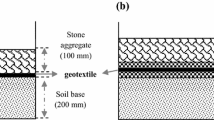
Abstract
During the last decade, the usage of geotextiles has tremendously grown into a needful auxiliary, particularly regarding soil protection. Although geotextiles made of natural fibers blended with synthetic materials are considered a modern achievement, backing up the basic concept of increasing the stability of roads and soils, they suffer from severe degradation. It includes the environmental exposure such as hydrolysis, and thermal, chemical, and biological degradation, affecting their long-term performance. This paper focuses on the jute-based geotextile having outstanding water repellency with a water contact angle of 169° and immutable tensile strength (~ 12 MPa) when incorporated with hexadecyltrimethoxysilane (HDTMS) modified titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles (nps) via drop casting technique. Herein, the durability of the coating was examined by sand (dropping sand particles) and impact (driving two-wheeler) tests on the coated jute sample. In addition, the coated samples were immersed in different aqueous mediums, and the behaviour in the tensile strength was noted. Similarly, the thermal degradation affecting the tensile strength was also evaluated. Lastly, biodegradability was judged by burying the samples for different periods in the soil. These outcomes demonstrate the potential of the HDTMS-TiO2 nps coating on jute geotextile having a suitable mechanically durable and sustainable superhydrophobic property that could be successfully used in roadway applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are included in this Article and its Supplementary Information files.
References
Ahuja D, Dhiman S, Rattan G, Monga S, Singhal S, Kaushik A (2021) Superhydrophobic modification of cellulose sponge fabricated from discarded jute bags for oil water separation. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105063
Akter N, Das SC, Saha J, Khan MA (2018) Effect of bitumen emulsion and polyester resin mixture on the physico-mechanical and degradable properties of jute fabrics. Fibers 6:44. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6030044
Akter N, Das SC, Grammatikos SA, Saha J, Khan MA (2020) Development of sustainable jute geotextiles by bitumen emulsion and polyester resin: effect of gamma radiation. J Eng Fibers Fabr 15:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1177/1558925020957
Ali ME, Yong CK, Ching YC, Chuah CH, Liou N-S (2014) Effect of single and double stage chemically treated kenaf fibers on mechanical properties of polyvinyl alcohol film. BioRes 10:822–838. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.10.1.822-838
Antonini C, Malavasi I, Marengo M, Bernagozzi I (2015) Assessing durability of superhydrophobic surfaces. Surf Innov 3:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1680/si.14.00001
Araújo JC, Ferreira DP, Teixeira P, Fangueiro R (2021) In-situ synthesis of CaO and SiO2 nanoparticles onto jute fabrics: exploring the multifunctionality. Cellulose 28:1123–1138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03564-1
Arfaoui M, Dolez P, Dubé M, David E (2017) Development and characterization of a hydrophobic treatment for jute fibres based on zinc oxide nanoparticles and a fatty acid. Appl Surf Sci 397:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.11.085
Arfaoui M, Dolez P, Dubé M, David E (2018) Preparation of a hydrophobic recycled jute-based nonwoven using a titanium dioxide/stearic acid coating. J Text Inst 110:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2018.1455313
Ayalew AA, Wodag A (2022) Characterization of chemically treated sisal fiber/polyester composites. J Eng 2022:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8583213
Bayer IS, Fragouli D, Martorana PJ et al (2011) Solvent resistant superhydrophobic films from self-emulsifying carnauba wax–alcohol emulsions. Soft Matter 7:7939–7943. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1SM05710C
Bhushan B (2009) Biomimetics: lessons from nature - an overview. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci 367:1445–1486. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2009.0011
Cassie ABD, Baxter S (1944) Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans Faraday Soc 40:546–551. https://doi.org/10.1039/TF9444000546
Chakrabarti SK, Saha SG, Paul P et al (2016) Specially treated woven jute geotextiles for river bank protection. Indian J Fibre Text Res 41:207–221. https://doi.org/10.56042/ijftr.v41i2.4599
Chauhan P, Kumar A (2020) Development of a microbial coating for cellulosic surface using aloe vera and silane. Carbohydr Polymer Technol Appl 1:100015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2020.100015
Dolez PI, Arfaoui MA, Dubé M, David É (2017) Hydrophobic treatments for natural fibers based on metal oxide nanoparticles and fatty acids. Procedia Eng 200:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.07.013
Dong A, Yu Y, Yuan J, Wang Q, Fan X (2014) Hydrophobic modification of jute fiber used for composite reinforcement via laccase-mediated grafting. Appl Surf Sci 301:418–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.02.092
Fujiura T, Nakamura R, Tanaka T, Arao Y (2015) Effect of jute fiber’s thermal degradation on the fiber strength and its polymer composites. Adv Mat Res 1110:7–12. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1110.7
Gassan J, Bledzki A (2001) Thermal degradation of flax and jute fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 82:1417–1422. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1979
Ghosh M, Saha R, Das M (2021) Application of jute - polypropylene blended geotextile in black cotton soil subgrade for low volume road construction. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 7:53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-021-00301-x
Gudayu AD, Steuernagel L, Meiners D, Gideon R (2020) Effect of surface treatment on moisture absorption, thermal, and mechanical properties of sisal fiber. J Ind Text 51:2853S-2873S. https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083720924774
Leão AL, Cherian BM, De Souza SF et al (2012) Natural fibres for geotextiles. Handbk Natural Fibres 2:280–311. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857095510.2.280
