Abstract
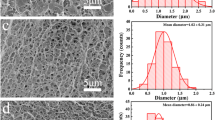
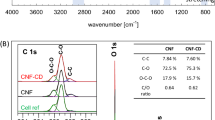
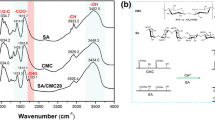
The design and construction of high-performance protein absorbents are of great significance for obtaining highly purified proteins in the field of biotechnology and more. In this study, the highly carboxylated absorption media were fabricated for selective absorption of positively charged proteins by using bacterial cellulose (BC) nanofibrous aerogel (NFA) as a substrate material in concert with citric acid (CA). The obtained BC/CA NFAs exhibited highly interconnected open porous structure, surface hydrophilicity, large specific surface area (14.2 m2/g), good elasticity and compression fatigue resistance. BC/CA NFAs displayed a high lysozyme absorption capacity of 868.9 mg/g and fast equilibrium within 2.5 h. A dynamic lysozyme absorption capacity of 655.35 mg/g was achieved under the drive of gravity, meeting the demands of actual applications. Furthermore, BC/CA NFAs exhibited unique absorption selectivity performance, good reusability, as well as acid and alkaline resistance. A successful scale-up of such environmental friendliness, low cost and good reproducibility absorbents could provide a new perspective to develop next generation three-dimensional chromatographic media for substantial bio-separation applications.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Amaly N, Ma Y, El-Moghazy AY, Sun G (2020) Copper complex formed with pyridine rings grafted on cellulose nanofibrous membranes for highly efficient lysozyme adsorption. Sep Purif Technol 250:117086
Arabkhani P, Asfaram A (2020) Development of a novel three-dimensional magnetic polymer aerogel as an efficient adsorbent for malachite green removal. J Hazard Mater 384:121394
Arbita AA, Paul NA, Cox J, Zhao J (2022) Amino acid sequence of two new milk-clotting proteases from the macroalga Gracilaria edulis. Int J Biol Macromol 211:499–505
Beaumont M, Jusner P, Gierlinger N, King AWT, Potthast A, Rojas OJ, Rosenau T (2021a) Unique reactivity of nanoporous cellulosic materials mediated by surface-confined water. Nat Commun 12(1):2513
Beaumont M, Nypelo T, Konig J, Zirbs R, Opietnik M, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2016) Synthesis of redispersible spherical cellulose II nanoparticles decorated with carboxylate groups. Green Chem 18(6):1465–1468
Beaumont M, Tardy BL, Reyes G, Koso TV, Schaubmayr E, Jusner P, King AWT, Dagastine RR, Potthast A, Rojas OJ, Rosenau T (2021b) Assembling native elementary cellulose nanofibrils via a reversible and regioselective surface functionalization. J Am Chem Soc 143(41):17040–17046
Chen H, Sharma SK, Sharma PR, Yeh HD, Johnson K, Hsiao BS (2019) Arsenic(III) removal by nanostructured dialdehyde cellulose-cysteine microscale and nanoscale fibers. ACS Omega 4(26):22008–22020
Cheng P, Liu K, Wan YC, Hu W, Ji CC, Huang P, Guo QH, Xu J, Cheng Q, Wang D (2022) Solution viscosity-mediated structural control of nanofibrous sponge for RNA separation and purification. Adv Funct Mater 32(20):2112023
Chiou BS, Jafri H, Cao T, Robertson GH, Gregorski KS, Imam SH, Glenn GM, Orts WJ (2013) Modification of wheat gluten with citric acid to produce superabsorbent materials. J Appl Polym Sci 129(6):3192–3197
Chiu HT, Lin JM, Cheng TH, Chou SY, Huang CC (2012) Direct purification of lysozyme from chicken egg white using weak acidic polyacrylonitrile nanofiber-based membranes. J Appl Polym Sci 125:E616–E621
Das R, Lindstrom T, Sharma PR, Chi K, Hsiao BS (2022) Nanocellulose for sustainable water purification. Chem Rev 122(9):8936–9031
