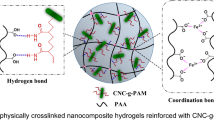
Abstract
Hydrogels are attracting widespread attention due to their unique mechanical flexibility, which holds great promise for application in various fields. However, the high water-richness of hydrogels make them inevitably freeze at sub-zero temperatures conditions and severely limit the range of applications. Herein, we presented a novel anti-freezing strategy based on betaine/CaCl2 and CNCs as both reinforcing agent and physical cross-linking agent to achieve the simultaneous upgrading of anti-freezing and mechanical properties of hydrogels. Under the synergistic effect of betaine and CaCl2, the GA/PAA-CNC/betaine/CaCl2 hydrogels maintained exceptional fracture toughness (1.5 MPa) and tensile properties (1000%) even at − 30 °C. This work offers a neoteric antifreeze strategy to design self-healing, high intensity and anti-freezing arabic gum hydrogels.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are included in this Article.
References
Asadi N, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Del Bakhshayesh AR, Akbarzadeh A, Davaran S, Annabi N (2021) Multifunctional hydrogels for wound healing: special focus on biomacromolecular based hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol 170:728–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.202
Culebras M, Barrett A, Pishnamazi M, Walker GM, Collins MN (2021) Wood-derived hydrogels as a platform for drug-release systems. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9:2515–2522. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c08022
Dong J, Ozaki Y, Nakashima K (1997) Infrared, raman, and near-infrared spectroscopic evidence for the coexistence of various hydrogen-bond forms in poly(acrylic acid). Macromolecules 30:1111–1117. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma960693x
Du WB, Deng AM, Guo J, Chen J, Li HM, Gao Y (2019) An injectable self-healing hydrogel-cellulose nanocrystals conjugate with excellent mechanical strength and good biocompatibility. Carbohydr Polym 223:115084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115084
El-Husseiny HM, Mady EA, Hamabe L, Abugomaa A, Shimada K, Yoshida T, Tanaka T, Yokoi A, Elbadawy M, Tanaka R (2022) Smart/stimuli-responsive hydrogels: cutting-edge platforms for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. Mater Today Bio 13:100186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100186
Fan QC, Jiang CJ, Wang WX, Bai LJ, Chen H, Yang HW, Wei DL, Yang LX (2020) Eco-friendly extraction of cellulose nanocrystals from grape pomace and construction of self-healing nanocomposite hydrogels. Cellulose 27:2541–2553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-02977-2
Feng YF, Yu J, Sun D, Dang C, Ren WF, Shao CY, Sun RC (2022) Extreme environment-adaptable and fast self-healable eutectogel triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. Nano Energy 98:107284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107284
Guan L, Yan S, Liu X, Li XY, Gao GH (2019) Wearable strain sensors based on casein-driven tough, adhesive and anti-freezing hydrogels for monitoring human-motion. J Mater Chem B 7:5230–5236. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tb01340g
Guan QF, Han ZM, Zhu Y, Xu WL, Yang HB, Ling ZC, Yan BB, Yang KP, Yin CH, Wu H, Yu SH (2021) Bio-inspired lotus-fiber-like spiral hydrogel bacterial cellulose fibers. Nano Lett 21:952–958. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c03707
Hong S, Yuan Y, Li PP, Zhang KT, Lian HL, Liimatainen H (2020) Enhancement of the nanofibrillation of birch cellulose pretreated with natural deep eutectic solvent. Ind Crops Prod 154:112677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112677
Islam MS, Alam MN, van de Ven TGM (2020) Sustainable cellulose-based hydrogel for dewatering of orange juice. Cellulose 27:7637–7648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03295-3
Jiao Q, Cao LL, Zhao ZJ, Zhang H, Li JJ, Wei YP (2021) Zwitterionic hydrogel with high transparency, ultrastretchability, and remarkable freezing resistance for wearable strain sensors. Biomacromolecules 22:1220–1230. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c01724
Kalinoski RM, Shi J (2019) Hydrogels derived from lignocellulosic compounds: evaluation of the compositional, structural, mechanical and antimicrobial properties. Ind Crops Prod 128:323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.11.002
Kang SF, Xiao YQ, Wang KH, Cui MD, Chen D, Guan D, Luan GZ, Xu HD (2021) Development and evaluation of gum arabic-based antioxidant nanocomposite films incorporated with cellulose nanocrystals and fruit peel extracts. Food Packag Shelf Life 30:100768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2021.100768
Kanyuck KM, Mills TB, Norton IT, Norton-Welch AB (2021) Swelling of high acyl gellan gum hydrogel: characterization of network strengthening and slower release. Carbohydr Polym 259:117758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117758
Kelleppan VT, King JP, Butler CSG, Williams AP, Tuck KL, Tabor RF (2021) Heads or tails? The synthesis, self-assembly, properties and uses of betaine and betaine-like surfactants. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 297:102528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102528
Laitinen O, Ojala J, Sirviö JA, Liimatainen H (2017) Sustainable stabilization of oil in water emulsions by cellulose nanocrystals synthesized from deep eutectic solvents. Cellulose 24:1679–1689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1226-9