Li Y, Chen S, Wu M, Sun J (2014) All spraying processes for the fabrication of robust, self-healing, superhydrophobic coatings. Adv Mater 26:3344–3348. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201306136
Li K, Zeng X, Lai X, Chai S (2017) Study on the anti-abrasion resistance of superhydrophobic coatings based on fluorine-containing acrylates with different Tg and SiO2. RSC Adv 7:47738–47745. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA07865J
Lv N, Wang X, Peng S, Zhang H, Luo L (2018) Study of the kinetics and equilibrium of the adsorption of oils onto hydrophobic jute fiber modified via the sol–gel method. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050969
Malis D, Jeršek B, Tomšič B et al (2019) Antibacterial activity and biodegradation of cellulose fiber blends with incorporated ZnO. Mater 12:20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203399
Marques AR, de Oliveira S, Patrício P, Soares dos Santos F et al (2014) Effects of the climatic conditions of the southeastern Brazil on degradation the fibers of coir-geotextile: evaluation of mechanical and structural properties. Geotext Geomembr 42:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2013.07.004
Meena MK, Tudu BK, Kumar A, Bhushan B (2020) Development of polyurethane-based superhydrophobic coatings on steel surfaces. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci 378:20190446. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2019.0446
Midha VK, Joshi S, Kumar SS (2017) Performance of chemically treated jute geotextile in unpaved roads at different in situ conditions. J Inst Eng India E 98:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-017-0093-0
Mohanty A, Misra M, Hinrichsen G (2000) Biofibres, biodegradable polymers and biocomposites: an overview. Macromol Mater Eng 276–277:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1439-2054(20000301)276:1%3c1::AID-MAME1%3e3.0.CO;2-W
Nakano R, Hara M, Ishiguro H, Yao Y et al (2013) Broad spectrum microbicidal activity of photocatalysis by TiO2. Catalysts 3:310–323. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3010310
Odokonyero K, Gallo A, Mishra H (2021) Nature-inspired wax-coated jute bags for reducing post-harvest storage losses. Sci Rep 11:15354. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-93247-z
Orue A, Jauregi A, Unsuain U et al (2016) The effect of alkaline and silane treatments on mechanical properties and breakage of sisal fibers and poly(lactic acid)/sisal fiber composites. Compos - a: Appl Sci Manuf 84:186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.01.021
Ouagne P, Renouard S, Michel D et al (2017) Mechanical properties of flax and hemp yarns designed for the manufacturing of geo textiles. Improvement of the resistance to soil born microorganisms. J Textile Eng Fashion Technol 1:210–215. https://doi.org/10.15406/jteft.2017.01.00034
Prambauer M, Wendeler C, Weitzenböck J, Burgstaller C (2019) Biodegradable geotextiles - An overview of existing and potential materials. Geotext Geomembr 47:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2018.09.006
Prasad V, Sekar K, Joseph MA (2021) Mechanical and water absorption properties of nano TiO2 coated flax fibre epoxy composites. Constr Build Mater 284:122803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122803
Ren J, Tao F, Liu L, Wang X, Cui Y (2020) A novel TiO2@stearic acid/chitosan coating with reversible wettability for controllable oil/water and emulsions separation. Carbohydr Polym 232:115807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115807
Saha P, Roy D, Manna S, Adhikari B, Sen R, Roy S (2012) Durability of transesterified jute geotextiles. Geotext Geomembr 35:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2012.07.003
Sayed A, Salam MZ, Roy S, Rahman MT (2016) Effect of moisture content on the tensile strength of jute geotextile. IOSR J Mech Civ Eng 13:79–87. https://doi.org/10.9790/1684-1305067987
Sumi S, Unnikrishnan N, Mathew L (2016) Experimental investigations on biological resistance of surface modified coir geotextiles. Int J Geosynth Ground Eng 2:31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40891-016-0073-3
Sumi S, Unnikrishnan N, Mathew LS (2017) Surface modification of coir fibers for extended hydrophobicity and antimicrobial property for possible geotextile application. J Nat Fibers 14:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2016.1209714
Teklu T, Wangatia LM, Alemayehu E (2019) Effect of surface modification of sisal fibers on water absorption and mechanical properties of polyaniline composite. Polym Compos 40:E46–E52. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.24462
Wang Y, Li H, Liu X, Yu C (2021) Cellulosic fiber filter with special wettability for efficient water/fuel oil separation. J Wood Chem Technol 41:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1080/02773813.2020.1856881
Wu H, Yao C, Li C, Miao M, Zhong Y, Lu Y, Liu T (2020) Review of application and innovation of geotextiles in geotechnical engineering. Mater 13:1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071774
Yuce I, Canoglu S, Yukseloglu SM et al (2022) Titanium and silicon dioxide-coated fabrics for management and tuning of infrared radiation. Sensors 22:3918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115807
Acknowledgments
This work made use of the Indian Institute of Technology (ISM), Dhanbad facilities.
Funding
The authors receive no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Srishti conceptualization, experiment, characterization, manuscript writing. AS supervision. AK writing-review, editing, supervision, funding.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
The authors give their consent for the publication of identifiable details, which include photographs and details within the text to be published in the “Cellulose” Journal and Article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Srishti, Sinhamahapatra, A. & Kumar, A. Assessing the non-wettability and sustainability of cellulosic jute for roadway applications. Cellulose 30, 7839–7852 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05358-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05358-7