Dou XY, Wang Q, Li ZL, Ju JP, Wang S, Hao LY, Sui KY, Xia YZ, Tan YQ (2019) Seaweed-derived electrospun nanofibrous membranes for ultrahigh protein adsorption. Adv Funct Mater 29(46):1905610
Ebrahimi A, Pazuki G, Mozaffarian M, Ahsaie FG, Abedini H (2023) Separation and purification of C-phycocyanin from spirulina platensis using aqueous two-phase systems based on triblock thermosensitive copolymers. Food Bioprocess Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03057-6
Fang K, Deng LG, Yin JY, Yang TH, Li JB, He W (2022) Recent advances in starch-based magnetic adsorbents for the removal of contaminants from wastewater: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 218:909–929
Fu QX, Duan C, Yan ZS, Si Y, Liu LF, Yu JY, Ding B (2018) Electrospun nanofibrous composite materials: a versatile platform for high efficiency protein adsorption and separation. Compos Commun 8:92–100
Fu QX, Liu LF, Si Y, Yu JY, Ding B (2019a) Shapeable, underwater superelastic, and highly phosphorylated nanofibrous aerogels for large-capacity and high-throughput protein separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(47):44874–44885
Fu QX, Si Y, Duan C, Yan ZS, Liu LF, Yu JY, Ding B (2019b) Highly carboxylated, cellular structured, and underwater superelastic nanofibrous aerogels for efficient protein separation. Adv Funct Mater 29(13):1808234
Fu QX, Wang XQ, Si Y, Liu LF, Yu JY, Ding B (2016) Scalable fabrication of electrospun nanofibrous membranes functionalized with citric acid for high-performance protein adsorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(18):11819–11829
Ge MY, Shen Y, Chen WM, Peng YT, Pan ZY (2019) Adsorption of bovine hemoglobin by sulfonated polystyrene nanospheres. ChemistrySelect 4(10):2874–2880
Ghorpade VS, Yadav AV, Dias RJ, Mali KK (2018) Fabrication of citric acid crosslinked -cyclodextrin/hydroxyethylcellulose hydrogel films for controlled delivery of poorly soluble drugs. J Appl Polym Sci 135(27):4652
Ghosh R (2002) Protein separation using membrane chromatography: opportunities and challenges. J Chromatogr A 952(1–2):13–27
He XM, Zhu GT, Lu W, Yuan BF, Wang H, Feng YQ (2015) Nickel(II)-immobilized sulfhydryl cotton fiber for selective binding and rapid separation of histidine-tagged proteins. J Chromatogr A 1405:188–192
Hu XD, Yang B, Hao M, Chen ZJ, Liu YB, Ramakrishna S, Wang XX, Yao JB (2023) Preparation of high elastic bacterial cellulose aerogel through thermochemical vapor deposition catalyzed by solid acid for oil-water separation. Carbohydr Polym 305:120538
Huang JY, Zhao M, Hao Y, Wei QF (2022) Recent advances in functional bacterial cellulose for wearable physical sensing applications. Adv Mater Technol 7(1):2100617
Jain P, Sun L, Dai JH, Baker GL, Bruening ML (2007) High-capacity purification of his-tagged proteins by affinity membranes containing functionalized polymer brushes. Biomacromol 8(10):3102–3107
Janusz W, Skwarek E, Sternik D, Pikus S, Pawlak D, Parus JL, Mikolajczak R (2020) Synthesis of yttrium citrate from yttrium carbonate hydroxide and citric acid. Mater Chem Phys 250:123113
Jiang Y, Lu J, Guo L (2023) Fabrication of highly carboxylated thermoplastic nanofibrous membranes for efficient absorption and separation of protein. Colloid Surf A 665:131203
Kluszczynska K, Peczek L, Rozanski A, Czernek L, Duchler M (2022) U6/miR-211 expression ratio as a purity parameter for HEK293 cell-derived exosomes. Acta Biochim Pol 69(2):409–415
Leitch ME, Li CK, Ikkala O, Mauter MS, Lowry GV (2016) Bacterial nanocellulose aerogel membranes: novel high-porosity materials for membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol Lett 3(3):85–91