Liu X, Zhang Q, Gao GH (2020) DNA-inspired anti-freezing wet-adhesion and tough hydrogel for sweaty skin sensor. Chem Eng J 394:124898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124898
Liu S, Zhang Q, Gou S, Zhang L, Wang Z (2021) Esterification of cellulose using carboxylic acid-based deep eutectic solvents to produce high-yield cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 251:117018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117018
Li P, Sirvio JA, Asante B, Liimatainen H (2018) Recyclable deep eutectic solvent for the production of cationic nanocelluloses. Carbohydr Polym 199:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.024
Li SH, Pan HY, Wang YT, Sun JQ (2020a) Polyelectrolyte complex-based self-healing, fatigue-resistant and anti-freezing hydrogels as highly sensitive ionic skins. J Mater Chem A 8:3667–3675. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta13213a
Li TQ, Wang YT, Li SH, Liu XK, Sun JQ (2020b) Mechanically robust, elastic, and healable ionogels for highly sensitive ultra-durable ionic skins. Adv Mater 32:2002706. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202002706
Li MC, Wu Q, Moon RJ, Hubbe MA, Bortner MJ (2021) Rheological aspects of cellulose nanomaterials: governing factors and emerging applications. Adv Mater 33:2006052. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202006052
Long W, Ouyang H, Hu X, Liu MY, Zhang XY, Feng YL, Wei Y (2021) State-of-art review on preparation, surface functionalization and biomedical applications of cellulose nanocrystals-based materials. Int J Biol Macromol 186:591–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.066
Lu CY, Qiu JH, Zhao W, Sakai E, Zhang GH, Nobe R, Kudo M, Komiyama T (2021) Low-temperature adaptive conductive hydrogel based on ice structuring proteins/CaCl2 anti-freeze system as wearable strain and temperature sensor. Int J Biol Macromol 188:534–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.060
Morelle XP, Illeperuma WR, Tian K, Bai R, Suo Z, Vlassak JJ (2018) Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels below water freezing temperature. Adv Mater 30:1801541. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201801541
Mota HP, Fajardo AR (2021) Development of superabsorbent hydrogel based on gum arabic for enhanced removal of anxiolytic drug from water. J Environ Manage 288:112455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112455
Nie Y, Yue DQ, Xiao WM, Wang WX, Chen H, Bai LJ, Yang LX, Yang HW, Wei DL (2022) Anti-freezing and self-healing nanocomposite hydrogels based on poly (vinyl alcohol) for highly sensitive and durable flexible sensors. Chem Eng J 436:135243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135243
Ohm YS, Pan CF, Ford MJ, Huang XN, Liao JH, Majidi C (2021) An electrically conductive silver-polyacrylamide-alginate hydrogel composite for soft electronics. Nat Electron 4:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00545-5
Peng ZY, Wang CZ, Zhang ZC, Zhong WB (2019) Synthesis and enhancement of electroactive biomass/polypyrrole hydrogels for high performance flexible all-solid‐state supercapacitors. Adv Mater Interfaces 6:1901393. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201901393
Pereira AGB, Nunes CS, Rubira AF, Muniz EC, Fajardo AR (2021) Effect of chitin nanowhiskers on mechanical and swelling properties of gum arabic hydrogels nanocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 266:118116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118116
Qiao HY, Qi PF, Zhang XH, Wang LN, Tan YQ, Luan ZH, Xia YZ, Li YH, Sui KY (2019) Multiple weak H-bonds lead to highly sensitive, stretchable, self-adhesive, and self-healing ionic sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:7755–7763. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b20380
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the x-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Shao Q, Jiang SY (2015) Molecular understanding and design of zwitterionic materials. Adv Mater 27:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201404059
Sharma G, Kumar A, Sharma S, Al-Muhtaseb AH, Naushad M, Ghfar AA, Ahamad T, Stadler FJ (2019) Fabrication and characterization of novel Fe-0@Guar gum-crosslinked-soya lecithin nanocomposite hydrogel for photocatalytic degradation of methyl violet dye. Sep Purif Technol 211:895–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.10.028
Song ML, Yu HY, Zhu JY, Ouyang ZF, Abdalkarim SYH, Tam KC, Li YZ (2020) Constructing stimuli-free self-healing, robust and ultrasensitive biocompatible hydrogel sensors with conductive cellulose nanocrystals. Chem Eng J 398:125547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125547
Sui XJ, Guo HS, Chen PG, Zhu YN, Wen CY, Gao YH, Yang J, Zhang XY, Zhang L (2019) Zwitterionic osmolyte-based hydrogels with antifreezing property, high conductivity, and ctable flexibility at subzero temperature. Adv Funct Mater 30:1907986. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201907986
Sun D, Feng YF, Sun SC, Yu J, Jia SY, Dang C, Hao X, Yang J, Ren WF, Sun RC, Shao CY, Peng F (2022) Transparent, self-adhesive, conductive organohydrogels with fast gelation from lignin‐based self‐catalytic system for extreme environment‐resistant triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv Funct Mater 32:2201335. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202201335
Thakur S, Verma A, Kumar V, Jin Yang X, Krishnamurthy S, Coulon F, Thakur VK (2022) Cellulosic biomass-based sustainable hydrogels for wastewater remediation: chemistry and prospective. Fuel 309:122114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122114
