulose 19(5):1771–1779
Dalrymple OK, Yeh DH, Trotz MA (2007) Removing pharmaceuticals and endocrine-disrupting compounds from wastewater by photocatalysis. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 82(2):121–134
Dhaka S, Kumar R, Deep A, Kurade MB, Ji S-W, Jeon B-H (2019) Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) for the removal of emerging contaminants from aquatic environments. Coord Chem Rev 380:330–352
Dutra FVA, Pires BC, Nascimento TA, Mano V, Borges KB (2017) Polyaniline-deposited cellulose fiber composite prepared via in situ polymerization: enhancing adsorption properties for removal of meloxicam from aqueous media. RSC Adv 7(21):12639–12649
Emam HE, Manian AP, Široká B, Bechtold T (2012) Copper inclusion in cellulose using sodium D-gluconate complexes. Carbohydr Polym 90(3):1345–1352
Hashem T, Ibrahim AH, Wöll C, Alkordi MH (2019) Grafting zirconium-based metal–organic framework UiO-66-NH2 nanoparticles on cellulose fibers for the removal of Cr (VI) ions and methyl orange from water. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2(9):5804–5808
Heine J, Müller-Buschbaum K (2013) Engineering metal-based luminescence in coordination polymers and metal-organic framework. Chem Soc Rev 42(24):9332–9342
Joshi DR, Adhikari N (2019) An overview on common organic solvents and their toxicity. J Pharm Res Int 28(3):1–18
Kamrani M, Akbari A (2018) Chitosan-modified acrylic nanofiltration membrane for efficient removal of pharmaceutical compounds. J Environ Chem Eng 6(1):583–587
Lange LE, Obendorf SK (2015) Functionalization of cotton fiber by partial etherification and self-assembly of polyoxometalate encapsulated in Cu3 (BTC)2 metal–organic framework. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(7):3974–3980
Li Z, Hori N, Takemura A (2020) A comparative study of depositing Cu-BTC metal–organic framework onto cellulosic filter paper via different procedures. Cellulose 27(8):6537–6547
Licona K, Geaquinto LDO, Nicolini J, Figueiredo N, Chiapetta S, Habert A, Yokoyama L (2018) Assessing potential of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis for removal of toxic pharmaceuticals from water. JWPE 25:195–204
Lin K-YA, Hsieh Y-T (2015) Copper-based metal organic framework (MOF), HKUST-1, as an efficient adsorbent to remove p-nitrophenol from water. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 50:223–228
Liu F, Xiong W, Feng X, Shi L, Chen D, Zhang Y (2019a) A novel monolith ZnS-ZIF-8 adsorption material for ultraeffective Hg (II) capture from wastewater. J Hazard Mater 367:381–389
Liu S, Zhao Y, Wang T, Liang N, Hou X (2019b) Core−shell Fe3O4 @MIL-100(Fe) magnetic nanoparticle for effective removal of meloxicam and naproxen in aqueous solution. J Chem Eng Data 64(7):2997–3007
Liu Q, Yu H, Zeng F, Li X, Sun J, Li C et al (2021) HKUST-1 modified ultrastability cellulose/chitosan composite aerogel for highly efficient removal of methylene blue. Carbohydr Polym 255:117402–117049
Misurac JM, Knoderer CA, Leiser JD, Nailescu C, Wilson AC, Andreoli SP (2013) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are an important cause of acute kidney injury in children. J Pediatr 162(6):1153–1159
Mohammadnejad M, Fakhrefatemi M (2021) Synthesis of magnetic HKUST-1 metal-organic framework for efficient removal of mefenamic acid from water. J Mol Struct 1224:129041
Nam S-W, Choi D-J, Kim S-K, Her N, Zoh K-D (2014) Adsorption characteristics of selected hydrophilic and hydrophobic micropollutants in water using activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 270:144–152
Neufeld MJ, Harding JL, Reynolds MM (2015) Immobilization of metal–organic framework copper (II) benzene-1, 3, 5-tricarboxylate (CuBTC) onto cotton fabric as a nitric oxide release catalyst. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(48):26742–26750
Park J, Oh M (2017) Construction of flexible metal–organic framework (MOF) papers through MOF growth on filter paper and their selective dye capture. Nanoscale 9(35):12850–12854
Pendergast MM, Hoek EM (2011) A review of water treatment membrane nanotechnologies. Energy Environ Sci 4(6):1946–1971
Pi Y, Li X, Xia Q, Wu J, Li Y, Xiao J, Li Z (2018) Adsorptive and photocatalytic removal of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in water by metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). J Chem Eng 337:351–371
Ravanchi MT, Kaghazchi T, Kargari A (2009) Application of membrane separation processes in petrochemical industry: a review. Desalination 235(1–3):199–244
Rickhoff T, Sullivan E, Werth L, Kissel D, Keleher J (2019) A biomimetic cellulose-based composite material that incorporates the antimicrobial metal-organic framework HKUST-1. J Appl Polym Sci 136(3):46978
Saadi R, Saadi Z, Fazaeli R, Fard NE (2015) Monolayer and multilayer adsorption isotherm models for sorption from aqueous media. Korean J Chem Eng 32(5):787–799
Sayadi M, Trivedy R, Pathak R (2010) Pollution of pharmaceuticals in environment. J Ind Pollut Control 26(1):89–94
Seedher N, Bhatia S (2003) Solubility enhancement of Cox-2 inhibitors using various solvent systems. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech 4(3):36–44
Thakur VK, Voicu SI (2016) Recent advances in cellulose and chitosan based membranes for water purification: a concise review. Carbohydr Polym 146:148–165
Wang Y, Ye G, Chen H, Hu X, Niu Z, Ma S (2015) Functionalized metal–organic framework as a new platform for efficient and selective removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solution. J Mater Chem 3(29):15292–15298
Wang T, Liu S, Gao G, Zhao P, Lu N, Lun X, Hou X (2017) Magnetic solid phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from water samples using a metal organic framework of type Fe3O4/MIL-101 (Cr), and their quantitation by UPLC-MS/MS. Micro Chim Acta 184(8):2981–2990
Yang Ch, Wang J, Yan W, Xia Y (2022) Facile synthesis disposable MOF membrane filter: growth of NH2-MIL-125 (Ti) on filter paper for fast removal of organophosphorus pesticides in aqueous solution and vegetables. Food Chem 389:133056–133061
Yu J, Xiong W, Li X, Yang Z, Cao J, Jia M et al (2019) Functionalized MIL-53 (Fe) as efficient adsorbents for removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mat 290:109642–109649
Zhang Q-Q, Zhu Y-J, Wu J, Shao Y-T, Cai A-Y, Dong L-Y (2019) Ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire-based filter paper for high-performance water purification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(4):4288–4301
Zhao H, Kwak JH, Zhang ZC, Brown HM, Arey BW, Holladay JE (2007) Studying cellulose fiber structure by SEM, XRD NMR and acid hydrolysis. Carbohydr Polym 68(2):235–241
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Research Council of Alzahra University
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed with the content and that all gave explicit consent to submit the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadnejad, M., Roshan, A. & Geranmayeh, S. Facile synthesis of HKUST-1-cellulose filter for water purification from meloxicam. Cellulose 31, 535–550 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05627-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05627-5