Li C, Ding YW, Hu BC, Wu ZY, Gao HL, Liang HW, Chen JF, Yu SH (2020) Temperature-invariant superelastic and fatigue resistant carbon nanofiber aerogels. Adv Mater 32(2):1904331
Li GT, Li TT, Li YL, An LB, Li W, Zhang ZM (2017) Preparation of pH-controllable nanofibrous membrane functionalized with lysine for selective adsorption of protein. Colloid Surf A 531:173–181
Li Y, Wen YA, Wang LH, He JX, Al-Deyab SS, El-Newehy M, Yu JY, Ding B (2015) Simultaneous visual detection and removal of lead(II) ions with pyromellitic dianhydride-grafted cellulose nanofibrous membranes. J Mater Chem A 3(35):18180–18189
Lu JW, Jiang YG, Xiao R, Jacob KI, Tao L, Li SJ, Guo L (2022) Chemical vapor deposition based superelastic and superhydrophoboic thermoplastic polymeric nanofibrous aerogels for water purification. J Inorg Organomet Poly 32(8):2975–2985
Lu JW, Li Y, Song W, Losego MD, Monikandan R, Jacob KI, Xiao R (2020) Atomic layer deposition onto thermoplastic polymeric nanofibrous aerogel templates for tailored surface properties. ACS Nano 14(7):7999–8011
Lu JW, Xu DD, Wei JK, Yan S, Xiao R (2017) Superoleophilic and flexible thermoplastic polymer nanofiber aerogels for removal of oils and organic solvents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(30):25533–25541
Lv H, Wang XQ, Fu QX, Si Y, Yin X, Li XR, Sun G, Yu JY, Ding B (2017) A versatile method for fabricating ion-exchange hydrogel nanofibrous membranes with superb biomolecule adsorption and separation properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 506:442–451
Ma JC, Wang XQ, Fu QX, Si Y, Yu JY, Ding B (2015) Highly carbonylated cellulose nanofibrous membranes utilizing maleic anhydride grafting for efficient lysozyme adsorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(28):15658–15666
Ogata M, Sakamoto M, Yamauchi N, Nakazawa M, Koizumi A, Anazawa R, Kurumada K, Hidari KIPJ, Kono H (2022) Optimization of the conditions for the immobilization of glycopolypeptides on hydrophobic silica particulates and simple purification of lectin using glycopolypeptide-immobilized particulates. Carbohydr Res 519:108624
Orr V, Zhong LY, Moo-Young M, Chou CP (2013) Recent advances in bioprocessing application of membrane chromatography. Biotechnol Adv 31(4):450–465
Przybycien TM, Pujar NS, Steele LM (2004) Alternative bioseparation operations: life beyond packed-bed chromatography. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15(5):469–478
Qian LW, Yang MX, Chen HN, Xu Y, Zhang SF, Zhou QS, He B, Bai Y, Song WQ (2019) Preparation of a poly(ionic liquid)-functionalized cellulose aerogel and its application in protein enrichment and separation. Carbohydr Polym 218:154–162
Qiao LZ, Liao YX, Wang XW, Wang SS, Du KF (2022) Double-emulsion templated macroporous cellulose microspheres as a high-performance chromatographic media for protein separation. Cellulose 29(13):7263–7276
Rajesh S, Crandall C, Schneiderman S, Menkhaus TJ (2018) Cellulose-graft-polyethyleneamidoamine anion-exchange nanofiber membranes for simultaneous protein adsorption and virus filtration. ACS Appl Nano Mater 1(7):3321–3330
Sharma PR, Chattopadhyay A, Sharma SK, Hsiao BS (2017) Efficient removal of UO22+ from water using carboxycellulose nanofibers prepared by the nitro-oxidation method. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(46):13885–13893
Sharma PR, Sharma SK, Antoine R, Hsiao BS (2019) Efficient removal of arsenic using zinc oxide nanocrystal-decorated regenerated microfibrillated cellulose scaffolds. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(6):6140–6151
Sharma PR, Sharma SK, Lindstrom T, Hsiao BS (2020) Nanocellulose-enabled membranes for water purification: perspectives. Adv Sustain Syst 4(5):1900114
