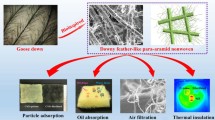
Abstract
Flame-retardant (FR) workwear with good flame/heat protection and washing durability is significant in various fields like petrochemical industry, and there are fast growing needs and new requirements to develop FR yarns with superior flame-resistance, high strength, low hairiness and reasonable cost. However, current aramid or FR viscose yarns cannot well meet these requirements. Herein, by using a cost-effective mid-length fiber vortex yarn technology, this work developed a newly FR viscose/meta-aramid blended yarn with enhanced mechanical properties and flame-resistance, including tensile strength up to 14.4 cN/tex, elongation up to 7.8%, hairiness S3 value as low as 40, and limiting oxygen index value as high as 39.6%. The unique yarn structure of wrapped fiber-sheath and straight fiber-core was studied in terms of twist angle, twist factor, and core ratio in the yarn. Moreover, spinning trials were conducted to systematically learn influences of fiber proportion and spinning parameters, and a statistical model was established by response surface methodology to predict the structure and properties of blended yarn under certain FR viscose/aramid fiber ratio and spinning parameters, which can serve as a guide to manipulate the yarn properties as well as minimizing the fiber cost. This study proposes a cost-effective method to develop high-performance FR blended yarns, which will greatly promote the development of high value-added FR textiles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ah Kim H (2019) Tactile hand and wear comfort of flame-retardant rayon/anti-static polyethylene terephthalate imbedded woven fabrics. Text Res J 89:4658–4669
Cao K, Liu Y, Yang Y, Yuan F, Wang J, Liu H, Jiang M, Yang J (2021) The preparation and characterization of a heterocyclic meta-aramid fiber with outstanding thermal stability. High Perform Polym 33:554–567
Duo X, Can G, Chong G, Yingcun L, Ziyi S, Changjin K, Keshuai L, Jian F, Weilin X (2022) Novel composite yarn with a wavy-network structure produced by various delivery speed ratios and untwisting factors. Text Res J 92:4551–4562
Eldessouki M, Ibrahim S, Farag R (2015) Dynamic properties of air-jet yarns compared to rotor spinning. Text Res J 85:1827–1837
Ertekin M, Kirtay E (2014) Burning behaviour and mechanical properties of fabrics woven with ring spun aramid and flame retardant polyester yarns. Text Appar 24:259–265
Feng J, Xu BG, Tao XM (2013) Systematic investigation and optimization of fine cotton yarns produced in a modified ring spinning system using statistical methods. Text Res J 83:238–248
Feng J, Zhang M, Hua T, Chan KH (2020) Study of a newly structuralized meta-aramid/cotton blended yarn for fabrics with enhanced flame-resistance. Text Res J 90:489–502
Flambard X, Bourbigot S, Kozlowski R, Muzyczek M, Mieleniak B, Ferreira M, Vermeulen B, Poutch F (2005) Progress in safety, flame retardant textiles and flexible fire barriers for seats in transportation. Polym Degrad Stab 88:98–105
Gu H (2009) Research on thermal properties of Nomex/Viscose FR fibre blended fabric. Mater Des 30:4324–4327
Han C, Xue W, Cheng L, Zou Z (2017) Theoretical analysis of the yarn fracture mechanism of self-twist jet vortex spinning. Text Res J 87:1394–1402
Hu J, Yao YN, Liu XS, Ao YH, Zhang HX (2009) The application of a novel flame retardant on viscose fiber. Fire Mater 33:145–156
Ji H, Song M, Wei T, Jiang Q, Ye F, Zhang Y, Zhang Y (2022) Microstructure design of polyester industrial yarns with excellent flame retardancy and high strength. J Ind Text 52:1–20
Kim HA, Kim SJ (2018) Flame-retardant and wear comfort properties of modacrylic/FR-rayon/anti-static PET blend yarns and their woven fabrics for clothing. Fiber Polym 19:1869–1879
Kim HA, Kim SJ (2019) Flame retardant, anti-static and wear comfort properties of modacrylic/Excel®/anti-static PET blend yarns and their knitted fabrics. J Text Inst 110:1318–1328
Li P, Liu C, Wang B, Tao Y, Xu Y-J, Liu Y, Zhu P (2021) Eco-friendly coating based on an intumescent flame-retardant system for viscose fabrics with multi-function properties: flame retardancy, smoke suppression, and antibacterial properties. Prog Org Coat 159:106400
