Abstract
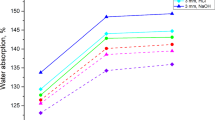
Agricultural wastes, cow manure and straw, are utilized in this study to produce biodegradable pots. Cow manure and 4 types of straw are employed for pots production. The effect of type and ratio of straw and drying method on characteristics of biodegradable pots was investigated. Two different drying methods were used to dry the pots (natural, electric oven); In natural drying, two types were used, drying at room temperature and plastic greenhouse, and drying at 50 °C, 80 °C, and 100 °C in electric convection-air oven. Among the four types of straw, rice straw-derived pots yielded highest values of 3020.67 N and 451.67 N for dry compression strength and dry penetration strength, respectively., while rape straw-based pots exhibited higher water absorption (137.38%) than pots contained any other type of straw. Additionally, the values of pots strength decrease when ratio of straw increase from 0 to 10%. Therefore, cow manure-derived pots exhibited higher dry and wet compression strength (6935.67 N and 2042.33 N, respectively) and higher dry and wet penetration strength (627.33 N, 225.33 N, respectively) than pots contained straw. The use of natural conditions in the drying process had a beneficial effect on quality and properties of biodegradable pots, where natural drying resulted in smooth bonded pots characterized by high strength and low water absorption, as compared to oven drying. Based on the results, drying in room condition could be an appropriate temperature to achieve final high quality product aspects with low cost.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data in this article are reliable and are available from the corresponding author.
References
Abasi S, Minaei S (2014) Effect of drying temperature on mechanical properties of dried corn. Drying Technol 32(7):774–780. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2013.845203
Aguirre-Loredo RY, Velazquez G, Gutierrez MC, Castro-Rosas J, Rangel-Vargas E, Gómez-Aldapa CA (2018) Effect of airflow presence during the manufacturing of biodegradable films from polymers with different structural conformation. Food Packag Shelf Life 17:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2018.06.007
Bledzki AK, Mamun AA, Volk J (2010) Barley husk and coconut shell reinforced polypropylene composites: The effect of fibre physical, chemical and surface properties. Compos Sci Technol 70(5):840–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.01.022
Cardozo VF, Lancheros CA, Narciso AM, Valereto EC, Kobayashi RK, Seabra AB, Nakazato G (2014) Evaluation of antibacterial activity of nitric oxide-releasing polymeric particles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli from bovine mastitis. Int J Pharm 473(1–2):20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.06.051
Castronuovo D, Picuno P, Manera C, Scopa A, Sofo A, Candido V (2015) Biodegradable pots for Poinsettia cultivation: agronomic and technical traits. Sci Hortic 197:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.09.025
Costa E, Benites N, Guerra J, Melville P (2000) Antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus spp. isolated from mammary parenchymas of slaughtered dairy cows. J of Vet Med Series B 47(2):99–103
Cucarella C, Tormo MÁ, Úbeda C, Trotonda MP, Monzón M, Peris C, Amorena B, Lasa Í, Penadés JR (2004) Role of biofilm-associated protein bap in the pathogenesis of bovine Staphylococcus aureus. J Infection Immun 72(4):2177–2185
Evans M, Taylor M, Kuehny J (2010) Physical properties of biocontainers for greenhouse crops production. HortTechnology 20:549–555. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTTECH.20.3.549
Evans MR, Karcher D (2004) Properties of plastic, peat, and processed poultry feather fiber growing containers. HortScience 39(5):1008–1011
Fuentes RA, Berthe JA, Barbosa SE, Castillo LA (2021) Development of biodegradable pots from different agroindustrial wastes and byproducts. Sust Mater Technol 30:e00338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00338
Hanifzadeh M, Nabati Z, Longka P, Malakul P, Apul D, Kim D-S (2017) Life cycle assessment of superheated steam drying technology as a novel cow manure management method. J Environ Manage 199:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.018
Harahap H, Agustini HE, Taslim I, Halimatuddahliana LYA (2018) The effect of drying temperature on natural rubber latex (NRL) films with modification of nanocrystal cellulose (NCC) filler. J Phys Conf Ser 1028:012061. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1028/1/012061
Houghton TP, Stevens DM, Pryfogle PA, Wright CT, Radtke CW (2009) The effect of drying temperature on the composition of biomass. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 153(1–3):4–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8406-x
Jamshidi AR, Tayari E, Neisy A, Boneobeydi MS, NeisyMorad H (2014) Production of biological pots: a strategy for useful utilization of sugar cane bagasse in Khuzestan Province. Bull Environ Pharmacol Life Sci 3(5):96–99
Jirapornvaree I, Suppadit T, Popan A (2017) Use of pineapple waste for production of decomposable pots. Int J Recyl Org Waste Agric 6(4):345–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-017-0183-5
Juanicó LE, Di Lalla N, González AD (2017) Full thermal-hydraulic and solar modeling to study low-cost solar collectors based on a single long LDPE hose. Renew Sust Energy Rev 73:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.126
Kulcu R, Yaldiz O (2014) The composting of agricultural wastes and the new parameter for the assessment of the process. Ecol Eng 69:220–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.03.097
Li H, Xie L, Ma Y, Zhang M, Zhao Y, Zhao X (2019) Effects of drying methods on drying characteristics, physicochemical properties and antioxidant capacity of okra. Lwt 101:630–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.11.076
