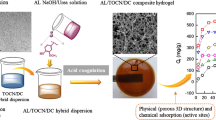
Abstract
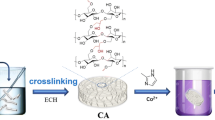
The development of all-biomass adsorbents capable of effectively removing metal ions from wastewater is urgently required in accordance with the trend toward sustainable development and the requirements for environmental protection. Herein, a strategy was proposed to achieve convenient preparation of cellulose/casein composite hydrogel bio-adsorbents via adopting ionic liquid as a corporate solvent. The favorable solubility of ionic liquid and its negligible vapor pressure enabled the bio-adsorbents to obtain a honeycomb-shaped surface structure while recycling ionic liquid in the material preparation process through simple vacuum evaporation technology. The well-designed bio-adsorbents exhibited a rapid adsorption rate (≤ 90 min), and possessed remarkably high adsorption capacities of 232.6 mg g−1 for Cu(II), 270.3 mg g−1 for Cd(II), and 306.6 mg g−1 for Pb(II), respectively. Besides, kinetic analysis displayed that the kinetic data was well described by pseudo-second-order model, while the equilibrium data was well fitted by Langmuir isotherm model. Furthermore, thermodynamic analysis evidenced that the removal of metal ions by bio-adsorbents was endothermic and spontaneous with a high value of ΔH (> 40 kJ mol−1). Further combined with the results of FT-IR and XPS analysis, it can be concluded that the binding of the bio-adsorbents to the metal ions was primarily achieved through chemisorption and monolayer adsorption, and both cellulose and casein contributed to the high adsorption capacity of adsorbent through chelation. Lastly, the bio-adsorbent can effectively treat simulated wastewater with low concentrations of metal ions (2–8.5 mg L−1), and displayed a satisfactory performance of removing heavy metals in actual industrial effluent.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study were included in this article.
References
Chen X, Cui J, Xu X, Sun B, Zhang L, Dong W, Chen C, Sun D (2020) Bacterial cellulose/attapulgite magnetic composites as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions and dye treatment. Carbohydr Polym 229:115512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115512
Choi HY, Bae JH, Hasegawa Y, An S, Kim IS, Lee H, Kim M (2020) Thiol-functionalized cellulose nanofiber membranes for the effective adsorption of heavy metal ions in water. Carbohydr Polym 234:115881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115881
Cui H, Si X, Tian J, Lang Y, Gao N, Tan H, Bian Y, Zang Z, Jiang Q, Bao Y et al (2022) Anthocyanins-loaded nanocomplexes comprising casein and carboxymethyl cellulose: stability, antioxidant capacity, and bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocolloids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107073
d’Halluin M, Rull-Barrull J, Bretel G, Labrugère C, Le Grognec E, Felpin F-X (2017) Chemically modified cellulose filter paper for heavy metal remediation in water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:1965–1973. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02768
Duan C, Tian C, Feng X, Tian G, Liu X, Ni Y (2023) Ultrafast process of microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent to improve properties of bamboo dissolving pulp. Bioresour Technol 370:128543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128543
Duan C, Tian C, Tian G, Wang X, Shen M, Yang S, Ni Y (2023b) Simultaneous microwave-assisted phosphotungstic acid catalysis for rapid improvements on the accessibility and reactivity of Kraft-based dissolving pulp. Int J Biol Macromol 227:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.182
Elsayed NH, Monier M, Alatawi RAS (2021) Thiosemicarbazide-modified/ion-imprinted phenolic resin for selective uptake of cadmium ions. Mater Chem Phys 264:124433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124433
Feng L, Chen Z-L (2008) Research progress on dissolution and functional modification of cellulose in ionic liquids. J Mol Liq 142:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2008.06.007
Ge H, Huang H, Xu M, Chen Q (2016) Cellulose/poly(ethylene imine) composites as efficient and reusable adsorbents for heavy metal ions. Cellulose 23:2527–2537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0973-3
Gupta AD, Pandey S, Jaiswal VK, Bhadauria V, Singh H (2019) Simultaneous oxidation and esterification of cellulose for use in treatment of water containing Cu(II) ions. Carbohydr Polym 222:114964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.06.003