Liang S, Wang F, Liang J, Chen S, Jiang M (2020) Synergistic effect between flame retardant viscose and nitrogen-containing intrinsic flame-retardant fibers. Cellulose 27:6083–6092
Liu X, Chen J, Shao Q, Cao J, Du Z, Liu H, Yu W (2021) Robust, flame-retardant and colorful superamphiphobic aramid fabrics for extreme conditions. Sci China Tech Sci 64:1765–1774
Liu Y, Ge C, Su Z, Chen Z, Gao C, Gong H, Xu W, Xu D, Liu K (2022) Enhancing the spun yarn properties by controlling fiber stress distribution in the spinning triangle with rotary heterogeneous contact surfaces. Polymers 15:176
Ndlovu LN, Han C, Yu C (2014) Mechanical and FR properties of different ratios of cotton/polysulfonamide (PSA) core spun and blended yarns. J Eng Fibers Fabr 9:24–32
Ndlovu LN, Siddiqui Q, Omollo E, Yu C (2015) Physical properties of plain single jersey-knitted fabrics made from blended and core-spun polysulfonamide/cotton yarns. Text Res J 85:262–271
Pei Z, Yu C (2010) Numerical and experimental research on the influence of parameters on the tensile properties of Murata vortex yarn. J Text Inst 101:931–940
Soe AK, Takahashi M, Nakajima M, Matsuo T, Matsumoto T (2004) Structure and properties of MVS yarns in comparison with ring yarns and open-end rotor spun yarns. Text Res J 74:819–826
Tao Y, Wang B, Liu C, Li P, Xu Y-J, Jiang Z-M, Liu Y, Zhu P (2021) Cotton/alginate blended knitted fabrics: flame retardancy, flame-retardant mechanism, water absorption and mechanical properties. Cellulose 28:4495–4510
Wang K, Fu C, Xu A, Wu M, Jia L, Xu W, Su B, Xia Z (2022) Skin-friendly and highly fireproof fabric up to 1142°C weaved by basalt@ polyimide yarns. Compos Part B 246:110238
Wang X, Li Q, Di Y, Xing G (2012) Preparation and properties of flame-retardant viscose fiber containing phosphazene derivative. Fiber Polym 13:718–723
Weil ED, Levchik SV (2008) Flame retardants in commercial use or development for textiles. J Fire Sci 26:243–281
Wu K, Yao Y, Yu J, Chen S, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wang H (2017) Cellulose/aromatic polysulfonamide blended fibers with improved properties. Cellulose 24:3377–3386
Xia Z, Tang J, Ye W (2019) A novel concept to produce periodic varied structural composite yarn via cyclical changing of the spacing between filaments and the strand. Text Res J 89:2998–3006
Xu D, Chen Z, Liu Y, Ge C, Gao C, Jiao L, Guo W, Zhang Q, Fang J, Xu W (2023) Hump-inspired hierarchical fabric for personal thermal protection and thermal comfort management. Adv Funct Mater 33:2212626
Yang RH, Pan B, Wang LJ, Li JW (2021) Blending effects and performance of ring-, rotor-, and air-jet-spun color-blended viscose yarns. Cellulose 28:1769–1780
Zhang F-Q, Wang B, Xu Y-J, Li P, Liu Y, Zhu P (2020) Convenient blending of alginate fibers with polyamide fibers for flame-retardant non-woven fabrics. Cellulose 27:8341–8349
Zhao Z, Di Y, Gao L, Wang W, Wu X (2020) Characterization of flame-retardant performance of polyester/flame-retardant viscose blended yarn. J Ind Text 49:1304–1316
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Innovation and Technology Commission of Hong Kong SAR Government, The Hong Kong Research Institute of Textiles and Apparel, Upper Wealth (HK) Ltd, Wuxi Gaoshikang New Materials Technology Co., Ltd for funding support the project titled “Development of High Value-added Vortex Yarn and Fabrics with Enhanced Flame-resistance and Comfort” (Grant No. ITP/008/21TP).
Funding
This research was financially supported by Innovation and Technology Commission of Hong Kong SAR Government, The Hong Kong Research Institute of Textiles and Apparel, Upper Wealth (HK) Ltd, Wuxi Gaoshikang New Materials Technology Co., Ltd. (Grant No. ITP/008/21TP)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the experiments of this study and approved the final manuscript. BN wrote the main manuscript text. TH provided the idea, supervised this work, and revised the paper draft. BN and XT contribute equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, B., Tian, X., Wong, M. et al. Toward high-performance FR viscose/meta-aramid blended yarns enabled by vortex spinning driven core-sheath assembly. Cellulose 30, 9829–9841 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05466-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05466-4