Si Y, Fu QX, Wang XQ, Zhu J, Yu JY, Sun G, Ding B (2015) Superelastic and superhydrophobic nanofiber-assembled cellular aerogels for effective separation of oil/water emulsions. ACS Nano 9(4):3791–3799
Si Y, Wang XQ, Li Y, Chen K, Wang JQ, Yu JY, Wang HJ, Ding B (2014) Optimized colorimetric sensor strip for mercury(II) assay using hierarchical nanostructured conjugated polymers. J Mater Chem A 2(3):645–652
Spinella S, Maiorana A, Qian Q, Dawson NJ, Hepworth V, McCallum SA, Ganesh M, Singer KD, Gross RA (2016) Concurrent cellulose hydrolysis and esterification to prepare a surface-modified cellulose nanocrystal decorated with carboxylic acid moieties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(3):1538–1550
Wang FF, Zhang Y, Shi J, Sun L, Ullah A, Zhu CH, Kim IS (2023) Bioinspired and biodegradable functionalized graphene oxide/deacetylated cellulose acetate composite janus membranes for water evaporation-induced electricity generation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 11(26):9792–9803
Wang P, Yin YK, Xu J, Chen SH, Wang H (2020) Facile synthesis of Cu2+-immobilized imprinted cotton for the selective adsorption of bovine hemoglobin. Cellulose 27(2):867–877
Wang XL, Fu QX, Wang XQ, Si Y, Yu JY, Wang XL, Ding B (2015) In situ cross-linked and highly carboxylated poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membranes for efficient adsorption of proteins. J Mater Chem B 3(36):7281–7290
Yi SX, Dai FY, Ma Y, Yan TS, Si Y, Sun G (2017) Ultrafine silk-derived nanofibrous membranes exhibiting effective lysozyme adsorption. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(10):8777–8784
Yi SX, Dai FY, Wu YH, Zhao CY, Si Y, Sun G (2018) Scalable fabrication of sulfated silk fibroin nanofibrous membranes for efficient lipase adsorption and recovery. Int J Biol Macromol 111:738–745
Yu LL, Sun Y (2013) Protein adsorption to poly(ethylenimine)-modified Sepharose FF: II. Effect of ionic strength. J Chromatogr A 1305:85–93
Zhan CB, Li YX, Sharma PR, He HR, Sharma SK, Wang RF, Hsiao BS (2019) A study of TiO2 nanocrystal growth and environmental remediation capability of TiO2/CNC nanocomposites. RSC Adv 9(69):40565–40576
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Lu CH, Deng YL (2012) Aerogels from crosslinked cellulose nano/micro-fibrils and their fast shape recovery property in water. J Mater Chem 22(23):11642–11650
Zhang YD, Zhang LQ, Hu JN, Wang ZW, Meng DM, Li H, Zhou ZK, Yang R (2023) The structural characterization and color stabilization of the pigment protein-phycoerythrin glycosylated with oligochitosan. Food Hydrocolloid 136:108241
Zhao L, Wang H, Fu J, Wu X, Liang XY, Liu XY, Wu X, Cao LL, Xu ZY, Dong M (2022) Microfluidic-based exosome isolation and highly sensitive aptamer exosome membrane protein detection for lung cancer diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 214:114487
Acknowledgments
Jiangsu University was acknowledged to provide characterization.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL conceptualized the work, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; YJ, ZW, ZL and YQ prepared bacterial cellulose nanofibrous aerogels and carried out protein absorption experiments; LG provided resources and guidance. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the final manuscript and the submission to this journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Jiang, Y., Wen, Z. et al. Bacterial cellulose nanofibrous aerogels grafted with citric acid for absorption and separation of protein. Cellulose 31, 349–361 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05621-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05621-x