Hu T, Hu X, Tang C, Liu D (2021) Adsorbent grafted on cellulose by in situ synthesis of EDTA-like groups and its properties of metal ion adsorption from aqueous solution. Cellulose 29:941–952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04324-5
Jiang X, Xia J, Luo X (2020) Simple, rapid, and highly sensitive colorimetric sensor strips from a porous cellulose membrane stained with Victoria blue B for efficient detection of trace Cd(II) in water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:5184–5191. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b07614
Jin X, Xiang Z, Liu Q, Chen Y, Lu F (2017) Polyethyleneimine-bacterial cellulose bioadsorbent for effective removal of copper and lead ions from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 244:844–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.072
Karami S, Zeynizadeh B (2019) Reduction of 4-nitrophenol by a disused adsorbent: EDA-functionalized magnetic cellulose nanocomposite after the removal of Cu(2). Carbohydr Polym 211:298–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.113
Lee S, Lingamdinne LP, Yang J-K, Chang Y-Y, Koduru JR (2021) Potential electromagnetic column treatment of heavy metal contaminated water using porous Gd2O3-doped graphene oxide nanocomposite: characterization and surface interaction mechanisms. J Water Process Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102083
Li S, Liu S, Huang F, Lin S, Zhang H, Cao S, Chen L, He Z, Lutes R, Yang J et al (2018) Preparation and characterization of cellulose-based nanofiltration membranes by interfacial polymerization with piperazine and trimesoyl chloride. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:13168–13176. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02720
Li B, Guo JZ, Liu JL, Fang L, Lv JQ, Lv K (2020) Removal of aqueous-phase lead ions by dithiocarbamate-modified hydrochar. Sci Total Environ 714:136897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136897
Lima EC, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Moreno-Piraján JC, Anastopoulos I (2019) A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van’t Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.048
Liu X, Chang PR, Zheng P, Anderson DP, Ma X (2014) Porous cellulose facilitated by ionic liquid [BMIM]Cl: fabrication, characterization, and modification. Cellulose 22:709–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0467-0
Liu Y, Jing S, Carvalho D, Fu J, Martins M, Cavaco-Paulo A (2021) Cellulose dissolved in ionic liquids for modification of the shape of keratin fibers. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9:4102–4110. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c08945
Liu Y, Fan H, Wang X, Zhang J, Li W, Wang R (2022) Controllable synthesis of bifunctional corn stalk cellulose as a novel adsorbent for efficient removal of Cu(2+) and Pb(2+) from wastewater. Carbohydr Polym 276:118763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118763
Lozano P, Bernal B, Recio I, Belleville M-P (2012) A cyclic process for full enzymatic saccharification of pretreated cellulose with full recovery and reuse of the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Green Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2GC35905G
Melo BC, Paulino FAA, Cardoso VA, Pereira AGB, Fajardo AR, Rodrigues FHA (2018) Cellulose nanowhiskers improve the methylene blue adsorption capacity of chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel. Carbohydr Polym 181:358–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.079
Mo L, Pang H, Tan Y, Zhang S, Li J (2019) 3D multi-wall perforated nanocellulose-based polyethylenimine aerogels for ultrahigh efficient and reversible removal of Cu(II) ions from water. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122157
Monier M (2012) Adsorption of Hg2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions from aqueous solution using formaldehyde cross-linked modified chitosan–thioglyceraldehyde Schiff’s base. Int J Biol Macromol 50(3):773–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.11.026
Monier M, Abdel-Latif DA (2012) Preparation of cross-linked magnetic chitosan-phenylthiourea resin for adsorption of Hg(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) ions from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 209–210:240–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.015
Monier M, Abdel-Latif DA (2013) Modification and characterization of PET fibers for fast removal of Hg(II), Cu(II) and Co(II) metal ions from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 250–251:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.01.056
Monier M, Ayad DM, Sarhan AA (2010) Adsorption of Cu(II), Hg(II), and Ni(II) ions by modified natural wool chelating fibers. J Hazard Mater 176(1):348–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.034