Li P, He C, Li G, Ding P, Lan M, Gao Z, Jiao Y (2020) Biological pretreatment of corn straw for enhancing degradation efficiency and biogas production. Bioengineered 11(1):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2020.1733733
Liu N, Charrua AB, Weng C-H, Yuan X, Ding F (2015) Characterization of biochars derived from agriculture wastes and their adsorptive removal of atrazine from aqueous solution: a comparative study. Bioresour Technol 198:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.129
Mazurkiewicz J, Marczuk A, Pochwatka P, Kujawa S (2019) Maize straw as a valuable energetic material for biogas plant feeding. Materials 12(23):3848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233848
Migo-Sumagang MVP, Van Hung N, Detras MCM, Alfafara CG, Borines MG, Capunitan JA, Gummert M (2020) Optimization of a downdraft furnace for rice straw-based heat generation. Renew Energy 148:953–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.11.001
Ming X, Chen H, Wang D (2019a) Optimization of processing parameters to increase thermal conductivity of rice straw fiber film. Appl Sci 9(21):4645. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214645
Ming X, Chen H, Han Y, Wang D (2019b) Optimization of technical parameters for making temperature-increasing film from titanium dioxide and rice straw fiber. AIP Adv. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5085031
Nechita P, Dobrin E, Ciolacu F, Bobu E (2010) The biodegradability and mechanical strength of nutritive pots for vegetable planting based on lignocellulose composite materials. BioResources 5(2):1102–1113
Piwińska M, Wyrwisz J, Kurek MA, Wierzbicka A (2016) Effect of drying methods on the physical properties of durum wheat pasta. CyTA - J Food 14(4):523–528. https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2016.1149226
Postemsky PD, Marinangeli PA, Curvetto NR (2016) Recycling of residual substrate from Ganoderma lucidum mushroom cultivation as biodegradable containers for horticultural seedlings. Sci Hortic 201:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2016.02.021
Pratibha, Saha S, Hariprasad P (2022) Paddy straw-based biodegradable horticultural pots: an integrated greener approach to reduce plastic waste, valorize paddy straw and improve plant health. J Cleaner Prod 337:130588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130588
Saepoo T, Sarak S, Mayakun J, Eksomtramage T, Kaewtatip K (2023) Thermoplastic starch composite with oil palm mesocarp fiber waste and its application as biodegradable seeding pot. Carbohydr Polym 299:120221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120221
Schettini E, Santagata G, Malinconico M, Immirzi B, Scarascia Mugnozza G, Vox G (2013) Recycled wastes of tomato and hemp fibres for biodegradable pots: physico-chemical characterization and field performance. Resour Conserv Recycl 70:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2012.11.002
Suderman N, Sarbon N, Mohamad Isa MIN (2016) Effect of drying temperature on the functional properties of biodegradable CMC-based film for potential food packaging. Int Food Res J 23:1075–1084
Vega-Galvez A, Zura-Bravo L, Lemus-Mondaca R, Martinez-Monzo J, Quispe-Fuentes I, Puente L, Di Scala K (2015) Influence of drying temperature on dietary fibre, rehydration properties, texture and microstructure of Cape gooseberry (Physalis peruviana L.). J Food Sci Technol 52(4):2304–2311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1235-0
Wang B, Dong F, Chen M, Zhu J, Tan J, Fu X, Wang Y, Chen S (2016) Advances in recycling and utilization of agricultural wastes in China: based on environmental risk, crucial pathways, influencing factors, policy mechanism. Procedia Environ Sci 31:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.002
Wei K, Lv C, Chen M, Zhou X, Dai Z, Shen D (2015) Development and performance evaluation of a new thermal insulation material from rice straw using high frequency hot-pressing. Energy Build 87:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2014.11.026
Xu C, Zhang X, Hussein Z, Wang P, Chen R, Yuan Q, Gao Y, Song N, Gouda SG (2021) Influence of the structure and properties of lignocellulose on the physicochemical characteristics of lignocellulose-based residues used as an environmentally friendly substrate. Sci Total Environ 790:148089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148089
Zhang L, Hu Y (2014) Novel lignocellulosic hybrid particleboard composites made from rice straws and coir fibers. Mater Des 55:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.09.066
Zhang X, Wang C, Chen Y (2019) Properties of selected biodegradable seedling plug-trays. Sci Hortic 249:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.01.055
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge The Major Science and Technology Innovation Plan of Hubei Province, China for financially supporting this work and the Chinese Scholarships Council Foundation.
Funding
This work is supported by The Major Science and Technology Innovation Plan of Hubei Province (No. 2019ACA153) and the Chinese Scholarships Council Foundation (No. 2017SLJ023756).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZH: conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, visualization, writing—original draft, review & editing. QY: funding acquisition, supervision, data curation, methodology, writing—review & editing. CX: writing original draft, resources, Investigation. XZ: writing original draft, resources, investigation. SG: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hussein, Z., Yuan, Q., Xu, C. et al. Effect of drying methods and conditions and straw type and ratio in the mixture on physical and mechanical properties of biodegradable pots-based sustainable biomaterials. Cellulose 30, 11071–11086 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05562-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05562-5