Viertorinne M, Valkonen J, Pitkänen I, Mathlouthi M, Nurmi J (1999) Crystal and molecular structure of anhydrous betaine, (CH3)3NCH2CO2. J Mol Struct 477:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2860(98)00613-9
Wang QH, Pan XF, Lin CM, Lin DZ, Ni YH, Chen LH, Huang LL, Cao SL, Ma XJ (2019) Biocompatible, self-wrinkled, antifreezing and stretchable hydrogel-based wearable sensor with PEDOT: sulfonated lignin as conductive materials. Chem Eng J 370:1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.287
Wang JF, Zhang DH, Chu FX (2021a) Wood-derived functional polymeric materials. Adv Mater 33:2001135. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202001135
Wang JK, Ma ZZ, Wang Y, Shao JW, Yan LF (2021b) Ultra-stretchable, self-healing, conductive, and transparent PAA/DES ionic gel. Macromol Rapid Commun 42:2000445. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.202000445
Wang LR, Xu TL, Zhang XJ (2021c) Multifunctional conductive hydrogel-based flexible wearable sensors. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 134:116130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116130
Wang HQ, Li Z, Zuo M, Zeng XH, Tang X, Sun Y, Lin L (2022) Stretchable, freezing-tolerant conductive hydrogel for wearable electronics reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals toward multiple hydrogen bonding. Carbohydr Polym 280:119018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.119018
Wei JJ, Xie JJ, Zhang PC, Zou ZY, Ping H, Wang WM, Xie H, Shen JZ, Lei LW, Fu ZY (2021) Bioinspired 3D printable, self-healable, and stretchable hydrogels with multiple conductivities for skin-like wearable strain sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:2952–2960. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c19512
Wen J, Tang J, Ning HM, Hu N, Zhu YY, Gong YK, Xu CH, Zhao QN, Jiang XP, Hu XL, Lei L, Wu D, Huang T (2021) Multifunctional ionic skin with sensing, UV-filtering, water‐retaining, and anti‐freezing capabilities. Adv Funct Mater 31:2011176. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202011176
Wong LC, Leh CP, Goh CF (2021) Designing cellulose hydrogels from non-woody biomass. Carbohydr Polym 264:118036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118036
Xue X, Hu Y, Deng YH, Su JC (2021) Recent advances in design of functional biocompatible hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Adv Funct Mater 31:2009432. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202009432
Yang WS, Bian HY, Jiao L, Wu WB, Deng YL, Dai HQ (2017) High wet-strength, thermally stable and transparent TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibril film via cross-linking with poly-amide epichlorohydrin resin. RSC Adv 7:31567–31573. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra05009g
Yang YY, Yang YT, Cao YX, Wang X, Chen YR, Liu HY, Gao YF, Wang JF, Liu C, Wang WJ, Yu JK, Wu DC (2021) Anti-freezing, resilient and tough hydrogels for sensitive and large-range strain and pressure sensors. Chem Eng J 403:126431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126431
Yu J, Feng YF, Sun D, Ren WF, Shao CY, Sun RC (2022) Highly conductive and mechanically robust cellulose nanocomposite hydrogels with antifreezing and antidehydration performances for flexible humidity sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14:10886–10897. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c00513
Zhang XF, Ma XF, Hou T, Guo KC, Yin JY, Wang ZG, Shu L, He M, Yao JF (2019) Inorganic salts induce thermally reversible and anti-freezing cellulose hydrogels. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:7366–7370. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201902578
Zhang W, Wu B, Sun S, Wu P (2021) Skin-like mechanoresponsive self-healing ionic elastomer from supramolecular zwitterionic network. Nat Commun 12:4082. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24382-4
Zheng WH, Xu LJ, Li YY, Huang YD, Li B, Jiang ZX, Gao GL (2021) Anti-freezing, moisturizing, resilient and conductive organohydrogel for sensitive pressure sensors. J Colloid Interface Sci 594:584–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.03.079
Zhu MS, Wang XJ, Tang HM, Wang JW, Hao Q, Liu LX, Li Y, Zhang K, Schmidt OG (2019) Antifreezing hydrogel with high zinc reversibility for flexible and durable aqueous batteries by cooperative hydrated cations. Adv Funct Mater 30:1907218. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201907218
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
The research was financial supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51973086), the Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science (Nos. 2019KJA011) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2021MB124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WX: Writing-original draft, Data curation; FJ: Writing-review & editing, Methodology; SZ: Writing-review & editing, Methodology; HC: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing-review & editing; LB: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing-review & editing; WW: Conceptualization; Resources; HY: Writing-review & editing; LY: Methodology, Resources; DW: Project administration, Methodology.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant conflicts to declare.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, W., Jing, F., Zhang, S. et al. Cellulose nanocrystal based self-healing and anti-freezing arabic gum hydrogels using betaine/CaCl2 anti-freeze strategy. Cellulose 30, 7667–7680 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05321-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05321-6