Monier M, Ayad DM, Abdel-Latif DA (2012) Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) ions by cross-linked magnetic chitosan-2-aminopyridine glyoxal Schiff’s base. Colloids Surf B 94:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.01.051
Monier M, Abdel-Latif DA, Mohammed HA (2015) Synthesis and characterization of uranyl ion-imprinted microspheres based on amidoximated modified alginate. Int J Biol Macromol 75:354–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.12.001
Monier M, Youssef I, El-Mekabaty A (2019) Preparation of functionalized ion-imprinted phenolic polymer for efficient removal of copper ions. Polym Int. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.5915
Phan D-N, Lee H, Huang B, Mukai Y, Kim I-S (2018) Fabrication of electrospun chitosan/cellulose nanofibers having adsorption property with enhanced mechanical property. Cellulose 26:1781–1793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2169-5
Priya P, Mohan Raj R, Vasanthakumar V, Raj V (2020) Curcumin-loaded layer-by-layer folic acid and casein coated carboxymethyl cellulose/casein nanogels for treatment of skin cancer. Arab J Chem 13:694–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.07.010
Pryshchepa O, Sagandykova GN, Pomastowski P, Railean-Plugaru V, Krol A, Rogowska A, Rodzik A, Sprynskyy M, Buszewski B (2019) A new approach for spontaneous silver ions immobilization onto casein. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163864
Stolarska O, Pawlowska-Zygarowicz A, Soto A, Rodriguez H, Smiglak M (2017) Mixtures of ionic liquids as more efficient media for cellulose dissolution. Carbohydr Polym 178:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2004.02.003
Tang J, Song Y, Zhao F, Spinney S, da Silva Bernardes J, Tam KC (2019) Compressible cellulose nanofibril (CNF) based aerogels produced via a bio-inspired strategy for heavy metal ion and dye removal. Carbohydr Polym 208:404–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.079
Tang C, Brodie P, Li Y, Grishkewich NJ, Brunsting M, Tam KC (2020) Shape recoverable and mechanically robust cellulose aerogel beads for efficient removal of copper ions. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124821
Tran HN, You S-J, Chao H-P (2016) Thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption onto orange peel calculated from various methods: a comparison study. J Environ Chem Eng 4(3):2671–2682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.05.009
Tu H, Yu Y, Chen J, Shi X, Zhou J, Deng H, Du Y (2017) Highly cost-effective and high-strength hydrogels as dye adsorbents from natural polymers: chitosan and cellulose. Polym Chem 8:2913–2921. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7PY00223H
Wang C, Zhan Y, Wu Y, Shi X, Du Y, Luo Y, Deng H (2021) TiO2/rectorite-trapped cellulose composite nanofibrous mats for multiple heavy metal adsorption. Int J Biol Macromol 183:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.085
Weidman JL, Mulvenna RA, Boudouris BW, Phillip WA (2017) Nanoporous block polymer thin films functionalized with bio-inspired ligands for the efficient capture of heavy metal ions from water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:19152–19160. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b04603
Wu S, Fitzpatrick J, Cronin K, Miao S (2019) The effect of pH on the wetting and dissolution of milk protein isolate powder. J Food Eng 240:114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.07.022
Xiao M, Hu J (2017) Cellulose/chitosan composites prepared in ethylene diamine/potassium thiocyanate for adsorption of heavy metal ions. Cellulose 24(6):2545–2557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1287-9
Xu R, Zhou G, Tang Y, Chu L, Liu C, Zeng Z, Luo S (2015) New double network hydrogel adsorbent: Highly efficient removal of Cd(II) and Mn(II) ions in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 275:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.040
Xu F, Zhong L, Zhang C, Wang P, Zhang F, Zhang G (2019) Novel high-efficiency casein-based P–N-containing flame retardants with multiple reactive groups for cotton fabrics. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:13999–14008. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02474
Yadav S, Asthana A, Singh AK, Chakraborty R, Vidya SS, Susan MABH, Carabineiro SAC (2021) Adsorption of cationic dyes, drugs and metal from aqueous solutions using a polymer composite of magnetic/β-cyclodextrin/activated charcoal/Na alginate: Isotherm, kinetics and regeneration studies. J Hazard Mater 409:124840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124840
Yang H, Sheikhi A, van de Ven TG (2016) Reusable green aerogels from cross-linked hairy nanocrystalline cellulose and modified chitosan for dye removal. Langmuir 32:11771–11779. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03084
Yang C, Jie S, Zhu R, Zhang N, Wang J, Liu Z (2017) Co–N–C catalysts synthesized viapyrolyzing the ionic liquids solution dissolved with casein and cobalt porphyrin for ethylbenzene oxidation. ChemistrySelect 2:4255–4260. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201700662
Yang Y, Zeng L, Lin Z, Jiang H, Zhang A (2021) Adsorption of Pb(2+), Cu(2+) and Cd(2+) by sulfhydryl modified chitosan beads. Carbohydr Polym 274:118622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118622
Yao Y, Wang H, Wang R, Chai Y (2019) Preparation and characterization of homogeneous and enhanced casein protein-based composite films via incorporating cellulose microgel. Sci Rep 9:1221. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37848-1
Zhang C, Liu R, Xiang J, Kang H, Liu Z, Huang Y (2014) Dissolution mechanism of cellulose in N, N-dimethylacetamide/lithium chloride: revisiting through molecular interactions. J Phys Chem B 118:9507–9514. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp506013c
Zhang N, Zang GL, Shi C, Yu HQ, Sheng GP (2016) A novel adsorbent TEMPO-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibrils modified with PEI: preparation, characterization, and application for Cu(II) removal. J Hazard Mater 316:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.018
Zhang L, Lu H, Yu J, Fan Y, Yang Y, Ma J, Wang Z (2018) Synthesis of lignocellulose-based composite hydrogel as a novel biosorbent for Cu2+ removal. Cellulose 25:7315–7328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2077-8
Zhao B, Jiang H, Lin Z, Xu S, Xie J, Zhang A (2019a) Preparation of acrylamide/acrylic acid cellulose hydrogels for the adsorption of heavy metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 224:115022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115022
Zhao M, Huang Z, Wang S, Zhang L, Zhou Y (2019b) Design of l-cysteine functionalized UiO-66 MOFs for selective adsorption of Hg(II) in aqueous medium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b17508
Zheng L, Zhang S, Cheng W, Zhang L, Meng P, Zhang T, Yu H, Peng D (2019) Theoretical calculations, molecular dynamics simulations and experimental investigation of the adsorption of cadmium(II) on amidoxime-chelating cellulose. J Mater Chem A 7:13714–13726. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta03622a
Zhou H, Zhu H, Xue F, He H, Wang S (2020) Cellulose-based amphoteric adsorbent for the complete removal of low-level heavy metal ions via a specialization and cooperation mechanism. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123879
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21805177), the Key Research and Development Project of Shaanxi (Grant No. 2021GY-240), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Grant No. 2022JQ-127), Special Scientific Research Project of Shaanxi Education Department (Grant No. 21JK0955) and Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Research Project (Grant No. DJNY2022-34 and DJNY-YB-2023-21). The authors are also grateful for the valuable comments of anonymous reviewers of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21805177), the Key Research and Development Project of Shaanxi (Grant No. 2021GY-240), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Grant No. 2022JQ-127), Special Scientific Research Project of Shaanxi Education Department (Grant No. 21JK0955) and Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group Research Project (Grant No. DJNY2022-34 and DJNY-YB-2023–21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LQ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-Reviewing and Editing, Funding acquisition. HC: Writing-Reviewing and Editing, Investigation, Visualization. S Z: Supervision, Reviewing and Editing. X Y: Investigation and Visualization. L Z: Reviewing and Editing. M Y: Investigation and Visualization. W S: Conceptualization, Writing-Reviewing and Editing. V N: Methodology, Supervision, Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved this submission.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, L., Chen, H., Zhang, S. et al. All-biomass cellulose/casein adsorbent fabricated via the “green solvent system” of ionic liquid for the efficient removal of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II). Cellulose 30, 10257–10272 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05484-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05484-2